Operation Jackpot
Encyclopedia
For the 1983–1986 South Carolina drug investigation see Operation Jackpot (drug investigation)
Operation Jackpot was the codename assigned to several different operations during the Bangladesh Liberation War
in 1971. The original "Operation Jackpot" was the logistical and training operation set up under the Indian Army
Eastern Command to aid the Mukti Bahini
-led insurgency. The commando
operation that sabotaged Pakistan Navy
and her assets in Chittagong, Chandpur, Mongla and Naryanganj on August 15 is known in Bangladesh as "Operation Jackpot". It was the first major involvement of Naval Special Service Group
, under Commodore David Felix, in the conflict and actively participated in the conflict. Ironically, SSG(N) also led their counter-operations under the same codename. Finally, the operational plan of Lt. General Sagat Singh
, commanding the Indian Army IV corps and Mukti Bahini personnel against Pakistan naval forces defending the eastern naval sector (Syhlet, Comilla, Noakhali and Chittagong districts) during December 3–16 may also have been named "Operation Jackpot".
launched Operation Searchlight
in March 1971 in a bid to curb all resistance (political and otherwise), the Indian government decided to open the borders to admit Bengali refugees and the Bengali
resistance fighters. By mid-May, Pakistan Army had occupied all major towns in Bangladesh and had driven the battered remnants of the Mukti Bahini across the border into India, forcing the Mukti Bahihi to switch to guerrilla warfare. The Indian BSF (Border Security Force) had given supplies locally to the Mukti Bahini since April, and had even made some incursions across the border in to East Pakistan, but these efforts had been disorganized, uncoordinated and inadequate to meet the needs of the Mukti Bahini. Once the Indian army took over aiding the Mukti Bahini, they decided to launch a fully fledged integrated operation, codenamed Operation Jackpot. The Indian Military Intelligence also recognize the operational abilities of Pakistan's Naval Special Service Group that had conducted the Operation Barisal
, which resulted in an ultimate success. Prior to launch of this operation, the Pakistan's Eastern Naval Command was well established by its Officer Commanding Rear-Admiral Mohammad Shariff. The part of the objective of this operation was to dismantle to Eastern Naval Command of Pakistan Navy, which had posed a significant threat to Indian Eastern Naval Command.
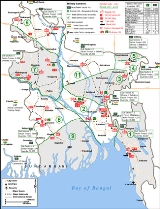
The Indian logistical sectors for this operation were:
Through this network, Mukti Bahini sector commanders communicated with the Bangladesh Forces Headquarters in Kolkata and coordinated all supply, training and operational efforts for the war. Lt. Gen. J. S. Aurora
, commander of Eastern Command, was closely involved in the operation.
Once Indian army reorganized and deployed 3 Infantry coprs to commence operations inside Bangladesh, some of the operation Jackpot formations were built up as combat formations. Foxtrot was designated FJ sector force, with Mukti Bahini Sector No. 11 troops and a BSF battalion and the 6 Bihar regiment, and was placed under 101 communication zone. Echo Sector became Echo Force, with Mukti Bahini Z force Brigade, Sector No. 5 troops, Indian 5/5 Gurkha and 86th BSF battalion, and it operated under the 8 Mountain division.
and the successful conclusion of Operation Barisal
, General A. O. Mittha (Quarter Master General of Pakistan Army) had recommended the creation of a port operating battalion for Chittagong
, in addition to separate River Transport and River Marine Battalion to operate an augmented Cargo and Tanker flotilla. These steps were not implemented, the Army commandeered civilian water crafts for logistics and posted Army and Razakar personnel to guard various ferries, bridges, ports and other naval installations. Pakistan Navy established a Marine academy in June 1971 to support riverine operations.
Rear Admiral Mohammad Shariff had only 4 Gunboats (PNS Comilla, Rajshahi, Jessore and Sylhet) and a patrol boat (PNS Balaghat) in East Pakistan, while the navy remodeled 17 civilian ships into gunboats by adding 12.7/20 mm guns, and .30/.50 caliber Browing Machine guns. These boats joined the fleet by August 1971, while several other boats had been fitted with 40X60 mm Bofors guns and .50 caliber machine guns in Khulna
and Chittagong
dockyards to serve as patrol boats. A few hundred officers and 2,000 crewmen were posted in East Pakistan in 1971. 300 Bengali seamen were transferred to West Pakistan as a precaution after March 25, 1971, while Navy SEAL teams were posted in East Pakistan.
on April 26, while Pakistani gunboats sank 3 Mukti Bahini boats commanded by Captail Jalil on May 5, 1971, at Gabura.
, a coastal city of southern France
. The operation was planned to take on Naval Special Service Group of Pakistan Navy, after it had conducted several other operations. In 1971, there were 11 East Pakistan naval submarine crewmen receiving training there aboard a Pakistani submarine. One commissioned officer (Mosharraf Hassain) and 8 crewmen decided to take control of the submarine and to fight against Pakistan. Their plan was disclosed, however, causing them to flee from death threats made by Pakistan's Naval Intelligence. Out of the 9 crewmen, one was killed by Pakistan Naval Intelligence, but the others managed to travel to the Indian Embassy in Geneva
, Switzerland
. From Geneva, embassy officials took them to New Delhi on April 9, where they began a program of top secret naval training.
and Operation Barisal
, the Army
and Navy
had driven the Mukti Bahini into India, where they entered a period of reorganization during June and July 1971 to train guerrillas, set up networks and safe house
s in the occupied territories to run the insurgency and rebuild the conventional forces. Col. M. a. G. Osmani
divided the country into 11 sectors, while planning to send 2,000–5,000 guerrillas inside Bangladesh every month with 3/4 weeks training to hit all targets of opportunity, while build up the regular force to seize territory in Sylhet
, Indian officials suggested fielding a force of 8,000 guerrillas with regular troops in leadership position with 3 or 4 month training. The solution was to activate the hitherto inactive Sector No. 10 as a special sector for naval commandos with Col. Osmani in charge from May 13 onwards, and this Naval commando force was to be trained as per the Indian suggestion, acting as an elite force for attacking riverine and seabourne targets.
