Outline of New York
Encyclopedia
New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
– U.S. state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
located on the Eastern seaboard
East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
. New York was one of the original Thirteen Colonies
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
. About one third of all the battles of the Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
took place in New York. New York became an independent state on July 9, 1776, and enacted its constitution
New York State Constitutions
The Constitution of the State of New York establishes the structure of the government of the State of New York, and enumerates the basic rights of the citizens of New York. Like most state constitutions in the United States, New York's constitution's provisions tend to be more detailed, and amended...
in 1777. The state ratified the United States Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
on July 26, 1788, to become the 11th member of the United States.
General reference
- Names
- Common name: New YorkNew YorkNew York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
- Pronunciation: njuːˈjɔrk
- Official name: State of New York
- Abbreviations and name codes
- Postal symbol: NY
- ISO 3166-2 code: US-NY
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
second-level domainSecond-level domainIn the Domain Name System hierarchy, a second-level domain is a domain that is directly below a top-level domain . For example, in example.com, example is the second-level domain of the .com TLD....
: .ny.us - Nicknames
- The Empire StateEmpire StateThe Empire State is the official nickname of the U.S. state New York. It may also refer to:*Empire State Building, skyscraper in New York City, one of the tallest buildings in the world*Empire State Plaza, state office complex in Albany, New York...
(currently used on license platesVehicle registration plates of New YorkNew York first issued license plates in 1910. Plates are currently issued by the New York State Department of Motor Vehicles.-Passenger baseplates 1957 to present:-1986: Statue of Liberty:...
)
- The Empire State
- Common name: New York
- Adjectival: New YorkNew YorkNew York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
- Demonym: New Yorker
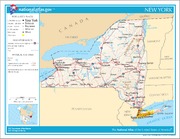
Geography of New York
- New York is: a U.S. stateU.S. stateA U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
, a federal state of the United States of America - Location
- Northern hemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
- Western hemisphereWestern HemisphereThe Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions...
- AmericasAmericasThe Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
- North AmericaNorth AmericaNorth America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
- Anglo America
- Northern AmericaNorthern AmericaNorthern America is the northernmost region of the Americas, and is part of the North American continent. It lies directly north of the region of Middle America; the land border between the two regions coincides with the border between the United States and Mexico...
- United States of America
- Contiguous United StatesContiguous United StatesThe contiguous United States are the 48 U.S. states on the continent of North America that are south of Canada and north of Mexico, plus the District of Columbia....
- Canadian border
- Eastern United StatesEastern United StatesThe Eastern United States, the American East, or simply the East is traditionally defined as the states east of the Mississippi River. The first two tiers of states west of the Mississippi have traditionally been considered part of the West, but can be included in the East today; usually in...
- East Coast of the United StatesEast Coast of the United StatesThe East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
- Northeastern United States
- Mid-Atlantic statesMid-Atlantic StatesThe Mid-Atlantic states, also called middle Atlantic states or simply the mid Atlantic, form a region of the United States generally located between New England and the South...
- East Coast of the United States
- Contiguous United States
- Great Lakes Region
- United States of America
- North America
- Americas
- Northern hemisphere
- Population of New York: 19,378,102 (2010 U.S. Census)
- Area of New York:
- Atlas of New York
- Places in New York
- National Historic Landmarks in New York
- National Register of Historic Places listings in New York
- National Natural Landmarks in New York
- State parks in New York
Environment of New York
- Climate of New YorkClimate of New YorkThe Climate of New York is generally humid continental, and features diverse weather.-General climate:Generally summers of New York have a humid continental climate...
- State forests of New York
- Superfund sites in New York
Natural geographic features of New York
- Lakes of New York
- Rivers of New York
Administrative divisions of New York
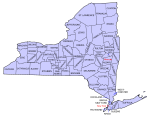
- The 62 Counties of the State of New York
- Cities in New York
- State capital of New York: AlbanyAlbany, New YorkAlbany is the capital city of the U.S. state of New York, the seat of Albany County, and the central city of New York's Capital District. Roughly north of New York City, Albany sits on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River...
- City nicknames in New York
- Sister cities in New York
- State capital of New York: Albany
- Towns in New York
- Cities in New York
- Census-designated places in New York
Government and politics of New York
- Form of government: U.S. state governmentState governments of the United StatesState governments in the United States are those republics formed by citizens in the jurisdiction thereof as provided by the United States Constitution; with the original 13 States forming the first Articles of Confederation, and later the aforementioned Constitution. Within the U.S...
