
Oxford Rewley Road railway station
Encyclopedia
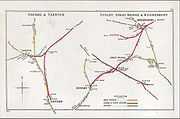
Oxford Rewley Road railway station was a railway station serving the city of Oxford
, England
, located immediately to the north of what is now Frideswide Square
on the site of the Saïd Business School
. It was the terminus
of the Buckinghamshire Railway
, which was worked, and later absorbed, by the London and North Western Railway
. In 1923 it became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
, "Varsity Line
" service from Cambridge
via Bletchley
and had features of significance in construction history. A picture of the station can be found here: http://www.bicesterlink.info/history.htm.
, a 13th century Cistercian monastery
.
The contractors for the main building were Fox, Henderson who were completing The Crystal Palace
at the same time, and they used similar — but not identical — prefabricated
cast iron
main structural components. The historic importance of this feature caused it to be made a Grade II* listed building. There were two platform
faces partly under a glass-roofed train shed
; the latter was replaced to a different design in 1888.
The other main feature of the site was a swing bridge
taking the line across the navigable Sheepwash channel which links the River Thames
and Oxford Canal
. The bridge remains in situ but not in use today. There were also extensive sidings for coal
and other freight traffic, and a motive power depot
.
The Great Western Railway
had opened its station in 1852 on an adjacent site, the location of the current Oxford railway station
, and the two stations came under joint management in 1933. Rewley Road was closed to passengers by the London Midland Region of British Railways
on 1 October 1951 and services transferred to the ex-GWR station. The goods yard remained available for use until 5 April 1984 and was cleared in 1998. After the station closed to passengers the main building was put to commercial use.
The station was described by various names. The station nameboards and official timetables simply stated "Oxford"; however, the name "Oxford Rooley Road" is shown in Bradshaw timetables of June 1869 and September 1885, whilst those of July 1906, June 1920 and January 1944 show "Oxford Rewley Road".
Plans to construct new premises for the Saïd Business School
of the University of Oxford
led to dismantling of the station building in 1999 with the financial support of the University. Official consent to this without a public inquiry
, together with associated road works and the cutting down of trees on the perimeter of the site, made the decision controversial and led to the building being occupied for six months culminating in a long and expensive eviction. The building's occupiers were supported by many local politicians and put forward alternative proposals for the junction design and alternative uses for the building, including an art gallery and tourist centre. Part of the controversy surrounding the building of the new business school involved the project's funding coming from Wafic Said
, a controversial Saudi arms dealer. The Business School opened in 2001 and the site of the station was subsequently marked by a commemorative plaque
. Parts of the goods yard were developed for housing.
The station building components were moved to the Buckinghamshire Railway Centre
at Quainton Road railway station
where they were refurbished and re-erected, with support from the Heritage Lottery Fund
, as a visitor centre and display building, formally opened in 2002, so that Rewley Road station once again houses railway train
s.
Oxford
The city of Oxford is the county town of Oxfordshire, England. The city, made prominent by its medieval university, has a population of just under 165,000, with 153,900 living within the district boundary. It lies about 50 miles north-west of London. The rivers Cherwell and Thames run through...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, located immediately to the north of what is now Frideswide Square
Frideswide Square
Frideswide Square is a square to the west of central Oxford, England. The square is named after the patron saint of Oxford, St Frideswide.The "square" is actually triangular in shape. Immediately to the north, the modern Saïd Business School of Oxford University dominates the square, established in...
on the site of the Saïd Business School
Saïd Business School
Saïd Business School is the business school of the University of Oxford in England, located on the north side of Frideswide Square on the former site of Oxford Rewley Road railway station. It is the University's centre of learning for graduate and undergraduate students in business, management...
. It was the terminus
Terminal Station
Terminal Station is a 1953 film by Italian director Vittorio De Sica. It tells the story of the love affair between an Italian man and an American woman. The film was entered into the 1953 Cannes Film Festival.-Production:...
of the Buckinghamshire Railway
Buckinghamshire Railway
The Buckinghamshire Railway was a railway company in Buckinghamshire and Oxfordshire, England that constructed railway lines connecting Bletchley, Banbury and Oxford...