Col. Osmani's initial strategy of sending 2000–5000 guerrillas inside Bangladesh every month since July and hitting the border outposts with regular battalions had not yielded expected results for various reasons, and Pakistani commanders were confident that they have contained the "Monsoon" offensive of Mukti Bahini. As the pace of military operations in Bangladesh slacked off, the civilian morale was adversely affected, which prompted East-Pakistan administrative authorities to claim that the situation had returned to "normal". In response to this declaration, the Mukti Bahini launched 2 operations: 1) Guerrilla attacks in targets in Dhaka by a crack commando group trained by Major ATM Haider (ex-SSG
commando), and 2) the simultaneous mining and damaging of ships in Chittagong
, Chandpur
, Mongla and Narayanganj on August 15, which became known in Bangladesh and international media as "Operation Jackpot".
in collaboration with top regional commanders established the secret camp, codenamed C2P, in Plassey, West Bengal on May 23 to train volunteers selected from various Mukti Bahini sectors (Bangladesh was divided in 10 operational sectors for Mukti Bahini operations) for this purpose. Initially 300 volunteers were chosen, ultimately 499 commandos were trained in the camp. The course included swimming, survival training, using limpet mine
s, hand to hand combat and navigation. By August 1971, the first batch of commandos were ready for operation. The Camp Commander at C2P was Commander M. N. Samanth, Training Coordinator was Lt. Commander G. Martis, both from the Indian Navy, while 20 indian instructors along with the 8 Bengali submariners became trainers. Pakistani Intelligence agents scouted the camp in June and July but Indian security measures prevented any harm to the camp and apprehended all infiltrators.
and Narayanganj
and Sector No. 9 assisted the group targeting Mongla. Each commando carried a pair of fins, a knife, a limpet mine, and swimming trunks. Some had compasses, 1 in 3 commandos had sten guns and hand grenades, the group leaders carried a transistor radio. All the groups carried their own equipment to their targets and after entering Bangladesh between August 3 and 9, reached their destinations by August 12, using the local Mukti Bahini network of safehouses. A pair of songs was played in India Radio (Akashbani) at specific times to convey the intended signal for commencing the operations. The first song (Amar putul ajke prothom jabe shoshur bari) was played on August 13, the second song (Ami tomay joto shuniyechilem gan tar bodole chaini kono dan) on August 14. The result of this operation was:
The simultaneous attacks on Pakistan naval shipping assets on August 16 destroyed the myth of normalcy in East Pakistan when the news was flashed in the international media. Pakistan Army investigation concluded that no one had imagined Mukti Bahini capable of conducting such an operation.
in November 1971, while the Marine base PNS Haider was established at Chittagong. Two Fast Gunboats were obtained from Royal Saudi Navy, but PNS Sadaqat and PNS Rifaqat were never deployed in East Pakistan. Pakistan Army increased security at bridges, ferries and ports, setting up numerous bunkers and strong points near these installations.
The Naval Special Service Group fought back to protect its naval assets. A small teams of Pakistan Naval SEALs and Marines were established that took aggressive counter-measure to eliminate the threat. Naval SEALs, under Commander David Felix, were ordered to kill Bengali commando leaders (a total failure, 7 Bengali submariners survived the war while one was KIA in October 1971), While the SEALs were successful in killing a number of Bengali guerrillas, they failed to protect naval assets in East Pakistan waters, which was the main objective of Operation Jackpot.
In total, 515 commandos received training at C2P. Eight commandos were killed, 34 wounded and 15 captured during August–December 1971. Naval commandoes managed to sink or damage 126 ships/coasters/ferries during that time span, while one source confirms at least 65 vessels of various types (15 Pakistani ships, 11 coasters, 7 gunboats, 11 barges, 2 tankers and 19 river craft by November 1971). had been sunk between August–November 1971. At least 100,000 tons of shipping was sunk or crippled, jetties and wharves were disabled and channels blocked, and the commandos kept East Pakistan in a state of siege without having a single vessel The operational capability of Pakistan Navy was reduced as a result of Operation Jackpot.
