
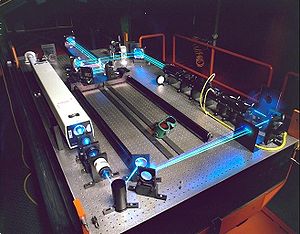
Optical table
Encyclopedia
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
s and engineering
Optical engineering
Optical engineering is the field of study that focuses on applications of optics. Optical engineers design components of optical instruments such as lenses, microscopes, telescopes, and other equipment that utilizes the properties of light. Other devices include optical sensors and measurement...
.
Explanation
In optical systems, especially those involving interferometryInterferometry
Interferometry refers to a family of techniques in which electromagnetic waves are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. An instrument used to interfere waves is called an interferometer. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy,...
, the alignment
Alignment
Alignment may refer to:* Alignment , secondary evidence used to associate features such as postholes* Alignment , in Israel from 1965 to 1992...
of each component must be extremely accurate—precise down to a fraction of a wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
—usually a few hundred nanometers. Even small vibrations or strain
Strain (materials science)
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory, sometimes called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory, deals with infinitesimal deformations of a continuum body...
in the table on which the elements are set up might lead to complete failure of an experiment. Hence, one requires an extremely rigid table which neither moves nor flexes, even under changing loads or vibrations. The surface of the table must also be quite flat, to allow precision optical mounts to make good contact with the table without rocking and facilitate easy assembly of the optical system.
Earlier optical table tops were sometimes made of a large slab of highly polished granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
. The heavy, dense material strongly suppresses the amplitude of high frequency mechanical vibrations producing a very stable surface that improves the stability of the optical system. Such tables were very heavy and expensive, however, and are not commonly available today.
Modern optical tables are typically made of top and bottom sheets of steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
, aluminum, or carbon fiber
Carbon fiber
Carbon fiber, alternatively graphite fiber, carbon graphite or CF, is a material consisting of fibers about 5–10 μm in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the long axis of the fiber...
, separated by a thick honeycomb lattice structure. The surface usually has a grid of threaded holes which allow the components to be bolted down to fit the optical system layout. Components may also be held to the steel surface by magnetic base
Magnetic base
A magnetic base is a magnetic fixture based on a magnet that can effectively be turned "on" and "off" at will; they are often used in optics and metalworking, e.g., to hold a dial indicator....
s. Often, the table's legs are pneumatic vibration damper
Damping
In physics, damping is any effect that tends to reduce the amplitude of oscillations in an oscillatory system, particularly the harmonic oscillator.In mechanics, friction is one such damping effect...
s. For even more accurate setups, one also prevents air movements and temperature gradients by enclosing the surface in a box of transparent plastic such as Plexiglas. One may also use a "flowbox", a device which produces a laminar stream of air flowing downwards, kept at constant temperature by special air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
.
The metal used to construct modern optical tables has a higher speed of sound than granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
and therefore a higher frequency of the first eigenmode. Any vibration produced on the table below this frequency does not produce a resonant response, making the setup less sensitive to vibrations from motorized optics, cooling water pumps, etc. Vibration damping may be added to tables during their construction. As with granite's composite structure, the combination of several stiff materials with different speeds of sound produces a table for which a wide range of vibrations are critically damped. Viscous
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
fluids are used in between the stiff materials, to aid in damping.
Hole thread and grid
There are versions using metric or imperial units.| Version | Hole thread | Hole grid |
|---|---|---|
| Metric | M6 ISO metric screw thread The ISO metric screw threads are the world-wide most commonly used type of general-purpose screw thread. They were one of the first international standards agreed when the International Organization for Standardization was set up in 1947.-Basic profile:... |
25 mm |
| Imperial | ¼-20" UNC | 1" (25.4mm) |
Breadboards
An alternative to an optical table is an optical breadboard. Some optical systems use breadboards made of solid aluminum for later integration with a larger system with some form of vibration control. Most optical breadboards are constructed fromsteel, aluminum, or carbon fiber sheets with honeycomb structure and can be placed on an ordinary table or workbench. Breadboards are not as good as optical tables, but weigh less and are adequate for smaller optical systems that do not require extremely high levels of mechanical stability. The low weight enables one to support these tables on soft air springs which reduce vibrations coming from the floor, although this increases vibrations due to acoustic noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
.
The honeycomb structure reduces bending due to the breadboard's own weight, so it can be tilted and forces applied via the soft spring supports accelerate the table as a whole without misalignment. Breadboards can therefore be used in mobile applications, such as on airplanes. Also, one can bolt a breadboard onto an optical table, build up a module of the experiment on it, and then transfer the module as a whole onto another table without the need to realign the components on the breadboard. Similarly, custom-built optical devices are assembled and aligned on breadboards, which are then enclosed in a case and shipped to the customer.
Rails and benches


