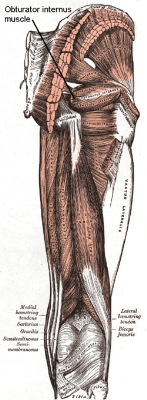
Obturator internus muscle
Encyclopedia
The obturator internus muscle originates on the medial surface of the obturator membrane
, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis
.
It exits the pelvic cavity
through the lesser sciatic foramen
.
The obturator internus is situated partly within the lesser pelvis
, and partly at the back of the hip-joint.
It functions to help laterally rotate extended thigh and abduct flexed thigh, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum.
, being attached to the inferior rami of the pubis
and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone
below and behind the pelvic brim
, reaching from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen
above and behind to the obturator foramen
below and in front.
It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane
except in the posterior part, from the tendinous arch
which completes the canal for the passage of the obturator vessels and nerve, and to a slight extent from the obturator fascia, which covers the muscle.
The fibers converge rapidly toward the lesser sciatic foramen
, and end in four or five tendinous bands, which are found on the deep surface of the muscle; these bands are reflected at a right angle over the grooved surface of the ischium between its spine and tuberosity.
The tendon inserts on the greater trochanter of the proximal femur.
Obturator Internis muscle is also innervated by the nerve to obturator internis (L5, S1).
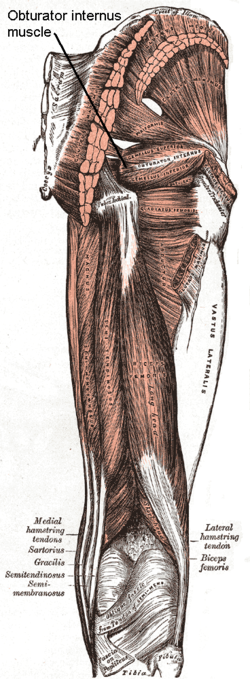
, and presents one or more ridges corresponding with the furrows between the tendinous bands.
These bands leave the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen and unite into a single flattened tendon, which passes horizontally across the capsule of the hip-joint, and, after receiving the attachments of the superior
and inferior gemellus muscle
s, is inserted into the forepart of the medial surface of the greater trochanter above the trochanteric fossa.
A bursa
, narrow and elongated in form, is usually found between the tendon and the capsule of the hip-joint; it occasionally communicates with the bursa between the tendon and the ischium.
Obturator membrane
The obturator membrane is a thin fibrous sheet, which almost completely closes the obturator foramen.Its fibers are arranged in interlacing bundles mainly transverse in direction; the uppermost bundle is attached to the obturator tubercles and completes the obturator canal for the passage of the...
, the ischium near the membrane, and the rim of the pubis
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubic bone is the ventral and anterior of the three principal bones composing either half of the pelvis.It is covered by a layer of fat, which is covered by the mons pubis....
.
It exits the pelvic cavity
Pelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
through the lesser sciatic foramen
Lesser sciatic foramen
An opening between the pelvis and the posterior thigh, the foramen is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial tuberosity and the sacrospinous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial spine.-Boundaries:...
.
The obturator internus is situated partly within the lesser pelvis
Lesser pelvis
The lesser pelvis is that part of the space enclosed by the skeleton of the pelvis which is situated between the pelvic inlet and the pelvic floor. Some authors call this cavity the pelvic cavity...
, and partly at the back of the hip-joint.
It functions to help laterally rotate extended thigh and abduct flexed thigh, as well as to steady the femoral head in the acetabulum.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the inner surface of the antero-lateral wall of the pelvis, where it surrounds the greater part of the obturator foramenObturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the hole created by the ischium and pubis bones of the pelvis through which nerves and muscles pass.- General structure :...
, being attached to the inferior rami of the pubis
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubic bone is the ventral and anterior of the three principal bones composing either half of the pelvis.It is covered by a layer of fat, which is covered by the mons pubis....
and ischium, and at the side to the inner surface of the hip bone
Hip bone
The hip bone, innominate bone or coxal bone is a large, flattened, irregularly shaped bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below...
below and behind the pelvic brim
Pelvic brim
The pelvic brim is the edge of the pelvic inlet. It is an approximately apple-shaped line passing through the prominence of the sacrum, the arcuate and pectineal lines, and the upper margin of the pubic symphysis....
, reaching from the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen
Greater sciatic foramen
-Boundaries:It is bounded as follows:* anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the illium* posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament* inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine* superiorly by the anterior sacroilliac ligament...
above and behind to the obturator foramen
Obturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the hole created by the ischium and pubis bones of the pelvis through which nerves and muscles pass.- General structure :...
below and in front.
It also arises from the pelvic surface of the obturator membrane
Obturator membrane
The obturator membrane is a thin fibrous sheet, which almost completely closes the obturator foramen.Its fibers are arranged in interlacing bundles mainly transverse in direction; the uppermost bundle is attached to the obturator tubercles and completes the obturator canal for the passage of the...
except in the posterior part, from the tendinous arch
Tendinous arch
At the level of a line extending from the lower part of the pubic symphysis to the spine of the ischium is a thickened whitish band in this upper layer of the diaphragmatic part of the pelvic fascia...
which completes the canal for the passage of the obturator vessels and nerve, and to a slight extent from the obturator fascia, which covers the muscle.
The fibers converge rapidly toward the lesser sciatic foramen
Lesser sciatic foramen
An opening between the pelvis and the posterior thigh, the foramen is formed by the sacrotuberous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial tuberosity and the sacrospinous ligament which runs between the sacrum and the ischial spine.-Boundaries:...
, and end in four or five tendinous bands, which are found on the deep surface of the muscle; these bands are reflected at a right angle over the grooved surface of the ischium between its spine and tuberosity.
The tendon inserts on the greater trochanter of the proximal femur.
Obturator Internis muscle is also innervated by the nerve to obturator internis (L5, S1).

Bursa/bands
This bony surface is covered by smooth cartilage, which is separated from the tendon by a bursaBursa (anatomy)
A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of slimy fluid . It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement...
, and presents one or more ridges corresponding with the furrows between the tendinous bands.
These bands leave the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen and unite into a single flattened tendon, which passes horizontally across the capsule of the hip-joint, and, after receiving the attachments of the superior
Superior gemellus muscle
The superior gemellus muscle is a muscle of the human body.The Gemelli are two small muscular fasciculi, accessories to the tendon of the Obturator internus which is received into a groove between them....
and inferior gemellus muscle
Inferior gemellus muscle
The inferior gemellus muscle is a muscle of the human body.The Gemelli are two small muscular fasciculi, accessories to the tendon of the Obturator internus which is received into a groove between them....
s, is inserted into the forepart of the medial surface of the greater trochanter above the trochanteric fossa.
A bursa
Bursa (anatomy)
A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of slimy fluid . It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement...
, narrow and elongated in form, is usually found between the tendon and the capsule of the hip-joint; it occasionally communicates with the bursa between the tendon and the ischium.