Major Jalil, Comander of Mukti bahini Sector No. 9 had obtained permission from Premier Tajuddin Ahmed to form a naval unit in August and had requested 4 Gunboats to Commander M. N. Samanth
In October 1971 Kolkata Port Trust donated 2 patrol crafts (Ajay and Akshay) to Mukti Bahini. The boats underwent a month long refitting at Khidirpur dockyard at the cost of 3.8 million Indian Rupees to carry 2 Canadian 40X60 mm Bofors Guns and 2 light engines and 8 ground mines, four on each side of the deck in addition to 11 ground mines. Renamed BNS Padma and Palash, the boats were crewed by 44 Bengali sailors and 12 Naval commandos, the boats were officered by India Navy personnel and handed over to Mukti Bahini on October 30, 1971. Bangladesh Government in Exile State Minister Captain Kamruzzaman was present when the boats were commissioned by Kolkata Port Trust Chairman Mr. P. K. Sen. Lt. Commander KP Roy and K. Mitra on Indian Navy commanded the boats. The mission for Bangladesh Navy flotilla was:
Escorted by an Indian Navy Frigate, on November 10 these boats successfully mined the entrance of Mongla port. They also chased the British ship "The City of St. Albans" away from Moingla on November 11, 1971.
, Maulaviabazar and Akhaura
, the 39th ad hoc division in Comilla
, Laksham and Feni
and the 97th independent infantry brigade stationed in Chittagong. Indian army had supported Mukti Bahini efforts to seize salients in the Eastern border from November 21, 1971. After Pakistan launched air attacks on India on December 3, the Indian army crossed the border into Bangladesh. By the end of the war on December 16, 1971, the Indian army and the Mukti Bahini had isolated and surrounded the remnants of the 14th division in Syhlet and Bhairabbazar, the 39th division was cornered in Comilla and Chittagong, with all other areas of Syhlet, Comilla, Noakhali and Chittagong clear of enemy forces. Part of the corps and Mukti Bahini forces had crossed the Meghna river using the "Meghna Heli Bridge" and using local boats collected by Mukti Bahini to drive towards Dhaka when the Pakistani army surrendered.
Operation Jackpot (drug investigation)
Operation Jackpot was a federal drug task force based in South Carolina that captured and convicted more than 100 marijuana smugglers from 1983 to 1986 during President Ronald Reagan's War on Drugs...
Operation Jackpot was the codename assigned to several different operations during the Bangladesh Liberation War
Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War was an armed conflict pitting East Pakistan and India against West Pakistan. The war resulted in the secession of East Pakistan, which became the independent nation of Bangladesh....
in 1971. The original "Operation Jackpot" was the logistical and training operation set up under the Indian Army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
Eastern Command to aid the Mukti Bahini
Mukti Bahini
Mukti Bahini , also termed as the "Freedom Fighters" or FFs, collectively refers to the armed organizations who fought against the Pakistan Army during the Bangladesh Liberation War. It was dynamically formed by Bengali regulars and civilians after the proclamation of Bangladesh's independence on...
-led insurgency. The commando
Commando
In English, the term commando means a specific kind of individual soldier or military unit. In contemporary usage, commando usually means elite light infantry and/or special operations forces units, specializing in amphibious landings, parachuting, rappelling and similar techniques, to conduct and...
operation that sabotaged Pakistan Navy
Pakistan Navy
The Pakistan Navy is the naval warfare/service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. Pakistan's Navy is responsible for Pakistan's coastline along the Arabian Sea and the defense of important civilian harbors and military bases...
and her assets in Chittagong, Chandpur, Mongla and Naryanganj on August 15 is known in Bangladesh as "Operation Jackpot". It was the first major involvement of Naval Special Service Group
Special Service Group Navy
The Special Service Group Navy, codename SSG, are the Pakistan Navy's elite principal special operations naval force component. Together with the PAF 312th SS Wing, Special Service Group, Pakistan Marines, and Rangers, they form Pakistan Special Operations Command under the joint administrative...
, under Commodore David Felix, in the conflict and actively participated in the conflict. Ironically, SSG(N) also led their counter-operations under the same codename. Finally, the operational plan of Lt. General Sagat Singh
Sagat Singh
Sagat Singh was a General in the Indian army notable for his participation in liberation of Goa and later in Bangladesh. He held man prestigious command and staff appointments throughout his military career....
, commanding the Indian Army IV corps and Mukti Bahini personnel against Pakistan naval forces defending the eastern naval sector (Syhlet, Comilla, Noakhali and Chittagong districts) during December 3–16 may also have been named "Operation Jackpot".
Indian Army and Mukti Bahini joint operation (May–December 1971)
After the Pakistan ArmyPakistan Army
The Pakistan Army is the branch of the Pakistani Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. The Pakistan Army came into existence after the Partition of India and the resulting independence of Pakistan in 1947. It is currently headed by General Ashfaq Parvez Kayani. The Pakistan...
launched Operation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in the erstwhile East Pakistan in March 1971. Ordered by the central government in West Pakistan, this was seen as the sequel to "Operation Blitz" which had been...
in March 1971 in a bid to curb all resistance (political and otherwise), the Indian government decided to open the borders to admit Bengali refugees and the Bengali
Bengali people
The Bengali people are an ethnic community native to the historic region of Bengal in South Asia. They speak Bengali , which is an Indo-Aryan language of the eastern Indian subcontinent, evolved from the Magadhi Prakrit and Sanskrit languages. In their native language, they are referred to as বাঙালী...
resistance fighters. By mid-May, Pakistan Army had occupied all major towns in Bangladesh and had driven the battered remnants of the Mukti Bahini across the border into India, forcing the Mukti Bahihi to switch to guerrilla warfare. The Indian BSF (Border Security Force) had given supplies locally to the Mukti Bahini since April, and had even made some incursions across the border in to East Pakistan, but these efforts had been disorganized, uncoordinated and inadequate to meet the needs of the Mukti Bahini. Once the Indian army took over aiding the Mukti Bahini, they decided to launch a fully fledged integrated operation, codenamed Operation Jackpot. The Indian Military Intelligence also recognize the operational abilities of Pakistan's Naval Special Service Group that had conducted the Operation Barisal
Operation Barisal
The Operation Barisal was a Pakistan naval operation in 1971 intended to free Barisal, East Pakistan from Mukti Bahinis and the dissidents/armed personnel of the Pakistan Defence Forces. It was the part of Operation Searchlight.-External links:*...