- United States congressional delegations from New YorkUnited States Congressional Delegations from New YorkThese are tables of congressional delegations from New York to the United States Senate and United States House of Representatives.Over the years, New York has demographically changed so that it is hard to consider each district to be a continuation of the same numbered district before...
- New York State CapitolNew York State CapitolThe New York State Capitol is the capitol building of the U.S. state of New York. Housing the New York State Legislature, it is located in the state capital city Albany, on State Street in Capitol Park. The building, completed in 1899 at a cost of $25 million , was the most expensive government...
- Elections in New YorkElections in New YorkUnlike in most states, New York electoral law permits electoral fusion. As a result, New York ballots tend to list a large number of political parties...
- Electoral reform in New YorkElectoral reform in New YorkElectoral reform in New York refers to efforts to change the voting and election laws in New York State.-Alternate voting systems:In 1936, voters in New York City adopted the single transferable vote method of proportional representation. In the election immediately preceding STV's adoption, the...
- Electoral reform in New York
- Political party strength in New YorkPolitical Party Strength in New YorkThe following table indicates the party of elected officials in the U.S. state of New York:*Governor*Lieutenant Governor*Secretary of State*Attorney General*State Comptroller*TreasurerThe table also indicates the historical party composition in the:...
Executive branch of the government of New York
- Governor of New YorkGovernor of New YorkThe Governor of the State of New York is the chief executive of the State of New York. The governor is the head of the executive branch of New York's state government and the commander-in-chief of the state's military and naval forces. The officeholder is afforded the courtesy title of His/Her...
- Lieutenant Governor of New YorkLieutenant Governor of New YorkThe Lieutenant Governor of New York is a constitutional office in the executive branch of the government of New York State. It is the second highest ranking official in state government. The lieutenant governor is elected on a ticket with the governor for a four year term...
- Secretary of State of New YorkSecretary of State of New YorkThe Secretary of State of New York is a cabinet officer in the government of the U.S. state of New York.The current Secretary of State of New York is Cesar A...
- Lieutenant Governor of New York
- State departments
- New York State Department of TransportationNew York State Department of TransportationThe New York State Department of Transportation is responsible for the development and operation of highways, railroads, mass transit systems, ports, waterways and aviation facilities in the U.S...
- New York State Department of Transportation
Legislative branch of the government of New York
- New York LegislatureNew York LegislatureThe New York State Legislature is the term often used to refer to the two houses that act as the state legislature of the U.S. state of New York. The New York Constitution does not designate an official term for the two houses together...
(bicameral)- Upper house: New York State SenateNew York State SenateThe New York State Senate is one of two houses in the New York State Legislature and has members each elected to two-year terms. There are no limits on the number of terms one may serve...
- Lower house: New York State AssemblyNew York State AssemblyThe New York State Assembly is the lower house of the New York State Legislature. The Assembly is composed of 150 members representing an equal number of districts, with each district having an average population of 128,652...
- Upper house: New York State Senate
Judicial branch of the government of New York
- Supreme Court of New YorkNew York Court of AppealsThe New York Court of Appeals is the highest court in the U.S. state of New York. The Court of Appeals consists of seven judges: the Chief Judge and six associate judges who are appointed by the Governor to 14-year terms...
Law and order in New York
- Capital punishment in New YorkCapital punishment in New YorkCapital punishment in New York has not been practiced since 1963, when Eddie Mays was electrocuted at Sing Sing Prison. The state was the first to adopt the electric chair as a method of execution, which replaced hanging. The state is third in recorded number of executions since 1608, after...
- Constitution of New York
- Crime in New YorkCrime in New York-Statistics:In 2008 there were 466,118 crimes reported in New York including 836 murders a full list can be found -Organized crime:Organized crime is especially common in New York City*see also Crime in New York City...
- Gun laws in New York
- Law enforcement in New YorkLaw enforcement in New YorkLaw enforcement in New York state is the responsibility of a very large number of law enforcement agencies. Law enforcement is conducted by police departments, fire departments, sections of other government departments, educational institutions, private companies and charities at federal, state,...
