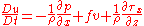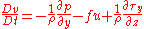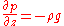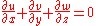Ocean dynamics
Encyclopedia
Ocean dynamics define and describe the motion of water within the oceans. Ocean temperature and motion fields can be separated into three distinct layers: mixed (surface) layer, upper ocean (above the thermocline
), and deep ocean.
Ocean dynamics has traditionally been investigated by sampling from instruments in situ
.
The mixed layer
is nearest to the surface and can vary in thickness from 10 to 500 meters. This layer has properties such as temperature, salinity
and dissolved oxygen which are uniform with depth reflecting a history of active turbulence (the atmosphere has an analogous planetary boundary layer
). Turbulence is high in the mixed layer. However, it becomes zero at the base of the mixed layer. Turbulence again increases below the base of the mixed layer due to shear instabilities. At extratropical latitudes this layer is deepest in late winter as a result of surface cooling and winter storms and quite shallow in summer. Its dynamics is governed by turbulent mixing as well as Ekman pumping, exchanges with the overlying atmosphere, and horizontal advection.
The upper ocean, characterized by warm temperatures and active motion, varies in depth from 100 m or less in the tropics and eastern oceans to in excess of 800 meters in the western subtropical oceans. This layer exchanges properties such as heat and freshwater with the atmosphere on timescales of a few years. Below the mixed layer the upper ocean is generally governed by the hydrostatic and geostrophic
relationships. Exceptions include the deep tropics and coastal regions.
The deep ocean is both cold and dark with generally weak velocities (although limited areas of the deep ocean are known to have significant recirculations). The deep ocean is supplied with water from the upper ocean in only a few limited geographical regions: the subpolar North Atlantic and several sinking regions around the Antarctic
. Because of the weak supply of water to the deep ocean the average residence time of water in the deep ocean is measured in hundreds of years. In this layer as well the hydrostatic and geostrophic relationships are generally valid and mixing is generally quite weak.
expressed as the Navier-Stokes equations
for a fluid element located at (x,y,z) on the surface of our rotating planet and moving at velocity (u,v,w) relative to that surface:
Here "u" is zonal velocity, "v" is meridional velocity, "w" is vertical velocity, "p" is pressure, "ρ" is density, "T" is temperature, "S" is salinity, "g" is acceleration due to gravity, "τ" is wind stress, and "f" is the Coriolis parameter. "Q" is the heat input to the ocean, while "P-E" is the freshwater input to the ocean.
is superimposed on geostrophic flow associated with horizontal gradients of density.
and Kuroshio
) exist in order to return water to higher latitude.
Thermocline
A thermocline is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid , in which temperature changes more rapidly with depth than it does in the layers above or below...
), and deep ocean.
Ocean dynamics has traditionally been investigated by sampling from instruments in situ
Situ
The words situ and situs are Latin for "site" . They also have other meanings .Situ can refer to:* in situ, Latin phrase meaning on-site or in-place...
.
The mixed layer
Mixed layer
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, cooling, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity...
is nearest to the surface and can vary in thickness from 10 to 500 meters. This layer has properties such as temperature, salinity
Salinity
Salinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
and dissolved oxygen which are uniform with depth reflecting a history of active turbulence (the atmosphere has an analogous planetary boundary layer
Planetary boundary layer
The planetary boundary layer , also known as the atmospheric boundary layer , is the lowest part of the atmosphere and its behavior is directly influenced by its contact with a planetary surface. On Earth it usually responds to changes in surface forcing in an hour or less...
). Turbulence is high in the mixed layer. However, it becomes zero at the base of the mixed layer. Turbulence again increases below the base of the mixed layer due to shear instabilities. At extratropical latitudes this layer is deepest in late winter as a result of surface cooling and winter storms and quite shallow in summer. Its dynamics is governed by turbulent mixing as well as Ekman pumping, exchanges with the overlying atmosphere, and horizontal advection.