, which resulted in an ultimate success. Prior to launch of this operation, the Pakistan's Eastern Naval Command was well established by its Officer Commanding Rear-Admiral Mohammad Shariff. The part of the objective of this operation was to dismantle to Eastern Naval Command of Pakistan Navy, which had posed a significant threat to Indian Eastern Naval Command.
The Operational Setup
On May 15, the Indian Army took over the task of aiding the Mukti Bahini, setting up a coordinated enterprise under the Eastern Command for meeting the logistical and training needs and, to some extent, lend operational support and planning advice. The operation was codenamed "Operation Jackpot". The operation was initially commanded by Maj. Gen. Onkar Singh Kalkat and after 2 months operational command was assumed by Maj. Gen. B. N. 'Jimmy' Sarcar. The border areas around Bangladesh was divided into 6 logistical sectors, each to be commanded by a Brigadier from the Indian army.The Indian logistical sectors for this operation were:
- Alpha (HQ: Murti Camp, West BengalWest BengalWest Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, C.O. Brig. B. C. Joshi—serving Mukti Bahini Sector No. 6). - Bravo (HQ: Rajgaunj, West Bengal, C.O. Brig. Prem Singh—handling logistics for Mukti Bahini Sector No. 7).
- Charlie (HQ: ChakuliaChakuliaChakulia is a city and a notified area in Purbi Singhbhum district in the state of Jharkhand, India.-Geography:Chakulia is located at . It has an average elevation of 115 metres .-History:...
, BiharBiharBihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, C.O. Brig. N. A. Salik, giving logistical support to Sectors No. 8 and 9). - Delta (HQ: Devta Mura, TripuraTripuraTripura is a state in North-East India, with an area of . It is the third smallest state of India, according to area. Tripura is surrounded by Bangladesh on the north, south, and west. The Indian states of Assam and Mizoram lie to the east. The capital is Agartala and the main languages spoken are...
, C.O. Brig. Sabeg Singh, supporting Sectors No. 1, 2 and 3). - Echo (HQ: Masimpur, AssamAssamAssam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
, C.O. Brig. M. B. Wadh, coordinating logistics for Mukti Bahini Sectors No. 4 and 5). - Foxtrot, (HQ: TuraTura-People:*Cosimo Tura , Italian painter*Will Tura , Belgian singer*Tura language-Places:*Tura Beach, New South Wales, a community in Australia*Tura, Egypt, a town in Cairo Governorate*Tura, Hungary, a city in Pest County...
, MeghalayaMeghalayaMeghalaya is a state in north-eastern India. The word "Meghalaya" literally means the Abode of Clouds in Sanskrit and other Indic languages. Meghalaya is a hilly strip in the eastern part of the country about 300 km long and 100 km wide, with a total area of about 8,700 sq mi . The...
, C.O. Brig. Sant Singh, supplying Sector No. 11).
Through this network, Mukti Bahini sector commanders communicated with the Bangladesh Forces Headquarters in Kolkata and coordinated all supply, training and operational efforts for the war. Lt. Gen. J. S. Aurora
Jagjit Singh Aurora
Lieutenant General Jagjit Singh Aurora was the General Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the Eastern Command of the Indian Army during the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971...
, commander of Eastern Command, was closely involved in the operation.
Effectiveness and Importance
Despite the limitations and challenges rising from the state of the Indian transport system (training camps were located inside India), remoteness of the guerrilla bases, unavailability and inadequacy of proper supplies, and the decision of Bangladesh High Command to put the maximum number of guerrillas into battle in the minimum time possible (often after 4 to 6 weeks of training, sometimes resulting in only 50% of the personnel receiving firearms initially), the operation was effective enough to support the 30,000 regular soldiers (8 infantry battalions, and sector troops) and 100,000 guerrillas that Bangladesh eventually fielded in 1971, and help run a Mukti Bahini campaign that destroyed or damaged at least 231 bridges, 122 railway lines and 90 power stations, while killing 237 officers, 136 JCOs/NCOs and 3,559 soldiers, of the Pakistan army and an unspecified number of EPCAF and police and an estimated 5,000 Razakar personnel during the period of April–November 1971. The Mukti Bahini efforts also demoralized the Pakistani Army to the extent that, by November, they left their bases only if the need arose. The contribution of the Mukti Bahini to the eventual defeat of Pakistan was enormous, which would not have been as effective without the aid of Operation Jackpot.Once Indian army reorganized and deployed 3 Infantry coprs to commence operations inside Bangladesh, some of the operation Jackpot formations were built up as combat formations. Foxtrot was designated FJ sector force, with Mukti Bahini Sector No. 11 troops and a BSF battalion and the 6 Bihar regiment, and was placed under 101 communication zone. Echo Sector became Echo Force, with Mukti Bahini Z force Brigade, Sector No. 5 troops, Indian 5/5 Gurkha and 86th BSF battalion, and it operated under the 8 Mountain division.