- Law enforcement agencies in New York
- New York State PoliceNew York State PoliceThe New York State Police is the state police force of over 4,600 sworn Troopers for the state of New York. It was established on April 11, 1917 by the New York Legislature, in response to the 1913 murder of a construction foreman named Sam Howell in Westchester County, which at that time did not...
- New York State Police
- Law enforcement agencies in New York
- Same-sex marriage in New YorkSame-sex marriage in New YorkSame-sex marriage in the U.S. state of New York became legal on July 24, 2011, under the Marriage Equality Act, which was passed on June 24, 2011, by the New York State Legislature and signed by Governor Andrew Cuomo on the same day...
History of New York by period
- FrenchFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
colony of CanadaCanada, New FranceCanada was the name of the French colony that once stretched along the St. Lawrence River; the other colonies of New France were Acadia, Louisiana and Newfoundland. Canada, the most developed colony of New France, was divided into three districts, each with its own government: Quebec,...
, 1534–(1609–1763) - DutchNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
colony of Nieuw-Nederland, 1624–1652- History of slavery in New YorkHistory of slavery in New YorkSlavery in New York was instituted when the New Amsterdam fur trading-post developed into a farming colony in the 17th century; the first African slaves were imported by the Dutch West Indies Company to New Amsterdam in 1626...
, 1626–1827
- History of slavery in New York
- Patroonship of Rensselaerswyck, 1630–1840s
- DutchNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
province of Nieuw-Nederland, 1652–1664 - EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Province of New-York, 1664–1673 - Third Anglo-Dutch WarThird Anglo-Dutch WarThe Third Anglo–Dutch War or Third Dutch War was a military conflict between England and the Dutch Republic lasting from 1672 to 1674. It was part of the larger Franco-Dutch War...
, 1672–1674- NetherlandsNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
military government of Nieuw-Nederland, 1673–1674 - Treaty of Westminster of 1674Treaty of Westminster (1674)The Treaty of Westminster of 1674 was the peace treaty that ended the Third Anglo-Dutch War. Signed by the Netherlands and England, it provided for the return of the colony of New Netherland to England and renewed the Treaty of Breda of 1667...
- Netherlands
- EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Province of New-York, 1674–1688 - EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Dominion of New-England in America, 1688–1689 - EnglishEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
Province of New-York, 1689–1707 - BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Province of New-York, 1707–1776 - King George's WarKing George's WarKing George's War is the name given to the operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession . It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in the British provinces of New York, Massachusetts Bay, New Hampshire, and Nova Scotia...
, 1740–1748- Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle of 1748Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748)The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle of 1748 ended the War of the Austrian Succession following a congress assembled at the Imperial Free City of Aachen—Aix-la-Chapelle in French—in the west of the Holy Roman Empire, on 24 April 1748...
- Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle of 1748
- French and Indian WarFrench and Indian WarThe French and Indian War is the common American name for the war between Great Britain and France in North America from 1754 to 1763. In 1756, the war erupted into the world-wide conflict known as the Seven Years' War and thus came to be regarded as the North American theater of that war...
, 1754–1763- Treaty of Paris of 1763Treaty of Paris (1763)The Treaty of Paris, often called the Peace of Paris, or the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763, by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. It ended the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
- Treaty of Paris of 1763
- BritishUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Indian ReserveIndian Reserve (1763)The Indian Reserve was a territory under British rule in North America set aside in the Royal Proclamation of 1763 for use by American Indians between 1763 and 1783....
, 1763–1783- Royal Proclamation of 1763Royal Proclamation of 1763The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued October 7, 1763, by King George III following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America after the end of the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
- Royal Proclamation of 1763
- American Revolutionary WarAmerican Revolutionary WarThe American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
, April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783- Capture of Fort TiconderogaCapture of Fort TiconderogaThe Capture of Fort Ticonderoga occurred during the American Revolutionary War on May 10, 1775, when a small force of Green Mountain Boys led by Ethan Allen and Colonel Benedict Arnold overcame a small British garrison at the fort and looted the personal belongings of the garrison...
, May 10, 1775 - New York and New Jersey campaignNew York and New Jersey campaignThe New York and New Jersey campaign was a series of battles for control of New York City and the state of New Jersey in the American Revolutionary War between British forces under General Sir William Howe and the Continental Army under General George Washington in 1776 and the winter months of 1777...
