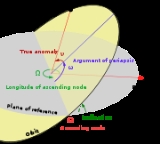
Orbital elements
Overview
Parameter
Parameter from Ancient Greek παρά also “para” meaning “beside, subsidiary” and μέτρον also “metron” meaning “measure”, can be interpreted in mathematics, logic, linguistics, environmental science and other disciplines....
s required to uniquely identify a specific orbit
Orbit
In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System...
. In celestial mechanics
Celestial mechanics
Celestial mechanics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the motions of celestial objects. The field applies principles of physics, historically classical mechanics, to astronomical objects such as stars and planets to produce ephemeris data. Orbital mechanics is a subfield which focuses on...
these elements are generally considered in classical
Classical mechanics
In physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a system of forces...
two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit
Kepler orbit
In celestial mechanics, a Kepler orbit describes the motion of an orbiting body as an ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola, which forms a two-dimensional orbital plane in three-dimensional space...
is used (derived from Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that form the basis for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between the forces acting on a body and its motion due to those forces...
and Newton's law of universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation
Newton's law of universal gravitation states that every point mass in the universe attracts every other point mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them...
). There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes each consisting of a set of six parameters are commonly used in astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
and orbital mechanics.
A real orbit (and its elements) changes over time due to gravitational perturbations
Perturbation (astronomy)
Perturbation is a term used in astronomy in connection with descriptions of the complex motion of a massive body which is subject to appreciable gravitational effects from more than one other massive body....
by other objects and the effects of relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
.
Unanswered Questions