Bangladesh naval commando operation (August 16, 1971)
Bangladesh is crisscrossed by hundreds of rivers in addition to 300 large navigable canals. The river transport is important because of the poor state of the road network, especially during the Monsoon, when the whole country turns into a morass of mud and many areas are only reachable only through water transport. The movement and logistics of Pakistan army largely depended on their control of the inland waterways, and of the Sea ports.Pakistan Naval Preparations
The importance waterways were not lost to Pakistan Eastern Command. After the launch of Operation SearchlightOperation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in the erstwhile East Pakistan in March 1971. Ordered by the central government in West Pakistan, this was seen as the sequel to "Operation Blitz" which had been...
and the successful conclusion of Operation Barisal
Operation Barisal
The Operation Barisal was a Pakistan naval operation in 1971 intended to free Barisal, East Pakistan from Mukti Bahinis and the dissidents/armed personnel of the Pakistan Defence Forces. It was the part of Operation Searchlight.-External links:*...
, General A. O. Mittha (Quarter Master General of Pakistan Army) had recommended the creation of a port operating battalion for Chittagong
Chittagong
Chittagong ) is a city in southeastern Bangladesh and the capital of an eponymous district and division. Built on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the city is home to Bangladesh's busiest seaport and has a population of over 4.5 million, making it the second largest city in the country.A trading...
, in addition to separate River Transport and River Marine Battalion to operate an augmented Cargo and Tanker flotilla. These steps were not implemented, the Army commandeered civilian water crafts for logistics and posted Army and Razakar personnel to guard various ferries, bridges, ports and other naval installations. Pakistan Navy established a Marine academy in June 1971 to support riverine operations.
Rear Admiral Mohammad Shariff had only 4 Gunboats (PNS Comilla, Rajshahi, Jessore and Sylhet) and a patrol boat (PNS Balaghat) in East Pakistan, while the navy remodeled 17 civilian ships into gunboats by adding 12.7/20 mm guns, and .30/.50 caliber Browing Machine guns. These boats joined the fleet by August 1971, while several other boats had been fitted with 40X60 mm Bofors guns and .50 caliber machine guns in Khulna
Khulna
Khulna is the third largest city in Bangladesh. It is located on the banks of the Rupsha and Bhairab rivers in Khulna District. It is the divisional headquarters of Khulna Division and a major industrial and commercial center. It has a seaport named Mongla on its outskirts, 38 km from Khulna...
and Chittagong
Chittagong
Chittagong ) is a city in southeastern Bangladesh and the capital of an eponymous district and division. Built on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the city is home to Bangladesh's busiest seaport and has a population of over 4.5 million, making it the second largest city in the country.A trading...
dockyards to serve as patrol boats. A few hundred officers and 2,000 crewmen were posted in East Pakistan in 1971. 300 Bengali seamen were transferred to West Pakistan as a precaution after March 25, 1971, while Navy SEAL teams were posted in East Pakistan.
Mukti Bahini Naval Operations
Mukti Bahini did not operate a separate naval wing during March–June 1971. River crafts were requisitioned as needed. Pakistan Navy and Air Force sank one such craft, MV Ostrich, during Operation BarisalOperation Barisal
The Operation Barisal was a Pakistan naval operation in 1971 intended to free Barisal, East Pakistan from Mukti Bahinis and the dissidents/armed personnel of the Pakistan Defence Forces. It was the part of Operation Searchlight.-External links:*...
on April 26, while Pakistani gunboats sank 3 Mukti Bahini boats commanded by Captail Jalil on May 5, 1971, at Gabura.
New Mukti Bahini initiative: Naval Commandos
The Bangladesh naval commando operation that was called "Operation Jackpot" was precipitated by events in ToulonToulon
Toulon is a town in southern France and a large military harbor on the Mediterranean coast, with a major French naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte-d'Azur region, Toulon is the capital of the Var department in the former province of Provence....
, a coastal city of southern France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. The operation was planned to take on Naval Special Service Group of Pakistan Navy, after it had conducted several other operations. In 1971, there were 11 East Pakistan naval submarine crewmen receiving training there aboard a Pakistani submarine. One commissioned officer (Mosharraf Hassain) and 8 crewmen decided to take control of the submarine and to fight against Pakistan. Their plan was disclosed, however, causing them to flee from death threats made by Pakistan's Naval Intelligence. Out of the 9 crewmen, one was killed by Pakistan Naval Intelligence, but the others managed to travel to the Indian Embassy in Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
, Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
. From Geneva, embassy officials took them to New Delhi on April 9, where they began a program of top secret naval training.
Mukti Bahini reorganization
At the conclusion of Operation SearchlightOperation Searchlight
Operation Searchlight was a planned military operation carried out by the Pakistan Army to curb the Bengali nationalist movement in the erstwhile East Pakistan in March 1971. Ordered by the central government in West Pakistan, this was seen as the sequel to "Operation Blitz" which had been...
and Operation Barisal
Operation Barisal
The Operation Barisal was a Pakistan naval operation in 1971 intended to free Barisal, East Pakistan from Mukti Bahinis and the dissidents/armed personnel of the Pakistan Defence Forces. It was the part of Operation Searchlight.-External links:*...
