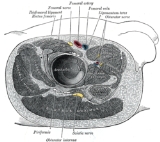
Obturator nerve
Encyclopedia
The obturator nerve in human anatomy
arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves
; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.
and ureter
, and runs along the lateral wall of the lesser pelvis
, above and in front of the obturator vessels
, to the upper part of the obturator foramen
.
Here it enters the thigh, through the obturator canal
, and divides into an anterior and a posterior branch, which are separated at first by some of the fibers of the Obturator externus, and lower down by the Adductor brevis.
.
It is also responsible for the motor innervation of the adductor muscles of the lower extremity (external obturator., adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gracilis
) and the pectineus (inconstant). It is, notably, not responsible for the innervation of the obturator internus, despite the similarity in name.
Human anatomy
Human anatomy is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye...
arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves
Lumbar nerves
The lumbar nerves are the five spinal nerves emerging from the lumbar vertebrae. They are divided into posterior and anterior divisions.-Posterior divisions:...
; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.
Path
It descends through the fibers of the Psoas major, and emerges from its medial border near the brim of the pelvis; it then passes behind the common iliac arteries, and on the lateral side of the internal iliac arteryInternal iliac artery
The internal iliac artery is the main artery of the pelvis.-Structure:The internal iliac artery supplies the walls and viscera of the pelvis, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compartment of the thigh...
and ureter
Ureter
In human anatomy, the ureters are muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually long and ~3-4 mm in diameter....
, and runs along the lateral wall of the lesser pelvis
Lesser pelvis
The lesser pelvis is that part of the space enclosed by the skeleton of the pelvis which is situated between the pelvic inlet and the pelvic floor. Some authors call this cavity the pelvic cavity...
, above and in front of the obturator vessels
Obturator vessels
Obturator vessels can refer to:* Obturator artery* Obturator veinsSee also Obturator canal...
, to the upper part of the obturator foramen
Obturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the hole created by the ischium and pubis bones of the pelvis through which nerves and muscles pass.- General structure :...
.
Here it enters the thigh, through the obturator canal
Obturator canal
The obturator canal is a passageway formed in the obturator foramen by part of the obturator membrane. It connects the pelvis to the thigh.The obturator artery, obturator vein, and obturator nerve all travel through the canal.-Pathology:...
, and divides into an anterior and a posterior branch, which are separated at first by some of the fibers of the Obturator externus, and lower down by the Adductor brevis.
Innervation
The Obturator nerve is responsible for the sensory innervation of the skin of the medial aspect of the thighThigh
In humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.The single bone in the thigh is called the femur...
.
It is also responsible for the motor innervation of the adductor muscles of the lower extremity (external obturator., adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gracilis
Gracilis muscle
The gracilis is the most superficial muscle on the medial side of the thigh. It is thin and flattened, broad above, narrow and tapering below.-Origin and insertion:...
) and the pectineus (inconstant). It is, notably, not responsible for the innervation of the obturator internus, despite the similarity in name.
Branches
- Articular branch
- Anterior branch of obturator nerveAnterior branch of obturator nerveThe anterior branch of the obturator nerve leaves the pelvis in front of the Obturator externus and descends in front of the Adductor brevis, and behind the Pectineus and Adductor longus; at the lower border of the latter muscle it communicates with the anterior cutaneous and saphenous branches of...
- Posterior branch of obturator nervePosterior branch of obturator nerveThe posterior branch of the obturator nerve pierces the anterior part of the Obturator externus, and supplies this muscle; it then passes behind the Adductor brevis on the front of the Adductor magnus, where it divides into numerous muscular branches which are distributed to the Adductor magnus and...
- cutaneous branch of the obturator nerveCutaneous branch of the obturator nerveOccasionally the communicating branch to the anterior cutaneous and saphenous branches of the femoral is continued down, as a cutaneous branch, to the thigh and leg, as the cutaneous branch of the obturator nerve....