, which was worked, and later absorbed, by the London and North Western Railway
London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. It was created by the merger of three companies – the Grand Junction Railway, the London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway...
. In 1923 it became part of the London, Midland and Scottish Railway
London, Midland and Scottish Railway
The London Midland and Scottish Railway was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railway companies into just four...
, "Varsity Line
Varsity Line
The Varsity Line is an informal name for the railway route that formerly linked the English university cities of Oxford and Cambridge, operated successively by the London and North Western Railway, the London, Midland and Scottish Railway, and British Railways...
" service from Cambridge
Cambridge railway station
Cambridge railway station is a railway station serving the city of Cambridge in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located at the end of Station Road, off Hills Road, 1 mile south-east of the city centre...
via Bletchley
Bletchley railway station
Bletchley is a railway station that serves the southern districts of Milton Keynes , and the north-eastern parts of the Buckinghamshire district of Aylesbury Vale....
and had features of significance in construction history. A picture of the station can be found here: http://www.bicesterlink.info/history.htm.
History
The line from Bletchley to Oxford was opened by the Buckinghamshire Railway (worked and later owned by the L&NWR) in 1851. The Oxford station was built on the site of Rewley AbbeyRewley Abbey
The Cistercian Abbey of Rewley was an Abbey in Oxford, England. It was founded in the 13th century by Edmund, 2nd Earl of Cornwall. Edmund's father, Richard, 1st Earl of Cornwall, founder of Hayles Abbey, had intended to establish a college or chantry of three secular priests to pray for his...
, a 13th century Cistercian monastery
Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
.
The contractors for the main building were Fox, Henderson who were completing The Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast-iron and glass building originally erected in Hyde Park, London, England, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. More than 14,000 exhibitors from around the world gathered in the Palace's of exhibition space to display examples of the latest technology developed in...
at the same time, and they used similar — but not identical — prefabricated
Prefabrication
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located...
cast iron
Cast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
main structural components. The historic importance of this feature caused it to be made a Grade II* listed building. There were two platform
Railway platform
A railway platform is a section of pathway, alongside rail tracks at a train station, metro station or tram stop, at which passengers may board or alight from trains or trams. Almost all stations for rail transport have some form of platforms, with larger stations having multiple platforms...
faces partly under a glass-roofed train shed
Train shed
A train shed is an adjacent building to a railway station where the tracks and platforms are covered by a roof. It is also known as an overall roof...
; the latter was replaced to a different design in 1888.
The other main feature of the site was a swing bridge
Swing bridge
A swing bridge is a movable bridge that has as its primary structural support a vertical locating pin and support ring, usually at or near to its centre of gravity, about which the turning span can then pivot horizontally as shown in the animated illustration to the right...
taking the line across the navigable Sheepwash channel which links the River Thames
River Thames
The River Thames flows through southern England. It is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom. While it is best known because its lower reaches flow through central London, the river flows alongside several other towns and cities, including Oxford,...
and Oxford Canal
Oxford Canal
The Oxford Canal is a narrow canal in central England linking Oxford with Coventry via Banbury and Rugby. It connects with the River Thames at Oxford, to the Grand Union Canal at the villages of Braunston and Napton-on-the-Hill, and to the Coventry Canal at Hawkesbury Junction in Bedworth just...
. The bridge remains in situ but not in use today. There were also extensive sidings for coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
and other freight traffic, and a motive power depot
Motive power depot
Motive power depot, usually abbreviated to MPD, is a name given to places where locomotives are stored when not being used, and also repaired and maintained. They were originally known as "running sheds", "engine sheds", or, for short, just sheds. Facilities are provided for refuelling and...
.
The Great Western Railway
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway was a British railway company that linked London with the south-west and west of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament in 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838...
had opened its station in 1852 on an adjacent site, the location of the current Oxford railway station
Oxford railway station
Oxford railway station is a mainline railway station serving the city of Oxford, England. It is about west of the city centre, northwest of Frideswide Square and the eastern end of Botley Road, and on the line linking with . It is also on the line for trains between and Hereford via...