, the Army
Pakistan Army
The Pakistan Army is the branch of the Pakistani Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. The Pakistan Army came into existence after the Partition of India and the resulting independence of Pakistan in 1947. It is currently headed by General Ashfaq Parvez Kayani. The Pakistan...
and Navy
Pakistan Navy
The Pakistan Navy is the naval warfare/service branch of the Pakistan Armed Forces. Pakistan's Navy is responsible for Pakistan's coastline along the Arabian Sea and the defense of important civilian harbors and military bases...
had driven the Mukti Bahini into India, where they entered a period of reorganization during June and July 1971 to train guerrillas, set up networks and safe house
Safe house
In the jargon of law enforcement and intelligence agencies, a safe house is a secure location, suitable for hiding witnesses, agents or other persons perceived as being in danger...
s in the occupied territories to run the insurgency and rebuild the conventional forces. Col. M. a. G. Osmani
M. A. G. Osmani
General Muhammad Ataul Ghani Osmany, popularly referred to as Bangabir General M.A.G. Osmany was the Commander-in-Chief of Bangladesh Forces during the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971...
divided the country into 11 sectors, while planning to send 2,000–5,000 guerrillas inside Bangladesh every month with 3/4 weeks training to hit all targets of opportunity, while build up the regular force to seize territory in Sylhet
Sylhet
Sylhet , is a major city in north-eastern Bangladesh. It is the main city of Sylhet Division and Sylhet District, and was granted metropolitan city status in March 2009. Sylhet is located on the banks of the Surma Valley and is surrounded by the Jaintia, Khasi and Tripura hills...
, Indian officials suggested fielding a force of 8,000 guerrillas with regular troops in leadership position with 3 or 4 month training. The solution was to activate the hitherto inactive Sector No. 10 as a special sector for naval commandos with Col. Osmani in charge from May 13 onwards, and this Naval commando force was to be trained as per the Indian suggestion, acting as an elite force for attacking riverine and seabourne targets.
Col. Osmani's initial strategy of sending 2000–5000 guerrillas inside Bangladesh every month since July and hitting the border outposts with regular battalions had not yielded expected results for various reasons, and Pakistani commanders were confident that they have contained the "Monsoon" offensive of Mukti Bahini. As the pace of military operations in Bangladesh slacked off, the civilian morale was adversely affected, which prompted East-Pakistan administrative authorities to claim that the situation had returned to "normal". In response to this declaration, the Mukti Bahini launched 2 operations: 1) Guerrilla attacks in targets in Dhaka by a crack commando group trained by Major ATM Haider (ex-SSG
SSG
- Organizations :* Chief of Naval Operations Strategic Studies Group, within the United States Navy* Safesoft Global, former name of Seioglobal, a Chinese IT company* Särskilda Skyddsgruppen, a special forces unit of the Swedish Defence Forces...
commando), and 2) the simultaneous mining and damaging of ships in Chittagong
Chittagong
Chittagong ) is a city in southeastern Bangladesh and the capital of an eponymous district and division. Built on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the city is home to Bangladesh's busiest seaport and has a population of over 4.5 million, making it the second largest city in the country.A trading...
, Chandpur
Chandpur
Chandpur is one of the most important city in Bijnor district, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India.Chandpur is 140 km from the capital of New Delhi, 110 km from Meerut, and 38 km from Gajraula on National Highway 24 ....
, Mongla and Narayanganj on August 15, which became known in Bangladesh and international media as "Operation Jackpot".
Setup and Training
After initial training in Delhi under commander Sharma and DFI chief Brd. Gupta, from April 25 to May 15, the Indian trainers planned for bigger actions. The river transport system was vital for economic activity given the primitive state of the road and railways system of East Pakistan. Indian Commander Bhattachariya, Major Jalil and Colonel M. A. G. OsmaniM. A. G. Osmani
General Muhammad Ataul Ghani Osmany, popularly referred to as Bangabir General M.A.G. Osmany was the Commander-in-Chief of Bangladesh Forces during the Bangladesh Liberation War of 1971...
in collaboration with top regional commanders established the secret camp, codenamed C2P, in Plassey, West Bengal on May 23 to train volunteers selected from various Mukti Bahini sectors (Bangladesh was divided in 10 operational sectors for Mukti Bahini operations) for this purpose. Initially 300 volunteers were chosen, ultimately 499 commandos were trained in the camp. The course included swimming, survival training, using limpet mine
Limpet mine
A limpet mine is a type of naval mine attached to a target by magnets; they are so named because of their superficial similarity to the limpet, a type of mollusk....
s, hand to hand combat and navigation. By August 1971, the first batch of commandos were ready for operation. The Camp Commander at C2P was Commander M. N. Samanth, Training Coordinator was Lt. Commander G. Martis, both from the Indian Navy, while 20 indian instructors along with the 8 Bengali submariners became trainers. Pakistani Intelligence agents scouted the camp in June and July but Indian security measures prevented any harm to the camp and apprehended all infiltrators.