, July 3, 1776 – July 26, 1777 - United States Declaration of IndependenceUnited States Declaration of IndependenceThe Declaration of Independence was a statement adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, which announced that the thirteen American colonies then at war with Great Britain regarded themselves as independent states, and no longer a part of the British Empire. John Adams put forth a...
, July 4, 1776 - Saratoga campaignSaratoga campaignThe Saratoga Campaign was an attempt by Great Britain to gain military control of the strategically important Hudson River valley in 1777 during the American Revolutionary War...
, June 14 – October 17, 1777- Siege of Fort Ticonderoga, July 2–6, 1777
- Battles of Saratoga, September 19 – October 7, 1777
- Treaty of ParisTreaty of Paris (1783)The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
, September 3, 1783
- Capture of Fort Ticonderoga
- State of New York since 1776
-
- Third state to ratify the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, signed July 9, 1778
- Western territorial claimsState cessionsThe state cessions are those areas of the United States that the separate states ceded to the federal government in the late 18th and early 19th century...
ceded 1782 - Eleventh State to ratify the Constitution of the United States of America on July 26, 1788
- War of 1812War of 1812The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
, June 18, 1812 – March 23, 1815- Battle of PlattsburghBattle of PlattsburghThe Battle of Plattsburgh, also known as the Battle of Lake Champlain, ended the final invasion of the northern states during the War of 1812...
, 1814 - Treaty of GhentTreaty of GhentThe Treaty of Ghent , signed on 24 December 1814, in Ghent , was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States of America and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland...
, December 24, 1814
- Battle of Plattsburgh
- Martin Van BurenMartin Van BurenMartin Van Buren was the eighth President of the United States . Before his presidency, he was the eighth Vice President and the tenth Secretary of State, under Andrew Jackson ....
becomes 8th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1837 - Mexican-American War, April 25, 1846 – February 2, 1848
- Millard FillmoreMillard FillmoreMillard Fillmore was the 13th President of the United States and the last member of the Whig Party to hold the office of president...
becomes 13th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on July 9, 1850 - American Civil WarAmerican Civil WarThe American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, April 12, 1861 – May 13, 1865- New York in the American Civil WarNew York in the American Civil WarThe state of New York during the American Civil War was a major influence in national politics, the Union war effort, and the media coverage of the war...
, 1861–1865
- New York in the American Civil War
- Chester A. ArthurChester A. ArthurChester Alan Arthur was the 21st President of the United States . Becoming President after the assassination of President James A. Garfield, Arthur struggled to overcome suspicions of his beginnings as a politician from the New York City Republican machine, succeeding at that task by embracing...
becomes 21st President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on September 19, 1881 - Grover ClevelandGrover ClevelandStephen Grover Cleveland was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States. Cleveland is the only president to serve two non-consecutive terms and therefore is the only individual to be counted twice in the numbering of the presidents...
becomes 22nd President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1885 - Grover ClevelandGrover ClevelandStephen Grover Cleveland was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States. Cleveland is the only president to serve two non-consecutive terms and therefore is the only individual to be counted twice in the numbering of the presidents...
also becomes 24th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1893 - Spanish-American WarSpanish-American WarThe Spanish–American War was a conflict in 1898 between Spain and the United States, effectively the result of American intervention in the ongoing Cuban War of Independence...
, April 25 – August 12, 1898 - AssassinationWilliam McKinley assassinationThe assassination of William McKinley occurred on September 6, 1901, inside the Temple of Music located on the grounds of the 1901 Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo, New York...
of PresidentPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
William McKinleyWilliam McKinleyWilliam McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
in BuffaloBuffalo, New YorkBuffalo is the second most populous city in the state of New York, after New York City. Located in Western New York on the eastern shores of Lake Erie and at the head of the Niagara River across from Fort Erie, Ontario, Buffalo is the seat of Erie County and the principal city of the...
on September 6, 1901- PresidentPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
McKinleyWilliam McKinleyWilliam McKinley, Jr. was the 25th President of the United States . He is best known for winning fiercely fought elections, while supporting the gold standard and high tariffs; he succeeded in forging a Republican coalition that for the most part dominated national politics until the 1930s...
dies in BuffaloBuffalo, New YorkBuffalo is the second most populous city in the state of New York, after New York City. Located in Western New York on the eastern shores of Lake Erie and at the head of the Niagara River across from Fort Erie, Ontario, Buffalo is the seat of Erie County and the principal city of the...
on September 14, 1901 - Vice PresidentVice President of the United StatesThe Vice President of the United States is the holder of a public office created by the United States Constitution. The Vice President, together with the President of the United States, is indirectly elected by the people, through the Electoral College, to a four-year term...
