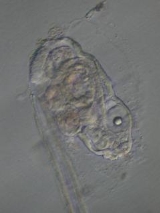
Oikopleura
Encyclopedia
Oikopleura is a genus
of Tunicata
(sea-squirts) in the class Appendicularia. It forms a mucus house every four hours at 20 degrees Celsius. This house has a coarse mesh to keep out big particles, and a fine mesh that collects the small particles, down to the nanoplankton that includes (pelagic) bacteria
.
Abandoned mucus houses sink to the deep, collecting organic particles during their descent. They make an important contribution to marine snow
, since Oikopleura is abundant and is a very active filterer, using powerful strokes of its tail. Its abundance is less obvious from preserved samples (that are usually analyzed) because the gelatinous body disappears in the preservation process while leaving hardly any trace.
It has only about 15,000 genes.
signaling which operates during chordate development. The loss raises the question of the evolutionary constraints that have prevented similar changes in the other chordates.
Oikopleura dioica hox genes are distributed in nine locations around the genome whereas other chordate
s have a cluster of hox genes.[Nature 2 Sept 2004]
Genus
In biology, a genus is a low-level taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms, which is an example of definition by genus and differentia...
of Tunicata
Tunicate
Tunicates, also known as urochordates, are members of the subphylum Tunicata, previously known as Urochordata, a group of underwater saclike filter feeders with incurrent and excurrent siphons that is classified within the phylum Chordata. While most tunicates live on the ocean floor, others such...
(sea-squirts) in the class Appendicularia. It forms a mucus house every four hours at 20 degrees Celsius. This house has a coarse mesh to keep out big particles, and a fine mesh that collects the small particles, down to the nanoplankton that includes (pelagic) bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
.
Abandoned mucus houses sink to the deep, collecting organic particles during their descent. They make an important contribution to marine snow
Marine snow
In the deep ocean, marine snow is a continuous shower of mostly organic detritus falling from the upper layers of the water column. It is a significant means of exporting energy from the light-rich photic zone to the aphotic zone below. The term was first coined by the explorer William Beebe as he...
, since Oikopleura is abundant and is a very active filterer, using powerful strokes of its tail. Its abundance is less obvious from preserved samples (that are usually analyzed) because the gelatinous body disappears in the preservation process while leaving hardly any trace.
It has only about 15,000 genes.
Oikopleura dioica
A species of particular interest under this genus is the Oikopleura dioica, which is an anomaly among chordates. It has retained the fundamental body plan of the chordate; yet, it has lost the mechanism for retinoic acidRetinoic acid
Retinoic acid is a metabolite of vitamin A that mediates the functions of vitamin A required for growth and development. Retinoic acid is required in chordate animals which includes all higher animals from fishes to humans...
signaling which operates during chordate development. The loss raises the question of the evolutionary constraints that have prevented similar changes in the other chordates.
Oikopleura dioica hox genes are distributed in nine locations around the genome whereas other chordate
Chordate
Chordates are animals which are either vertebrates or one of several closely related invertebrates. They are united by having, for at least some period of their life cycle, a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, an endostyle, and a post-anal tail...
s have a cluster of hox genes.[Nature 2 Sept 2004]