The Operation
The operation was planned in the last week of July, under tight security. Information on river tides, weather and East Pakistan naval infrastructure and deployment was collected through the Mukti Bahini. Selected commandos were sent from C2P to forward bases in Tripura and West Bengal, where a final briefing was given to them. Mukti Bahini in Sector No. 1 assisted the group going to Chittagong, Sector No. 2 aided the groups going to ChandpurChandpur
Chandpur is one of the most important city in Bijnor district, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India.Chandpur is 140 km from the capital of New Delhi, 110 km from Meerut, and 38 km from Gajraula on National Highway 24 ....
and Narayanganj
Narayanganj
Narayanganj is a city in central Bangladesh. It is located in the Narayanganj District, near the capital city of Dhaka and has a population of 220,000. The city is on the bank of the Shitalakshya River. The river port of Narayanganj is one of the oldest in Bangladesh...
and Sector No. 9 assisted the group targeting Mongla. Each commando carried a pair of fins, a knife, a limpet mine, and swimming trunks. Some had compasses, 1 in 3 commandos had sten guns and hand grenades, the group leaders carried a transistor radio. All the groups carried their own equipment to their targets and after entering Bangladesh between August 3 and 9, reached their destinations by August 12, using the local Mukti Bahini network of safehouses. A pair of songs was played in India Radio (Akashbani) at specific times to convey the intended signal for commencing the operations. The first song (Amar putul ajke prothom jabe shoshur bari) was played on August 13, the second song (Ami tomay joto shuniyechilem gan tar bodole chaini kono dan) on August 14. The result of this operation was:
- Chittagong: Submariner Abdul Wahed Chowdhury led the Chittagong Operation. Sixty commandoes were divided into 3 groups of 20 each, but one group failed to arrive due to Pakistani security on time. Out of 40 commandoes, 9 refused to take part, while 31 commandos mined 10 ships instead of 22 initially planned on August 166. Between 1:45 and 2:15 am, explosions sank the MV Al-Abbas, the MV Hormuz and the Orient barge no. 6, sinking 19,000 tons of arms and ammunition along with damaging/sinking 7 other barges/ships.
- Chandpur: Submariner Bodiul Alam led 20 commandoes to mine ships at Chandpur. Two commandoes ultimately refused to take part, the other 18 divided into 6 groups and mined 4 ships. 3 steamers/barges were damaged or sunk.
- NarayanganjNarayanganjNarayanganj is a city in central Bangladesh. It is located in the Narayanganj District, near the capital city of Dhaka and has a population of 220,000. The city is on the bank of the Shitalakshya River. The river port of Narayanganj is one of the oldest in Bangladesh...
: 20 commandos conducted the sabotage operation. Four ships were sunk or damaged. Submariner Abedur Rahman was in charge of the commando group sent to Narayanganj. - Mongla: Submariner Md. Ahsanullah led 60 commandoes to Mongla port. This team was divided into 5 groups of 12 members each. Ultimately 48 commandos mined 6 ships at Mongla. Twelve commandos had been sent on a separate mission.
The simultaneous attacks on Pakistan naval shipping assets on August 16 destroyed the myth of normalcy in East Pakistan when the news was flashed in the international media. Pakistan Army investigation concluded that no one had imagined Mukti Bahini capable of conducting such an operation.
Pakstani countermeasures
Pakistan Navy had taken measures to safeguard East Pakistan naval assets since March 25, 1971. Pakistan Marine battalion under Captain Zamir deployed 3 Naval Marine companies and a Naval platoon at ChittagongChittagong
Chittagong ) is a city in southeastern Bangladesh and the capital of an eponymous district and division. Built on the banks of the Karnaphuli River, the city is home to Bangladesh's busiest seaport and has a population of over 4.5 million, making it the second largest city in the country.A trading...
in November 1971, while the Marine base PNS Haider was established at Chittagong. Two Fast Gunboats were obtained from Royal Saudi Navy, but PNS Sadaqat and PNS Rifaqat were never deployed in East Pakistan. Pakistan Army increased security at bridges, ferries and ports, setting up numerous bunkers and strong points near these installations.
The Naval Special Service Group fought back to protect its naval assets. A small teams of Pakistan Naval SEALs and Marines were established that took aggressive counter-measure to eliminate the threat. Naval SEALs, under Commander David Felix, were ordered to kill Bengali commando leaders (a total failure, 7 Bengali submariners survived the war while one was KIA in October 1971), While the SEALs were successful in killing a number of Bengali guerrillas, they failed to protect naval assets in East Pakistan waters, which was the main objective of Operation Jackpot.
Assessment
Not all Naval Commando missions met with success. Tightened security prevented any operations in Chittagong after the first week of October, while four attempts to damage the Hardinge Bridge failed. Some Commando teams were ambushed and prevented from reaching their objectives. Misfortune and miscalculation caused some missions to fail. Security measures prevented any sabotage attempts on the Oil depots at Narayanganj, Bogura, Faridpur and Chittagong, and Mukti Bahini managed to damage the Oil depots at Chittagong and Naryanganj using Helicopters and Twin Otter plane in December 2, 1971.In total, 515 commandos received training at C2P. Eight commandos were killed, 34 wounded and 15 captured during August–December 1971. Naval commandoes managed to sink or damage 126 ships/coasters/ferries during that time span, while one source confirms at least 65 vessels of various types (15 Pakistani ships, 11 coasters, 7 gunboats, 11 barges, 2 tankers and 19 river craft by November 1971). had been sunk between August–November 1971. At least 100,000 tons of shipping was sunk or crippled, jetties and wharves were disabled and channels blocked, and the commandos kept East Pakistan in a state of siege without having a single vessel The operational capability of Pakistan Navy was reduced as a result of Operation Jackpot.