The upper ocean, characterized by warm temperatures and active motion, varies in depth from 100 m or less in the tropics and eastern oceans to in excess of 800 meters in the western subtropical oceans. This layer exchanges properties such as heat and freshwater with the atmosphere on timescales of a few years. Below the mixed layer the upper ocean is generally governed by the hydrostatic and geostrophic
Geostrophic
A geostrophic current is an oceanic flow in which the pressure gradient force is balanced by the Coriolis force. The direction of geostrophic flow is parallel to the isobars, with the high pressure to the right of the flow in the Northern Hemisphere, and the high pressure to the left in the...
relationships. Exceptions include the deep tropics and coastal regions.
The deep ocean is both cold and dark with generally weak velocities (although limited areas of the deep ocean are known to have significant recirculations). The deep ocean is supplied with water from the upper ocean in only a few limited geographical regions: the subpolar North Atlantic and several sinking regions around the Antarctic
Antarctic
The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence...
. Because of the weak supply of water to the deep ocean the average residence time of water in the deep ocean is measured in hundreds of years. In this layer as well the hydrostatic and geostrophic relationships are generally valid and mixing is generally quite weak.
Primitive equations
Ocean dynamics are governed by Newton's equations of motionNewton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that form the basis for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between the forces acting on a body and its motion due to those forces...
expressed as the Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations, named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of fluid substances. These equations arise from applying Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the fluid stress is the sum of a diffusing viscous...
for a fluid element located at (x,y,z) on the surface of our rotating planet and moving at velocity (u,v,w) relative to that surface:
- the zonal momentum equation:
- the meridional momentum equation:
- the vertical momentum equation (assumes the ocean is in hydrostatic balance):
- the continuityContinuity equationA continuity equation in physics is a differential equation that describes the transport of a conserved quantity. Since mass, energy, momentum, electric charge and other natural quantities are conserved under their respective appropriate conditions, a variety of physical phenomena may be described...
equation (assumes the ocean is incompressible):
- the temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
equation:
-
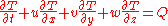 .
.
- the salinitySalinitySalinity is the saltiness or dissolved salt content of a body of water. It is a general term used to describe the levels of different salts such as sodium chloride, magnesium and calcium sulfates, and bicarbonates...
equation:
-
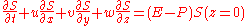 .
.
Here "u" is zonal velocity, "v" is meridional velocity, "w" is vertical velocity, "p" is pressure, "ρ" is density, "T" is temperature, "S" is salinity, "g" is acceleration due to gravity, "τ" is wind stress, and "f" is the Coriolis parameter. "Q" is the heat input to the ocean, while "P-E" is the freshwater input to the ocean.
Mixed layer dynamics
Mixed layer dynamics are quite complicated; however, in some regions some simplifications are possible. The wind-driven horizontal transport in the mixed layer is approximately described by Ekman Layer dynamics in which vertical diffusion of momentum balances the Coriolis effect and wind stress. This Ekman transportEkman transport
Ekman transport, part of Ekman motion theory first investigated in 1902 by Vagn Walfrid Ekman , is the term given for the 90 degree net transport of the surface layer due to wind forcings...
is superimposed on geostrophic flow associated with horizontal gradients of density.
Upper ocean dynamics
Horizontal convergences and divergences within the mixed layer due, for example, to Ekman transport convergence imposes a requirement that ocean below the mixed layer must move fluid particles vertically. But one of the implications of the geostrophic relationship is that the magnitude of horizontal motion must greatly exceed the magnitude of vertical motion. Thus the weak vertical velocities associated with Ekman transport convergence (measured in meters per day) cause horizontal motion with speeds of 10 centimeters per second or more. The mathematical relationship between vertical and horizontal velocities can be derived by expressing the idea of conservation of angular momentum for a fluid on a rotating sphere. This relationship (with a couple of additional approximations) is known to oceanographers as the Sverdrup relation. Among its implications is the result that the horizontal convergence of Ekman transport observed to occur in the subtropical North Atlantic and Pacific forces southward flow throughout the interior of these two oceans. Western boundary currents (the Gulf StreamGulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension towards Europe, the North Atlantic Drift, is a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates at the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean...
and Kuroshio
Kuroshio Current
The Kuroshio is a north-flowing ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean. It is similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic and is part of the North Pacific ocean gyre...
) exist in order to return water to higher latitude.