
Ocean turbidity
Encyclopedia
Turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality....
ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
waters are those with a large number of scattering particulates in them. In both highly absorbing and highly scattering water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
s, visibility into the water is reduced. The highly scattering (turbid) water still reflects a lot of light while the highly absorbing water, such as a blackwater river
Blackwater river
A blackwater river is a river with a deep, slow-moving channel that flows through forested swamps and wetlands. As vegetation decays in the water, tannins are leached out, resulting in transparent, acidic water that is darkly stained, resembling tea or coffee. Most major blackwater rivers are in...
or lake, is very dark. The scattering particles that cause the water to be turbid can be composed of many things, including sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
s and phytoplankton
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are the autotrophic component of the plankton community. The name comes from the Greek words φυτόν , meaning "plant", and πλαγκτός , meaning "wanderer" or "drifter". Most phytoplankton are too small to be individually seen with the unaided eye...
.
Measurement
There are a number of ways to measure ocean turbidity, including autonomous remote vehicles, shipcasts and satellites.From a satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
, a proxy measurement of the water turbidity can be made by examining the amount of reflectance in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
. For the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer
Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer
The Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer is a space-borne sensor embarked on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration family of polar orbiting platforms . AVHRR instruments measure the reflectance of the Earth in 5 relatively wide spectral bands...
(AVHRR), the logical choice is band 1, covering wavelengths 580 to 680 nanometers
Nanometre
A nanometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one billionth of a metre. The name combines the SI prefix nano- with the parent unit name metre .The nanometre is often used to express dimensions on the atomic scale: the diameter...
, the orange
Orange (colour)
The colour orange occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum at a wavelength of about 585–620 nm, and has a hue of 30° in HSV colour space. It is numerically halfway between red and yellow in a gamma-compressed RGB colour space, the expression of which is the RGB colour wheel. The...
and red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
. In order to make derived products that are comparable over time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
and space
Space
Space is the boundless, three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction. Physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum...
, an atmospheric
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
correction is required. To do this, the effects of Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering
Rayleigh scattering, named after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh, is the elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules. It can occur when light travels through...
are calculated based on the satellite viewing angle and the solar zenith angle and then subtracted from the band 1 radiance
Radiance
Radiance and spectral radiance are radiometric measures that describe the amount of radiation such as light or radiant heat that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle in a specified direction. They are used to characterize both emission from...
. For an aerosol correction, band 2 in the near infrared is used. It is first corrected for Rayleigh scattering and then subtracted from the Rayleigh corrected band 1. The Rayleigh corrected band 2 is assumed to be aerosol radiance
Radiance
Radiance and spectral radiance are radiometric measures that describe the amount of radiation such as light or radiant heat that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle in a specified direction. They are used to characterize both emission from...
because no return signal from water in the near infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
is expected since water is highly absorbing at those wavelengths. Because bands 1 and 2 are relatively close on the electromagnetic spectrum, we can reasonably assume their aerosol radiances are the same.
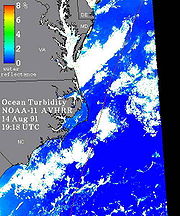
In these images the turbidity is quantified as the percent reflected light emerging from the water column in a range of 0 to 8 percent. The reflectance percentage can be correlated to attenuation
Attenuation
In physics, attenuation is the gradual loss in intensity of any kind of flux through a medium. For instance, sunlight is attenuated by dark glasses, X-rays are attenuated by lead, and light and sound are attenuated by water.In electrical engineering and telecommunications, attenuation affects the...
, Secchi disk depth or total suspended solids although the exact relationship will vary regionally and depends on the optical properties of the water. For example in Florida Bay
Florida Bay
Florida Bay is the bay located between the southern end of the Florida mainland and the Florida Keys. Its area is variously stated to be , or , or . Nearly all of Florida Bay is included in Everglades National Park. The southern edge, along the Florida Keys is in the Florida Keys National Marine...
