PKD1
Encyclopedia
Polycystin-1 is a protein
that in human
s is encoded by the PKD1 gene
.
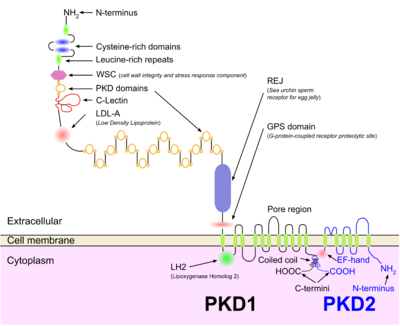
which contains a large N-terminal extracellular region, multiple transmembrane domains and a cytoplasmic C-tail. It may function as an integral membrane protein involved in cell-cell/matrix interactions, and may modulate intracellular calcium homoeostasis and other signal-transduction
pathways. It plays a role in renal tubular development, and mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
with polycystin-2 and RGS7
.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that in human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s is encoded by the PKD1 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
.
Gene product

Function
Polycystin-1 is a glycoproteinGlycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. In proteins that have segments extending...
which contains a large N-terminal extracellular region, multiple transmembrane domains and a cytoplasmic C-tail. It may function as an integral membrane protein involved in cell-cell/matrix interactions, and may modulate intracellular calcium homoeostasis and other signal-transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
pathways. It plays a role in renal tubular development, and mutations in this gene have been associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Interactions
Polycystin-1 has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with polycystin-2 and RGS7
RGS7
Regulator of G-protein signaling 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS7 gene.-Interactions:RGS7 has been shown to interact with PKD1, GNB5 and SNAPAP.-Further reading:...
.