Operation Hotpants
After The operation of August 16, all commandos returned to India. After this no pre-planned simultaneous operation was launched by the Naval Commandos. Instead, some groups were sent to destroy specific targets, and other commandoes benag to hit targets as opportunity presented itself.Major Jalil, Comander of Mukti bahini Sector No. 9 had obtained permission from Premier Tajuddin Ahmed to form a naval unit in August and had requested 4 Gunboats to Commander M. N. Samanth
In October 1971 Kolkata Port Trust donated 2 patrol crafts (Ajay and Akshay) to Mukti Bahini. The boats underwent a month long refitting at Khidirpur dockyard at the cost of 3.8 million Indian Rupees to carry 2 Canadian 40X60 mm Bofors Guns and 2 light engines and 8 ground mines, four on each side of the deck in addition to 11 ground mines. Renamed BNS Padma and Palash, the boats were crewed by 44 Bengali sailors and 12 Naval commandos, the boats were officered by India Navy personnel and handed over to Mukti Bahini on October 30, 1971. Bangladesh Government in Exile State Minister Captain Kamruzzaman was present when the boats were commissioned by Kolkata Port Trust Chairman Mr. P. K. Sen. Lt. Commander KP Roy and K. Mitra on Indian Navy commanded the boats. The mission for Bangladesh Navy flotilla was:
- Mine the Chalna port entry point
- Attack Pakistani shipping
Escorted by an Indian Navy Frigate, on November 10 these boats successfully mined the entrance of Mongla port. They also chased the British ship "The City of St. Albans" away from Moingla on November 11, 1971.
Naval Commandos killed in Operation Jackpot
- Commando Abdur Raquib, who was killed during the Foolchhori Ghat Operation
- Commando Hossain Farid, who was executed during the second Chittagong operation. He was captured by Pakistani army, who tortured him to death by placing him inside a manhole and bending his body until his vertebral column was shattered.
- Commando Khabiruzzaman, who was killed in second operation in Faridpur
- Commando Sirajul Islam, M. Aziz, Aftab Uddin, and Rafiqul Islam, nothing further is known about them.
Naval Commandos Who Received Bangladesh 'National Hero' Recognition
- Mr. A.W. Chowdhury- Bir Uttam
- Mr. Badiul Alam- Bir Uttam
- Dr. Shah Alam- Bir Uttam
- Mr. Mazhar Ullah- Bir Uttam
- Mr. Sheikh Md. Amin Ullah- Bir Uttam
- Mr. Abedur Rahman- Bir Uttam
- Mr. Mosharraf Hossain- Bir Uttam (His honor was revoked by the ruling Government of Bangladesh)
- Mohammad Khabiruzzan- Bir Bikrom
- Mr. Momin Ullah Patwari- Bir Protik
- Mr. Shahjahan Kabir- Bir Protik
- Mr. Faruq-e-Azam- Bir Protik
- Mohammad Rahmatullah-Bir Protik
- Mohammad Mojjamel Hossain- Bir Protik
- Amir Hossain- Bir Protik
Indian Army IV corps operation (November 21, 1971)
The plan of operation for the Indian Army IV corps (8 Mountain Div., 23 Mountain Div., 57 Mountain Div. and "Kilo Force") and the Bangladesh forces (8 infantry battalions, and guerrillas and sector troops of Sector No. 1-5 of Mukti Bahini) may have been codenamed "Operation Jackpot". The opposition forces included the Pakistani 14th Infantry division defending SylhetSylhet
Sylhet , is a major city in north-eastern Bangladesh. It is the main city of Sylhet Division and Sylhet District, and was granted metropolitan city status in March 2009. Sylhet is located on the banks of the Surma Valley and is surrounded by the Jaintia, Khasi and Tripura hills...
, Maulaviabazar and Akhaura
Akhaura Upazila
Akhaura is an Upazila of Brahmanbaria District in the Division of Chittagong, Bangladesh.-Geography:Akhaura is located at . It has 18783 units of house hold and it has no total area as it is a part of wonderland.-Demographics:...
, the 39th ad hoc division in Comilla
Comilla
Comilla is a city in south-eastern Bangladesh, located along the Dhaka-Chittagong Highway. It is the administrative center of the Comilla District, part of the Chittagong Division. The Eastern Wing of Bangladesh Highway Police is located in Comilla....
, Laksham and Feni
Feni
Feni may refer to:*Feni District, in Bangladesh**Feni Girls Cadet College*Feni Islands, in Papua New Guinea*Feni liquor, is a local alcoholic brew made in Goa, India*Feni River, in Bangladesh and India*Feni Rose, Indonesia TV presenter...
and the 97th independent infantry brigade stationed in Chittagong. Indian army had supported Mukti Bahini efforts to seize salients in the Eastern border from November 21, 1971. After Pakistan launched air attacks on India on December 3, the Indian army crossed the border into Bangladesh. By the end of the war on December 16, 1971, the Indian army and the Mukti Bahini had isolated and surrounded the remnants of the 14th division in Syhlet and Bhairabbazar, the 39th division was cornered in Comilla and Chittagong, with all other areas of Syhlet, Comilla, Noakhali and Chittagong clear of enemy forces. Part of the corps and Mukti Bahini forces had crossed the Meghna river using the "Meghna Heli Bridge" and using local boats collected by Mukti Bahini to drive towards Dhaka when the Pakistani army surrendered.
See also
- PNS Mehran raid—a recent and similar operation perpetuated by Pakistan Taliban militants.