, 10% reflectance corresponds to a sediment concentration of 30 milligram/liter and a Secchi depth of 0.5 meter. These relationships are approximately linear
Linear
In mathematics, a linear map or function f is a function which satisfies the following two properties:* Additivity : f = f + f...
so that 5% reflectance would correspond to a sediment concentration of approximately 15 milligram/liter and a Secchi depth of 1 meters. In the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
plume regions these same reflectance values would represent sediment concentrations that are about ten times or more higher.
Hurricanes
As one would expect, the majority of these images reveal large increases in turbidity in the regions where a hurricane has made landfall. The increases are primarily due to sediments that have been resuspended from the shallow bottom regions. In areas near shore some of the signal may also be due to sediments erodedErosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
from beach
Beach
A beach is a geological landform along the shoreline of an ocean, sea, lake or river. It usually consists of loose particles which are often composed of rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles or cobblestones...
es as well as from sediment laden river plumes. In some cases a post-hurricane phytoplankton bloom due to increased nutrient
Nutrient
A nutrient is a chemical that an organism needs to live and grow or a substance used in an organism's metabolism which must be taken in from its environment. They are used to build and repair tissues, regulate body processes and are converted to and used as energy...
availability may perhaps be detectable.
The examination of the turbidity after the passing of a hurricane can have potentially many uses for coastal resource management including:
- identifying regional "hot spots" where the erosion could be expected to be most severe
- estimating the total sediment concentration that has been mobilized by the hurricane
- determining the spatial extent of the sediment mobilization
- identifying the extent and contribution of river plumes
- assessing and predicting potential ecosystemEcosystemAn ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
impacts
With regard to these uses, determining the regions of high turbidity will allow managers to best decide on response strategies as well as help ensure that post-hurricane resources are most effectively utilized.
Interpreting images
Only a small fraction of the light incident on the ocean will be reflected and received by the satellite. The probability for a photonPhoton
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
to reflect and exit the ocean decreases exponentially with length of its path through the water because the ocean is an absorbing media. The more ocean a photon must travel through, the greater its chances of being absorbed by something. After absorption, it will eventually become part of the ocean's heat reservoir. The absorption and scattering characteristics of a water body determine the rate of vertical light attenuation and set a limit to the depths contributing to a satellite signal. A reasonable rule of thumb is that 90 percent of the signal coming from the water that is seen by the satellite is from the first attenuation length. How deep this is depends on the absorption and scattering properties of both the water itself and other constituents in the water. For wavelengths in the near infrared and longer, the penetration depth varies from a meter to a few micrometers
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
. For band 1, the penetration depth will usually be between 1 and 10 meters. If the water has a large turbidity spike below 10 meters, the spike
Spike
Spike may refer to:-Device to puncture or fasten:* Nail , especially one over ten inches long* Rail spike, or Screw spike used to construct railroad tracks* Tree spiking, making a tree dangerous to cut with a chainsaw...
is unlikely to be seen by a satellite.
For very shallow clear water there is a good chance the bottom may be seen. For example, in the Bahamas, the water is quite clear and only a few meters deep, resulting in an apparent high turbidity because the bottom reflects a lot of the band 1 light. For areas with consistently high turbidity signals, particularly areas with relatively clear water, part of the signal may be due to bottom reflection. Normally this will not be a problem with a post-hurricane turbidity image since the storm
Storm
A storm is any disturbed state of an astronomical body's atmosphere, especially affecting its surface, and strongly implying severe weather...
easily resuspends enough sediment such that bottom reflection is negligible.
Cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
s are also problematic for the interpretation of satellite derived turbidity. Cloud removal algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
s perform a satisfactory job for pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
s that are fully cloudy. Partially cloudy pixels are much harder to identify and typically result in false high turbidity estimates. High turbidity values near clouds are suspect.
Note: The information in this page has been incorporated from NOAA
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration , pronounced , like "noah", is a scientific agency within the United States Department of Commerce focused on the conditions of the oceans and the atmosphere...
, allowable under United States fair use
Fair use
Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders...
laws. Original source of the information is at http://www.csc.noaa.gov/crs/cohab/hurricane/turbid.htm