(and former GovernorGovernor of New YorkThe Governor of the State of New York is the chief executive of the State of New York. The governor is the head of the executive branch of New York's state government and the commander-in-chief of the state's military and naval forces. The officeholder is afforded the courtesy title of His/Her...
) Theodore RooseveltTheodore RooseveltTheodore "Teddy" Roosevelt was the 26th President of the United States . He is noted for his exuberant personality, range of interests and achievements, and his leadership of the Progressive Movement, as well as his "cowboy" persona and robust masculinity...
becomes 26th President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on September 14, 1901
- President
- Former GovernorGovernor of New YorkThe Governor of the State of New York is the chief executive of the State of New York. The governor is the head of the executive branch of New York's state government and the commander-in-chief of the state's military and naval forces. The officeholder is afforded the courtesy title of His/Her...
Franklin Delano Roosevelt becomes 32nd President of the United StatesPresident of the United StatesThe President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
on March 4, 1933
-
History of New York by region
- By city
- History of New York CityHistory of New York CityThe history of New York, New York begins with the first European documentation of the area by Giovanni da Verrazzano, in command of the French ship, La Dauphine, when he visited the region in 1524. It is believed he sailed in Upper New York Bay where he encountered native Lenape, returned through...
- History of Buffalo, New YorkHistory of Buffalo, New York-Origin of name:The city of Buffalo, formerly known as Buffalo Creek, received its name from the creek that flows through it. However, the origin of the creek's name is unclear, with several unproven theories existing. Early French explorers reported the abundance of buffalo on the south shore of...
- History of New York City
Culture of New York
- Museums in New York
- Religion in New York
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in New YorkThe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in New YorkAs of the end of 2007, The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints reported 78,031 members in 14 stakes, 3 districts, 152 Congregations , 4 missions, and 2 temples in New York.-History:A brief history can be found at...
- Episcopal Diocese of New YorkEpiscopal Diocese of New YorkThe Episcopal Diocese of New York is a diocese of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America, encompassing the boroughs of Manhattan, the Bronx, and Staten Island in New York City, and the New York state counties of Westchester, Rockland, Dutchess, Orange, Putnam, Sullivan, and...
- The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in New York
- Scouting in New YorkScouting in New YorkScouting in New York has a long history, from the 1910s to the present day, serving thousands of youth in programs that suit the environment in which they live...
- State symbols of New York
- Flag of the State of New York

- Great Seal of the State of New York

- Flag of the State of New York
Economy and infrastructure of New York
- Main article: Economy of New YorkEconomy of New YorkNew Yorks economy is dominated by New York City but has other productive cities, suburbs and rural areas. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis the Total Personal Income of the state in 2007 was $847 billion....
- Transportation in New YorkTransportation in New YorkTransportation in New York is made up of some of the most extensive and one of the oldest transportation infrastructures in the country. Engineering difficulties because of the terrain of New York State and the unique issues of New York City brought on by urban crowding have had to be overcome...
- Airports in New York
- Roads in New York
- Interstate Highways in New York
- State highways in New York
Education in New York
- Main article: Education in New YorkEducation in New YorkThe University of the State of New York , its policy-setting Board of Regents, and its administrative arm, the New York State Education Department, oversee all public primary, middle-level, and secondary education in the state...
- Schools in New York
- School districts in New York
- Colleges and universities in New York
- University of the State of New YorkUniversity of the State of New YorkThe University of the State of New York is the State of New York's governmental umbrella organization responsible for most institutions and people in any way connected with formal educational functions, public and private, in New York State...
- State University of New YorkState University of New YorkThe State University of New York, abbreviated SUNY , is a system of public institutions of higher education in New York, United States. It is the largest comprehensive system of universities, colleges, and community colleges in the United States, with a total enrollment of 465,000 students, plus...
- University of the State of New York
See also
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of North America
- Outline of the United States
- Outline of North America
- Index of New York-related articles