, and the two stations came under joint management in 1933. Rewley Road was closed to passengers by the London Midland Region of British Railways
London Midland Region of British Railways
The London Midland Region was one of the six regions created on the formation of the nationalised British Railways and consisted of ex-London, Midland and Scottish Railway lines in England and Wales. The region was managed first from buildings adjacent to Euston Station and later from Stanier...
on 1 October 1951 and services transferred to the ex-GWR station. The goods yard remained available for use until 5 April 1984 and was cleared in 1998. After the station closed to passengers the main building was put to commercial use.
The station was described by various names. The station nameboards and official timetables simply stated "Oxford"; however, the name "Oxford Rooley Road" is shown in Bradshaw timetables of June 1869 and September 1885, whilst those of July 1906, June 1920 and January 1944 show "Oxford Rewley Road".
Plans to construct new premises for the Saïd Business School
Saïd Business School
Saïd Business School is the business school of the University of Oxford in England, located on the north side of Frideswide Square on the former site of Oxford Rewley Road railway station. It is the University's centre of learning for graduate and undergraduate students in business, management...
of the University of Oxford
University of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a university located in Oxford, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest surviving university in the world and the oldest in the English-speaking world. Although its exact date of foundation is unclear, there is evidence of teaching as far back as 1096...
led to dismantling of the station building in 1999 with the financial support of the University. Official consent to this without a public inquiry
Public inquiry
A Tribunal of Inquiry is an official review of events or actions ordered by a government body in Common Law countries such as the United Kingdom, Ireland or Canada. Such a public inquiry differs from a Royal Commission in that a public inquiry accepts evidence and conducts its hearings in a more...
, together with associated road works and the cutting down of trees on the perimeter of the site, made the decision controversial and led to the building being occupied for six months culminating in a long and expensive eviction. The building's occupiers were supported by many local politicians and put forward alternative proposals for the junction design and alternative uses for the building, including an art gallery and tourist centre. Part of the controversy surrounding the building of the new business school involved the project's funding coming from Wafic Said
Wafic Saïd
Wafic Rida Saïd is a Syrian-Saudi Arabian businessman living in Monaco and Paris.-Personal life:Saïd married British born Ann Rosemary Thompson in 1969...
, a controversial Saudi arms dealer. The Business School opened in 2001 and the site of the station was subsequently marked by a commemorative plaque
Commemorative plaque
A commemorative plaque, or simply plaque, is a plate of metal, ceramic, stone, wood, or other material, typically attached to a wall, stone, or other vertical surface, and bearing text in memory of an important figure or event...
. Parts of the goods yard were developed for housing.
The station building components were moved to the Buckinghamshire Railway Centre
Buckinghamshire Railway Centre
Buckinghamshire Railway Centre is a railway museum operated by the Quainton Railway Society Ltd. at Quainton Road railway station, in the far depths of "Metro-land", about 5 miles west of Aylesbury in Buckinghamshire. The site is divided into two halves which are joined by two foot-bridges, one of...
at Quainton Road railway station
Quainton Road railway station
Quainton Road railway station was opened in 1868 in undeveloped countryside near Quainton, Buckinghamshire, from London. Built by the Aylesbury and Buckingham Railway, it was the result of pressure from the 3rd Duke of Buckingham to route the railway near his home at Wotton House and to open a...
where they were refurbished and re-erected, with support from the Heritage Lottery Fund
Heritage Lottery Fund
The Heritage Lottery Fund is a fund established in the United Kingdom under the National Lottery etc. Act 1993. The Fund opened for applications in 1994. It uses money raised through the National Lottery to transform and sustain the UK’s heritage...
, as a visitor centre and display building, formally opened in 2002, so that Rewley Road station once again houses railway train
Train
A train is a connected series of vehicles for rail transport that move along a track to transport cargo or passengers from one place to another place. The track usually consists of two rails, but might also be a monorail or maglev guideway.Propulsion for the train is provided by a separate...
s.
Routes


