
Occupancy grid mapping
Encyclopedia
Occupancy Grid Mapping refers to a family of computer algorithms
in probabilistic robotics for mobile robots
which address the problem of generating maps from noisy and uncertain sensor measurement data, with the assumption that the robot pose is known.
The basic idea of the occupancy grid is to represent a map of the environment as an evenly spaced field of binary random variables
each representing the presence of an obstacle at that location in the environment. Occupancy grid algorithms compute approximate posterior estimates for these random variables.
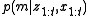 , where
, where 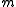 is the map,
is the map, 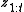 is the set of measurements from time 1 to t, and
is the set of measurements from time 1 to t, and 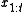 is the set of robot poses from time 1 to t. The controls and odometry data play no part in the occupancy grid mapping algorithm since the path is assumed known.
is the set of robot poses from time 1 to t. The controls and odometry data play no part in the occupancy grid mapping algorithm since the path is assumed known.
Occupancy grid algorithms represent the map as a fine-grained grid over the continuous space of locations in the environment. The most common type of occupancy grid maps are 2d maps that describe a slice of the 3d world.
as a fine-grained grid over the continuous space of locations in the environment. The most common type of occupancy grid maps are 2d maps that describe a slice of the 3d world.
If we let denote the grid cell with index i (often in 2d maps, two indices are used to represent the two dimensions), then the notation
denote the grid cell with index i (often in 2d maps, two indices are used to represent the two dimensions), then the notation  represents the probability that cell i is occupied.
represents the probability that cell i is occupied.
The computational problem with estimating the posterior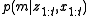 is the dimensionality of the problem: if the map contains 10,000 grid cells (a relatively small map), then the number of possible maps that can be represented by this gridding is
is the dimensionality of the problem: if the map contains 10,000 grid cells (a relatively small map), then the number of possible maps that can be represented by this gridding is 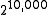 . Thus calculating a posterior probability for all such maps is infeasible.
. Thus calculating a posterior probability for all such maps is infeasible.
The standard approach, then, is to break the problem down into smaller problems of estimating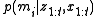 for all grid cells
for all grid cells 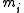 . Each of these estimation problems is then a binary problem. This breakdown is convenient but does lose some of the structure of the problem, since it does not enable modelling dependencies between neighboring cells. Instead , the posterior of a map is approximated by factoring it into
. Each of these estimation problems is then a binary problem. This breakdown is convenient but does lose some of the structure of the problem, since it does not enable modelling dependencies between neighboring cells. Instead , the posterior of a map is approximated by factoring it into
 . Due to this factorization, a binary Bayes filter can be used to estimate the occupancy probability for each grid cell. It is frequent to use a log-odds
. Due to this factorization, a binary Bayes filter can be used to estimate the occupancy probability for each grid cell. It is frequent to use a log-odds
representation of the probability that each grid cell is occupied.
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
in probabilistic robotics for mobile robots
Mobile robot
A mobile robot is an automatic machine that is capable of movement in a given environment.-Overview:Mobile robots have the capability to move around in their environment and are not fixed to one physical location...
which address the problem of generating maps from noisy and uncertain sensor measurement data, with the assumption that the robot pose is known.
The basic idea of the occupancy grid is to represent a map of the environment as an evenly spaced field of binary random variables
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
each representing the presence of an obstacle at that location in the environment. Occupancy grid algorithms compute approximate posterior estimates for these random variables.
Algorithm Outline
There are four major components of occupancy grid mapping approach. They are:- Interpretation,
- Integration,
- Position estimation, and
- Exploration.
Occupancy Grid Mapping Algorithm
The goal of an occupancy mapping algorithm is to estimate the posterior probability over maps given the data: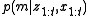 , where
, where 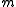 is the map,
is the map, 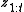 is the set of measurements from time 1 to t, and
is the set of measurements from time 1 to t, and 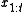 is the set of robot poses from time 1 to t. The controls and odometry data play no part in the occupancy grid mapping algorithm since the path is assumed known.
is the set of robot poses from time 1 to t. The controls and odometry data play no part in the occupancy grid mapping algorithm since the path is assumed known.Occupancy grid algorithms represent the map
 as a fine-grained grid over the continuous space of locations in the environment. The most common type of occupancy grid maps are 2d maps that describe a slice of the 3d world.
as a fine-grained grid over the continuous space of locations in the environment. The most common type of occupancy grid maps are 2d maps that describe a slice of the 3d world.If we let
 denote the grid cell with index i (often in 2d maps, two indices are used to represent the two dimensions), then the notation
denote the grid cell with index i (often in 2d maps, two indices are used to represent the two dimensions), then the notation  represents the probability that cell i is occupied.
represents the probability that cell i is occupied.The computational problem with estimating the posterior
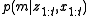 is the dimensionality of the problem: if the map contains 10,000 grid cells (a relatively small map), then the number of possible maps that can be represented by this gridding is
is the dimensionality of the problem: if the map contains 10,000 grid cells (a relatively small map), then the number of possible maps that can be represented by this gridding is 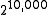 . Thus calculating a posterior probability for all such maps is infeasible.
. Thus calculating a posterior probability for all such maps is infeasible.The standard approach, then, is to break the problem down into smaller problems of estimating
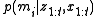 for all grid cells
for all grid cells 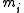 . Each of these estimation problems is then a binary problem. This breakdown is convenient but does lose some of the structure of the problem, since it does not enable modelling dependencies between neighboring cells. Instead , the posterior of a map is approximated by factoring it into
. Each of these estimation problems is then a binary problem. This breakdown is convenient but does lose some of the structure of the problem, since it does not enable modelling dependencies between neighboring cells. Instead , the posterior of a map is approximated by factoring it into . Due to this factorization, a binary Bayes filter can be used to estimate the occupancy probability for each grid cell. It is frequent to use a log-odds
. Due to this factorization, a binary Bayes filter can be used to estimate the occupancy probability for each grid cell. It is frequent to use a log-oddsLogit
The logit function is the inverse of the sigmoidal "logistic" function used in mathematics, especially in statistics.Log-odds and logit are synonyms.-Definition:The logit of a number p between 0 and 1 is given by the formula:...
representation of the probability that each grid cell is occupied.

