
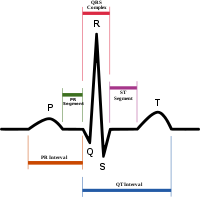
P wave (electrocardiography)
Encyclopedia
Atrium (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atrium , sometimes called auricle , refers to a chamber or space. For example, the term is used for a portion of the lateral ventricle in the brain and the blood collection chamber of the heart...
to the left atrium
Atrium (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atrium , sometimes called auricle , refers to a chamber or space. For example, the term is used for a portion of the lateral ventricle in the brain and the blood collection chamber of the heart...
. This turns into the P wave on the ECG.
The P wave is upright in II, III, and aVF (since the general electrical activity is going toward the positive electrode in those leads), and inverted in aVR (since it is going away from the positive electrode for that lead).
A P wave must be upright in leads II and aVF and inverted in lead aVR to designate a cardiac rhythm as sinus rhythm
Sinus rhythm
In medicine, sinus rhythm is the normal beating of the heart, as measured by an electrocardiogram . It has certain generic features that serve as hallmarks for comparison with normal ECGs.- ECG structure :...
.
Clinical significance
With mild to moderate hyperkalemiaHyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
, there is reduction of the size of the P wave
The relationship between P waves and QRS complex
QRS complex
The QRS complex is a name for the combination of three of the graphical deflections seen on a typical electrocardiogram . It is usually the central and most visually obvious part of the tracing. It corresponds to the depolarization of the right and left ventricles of the human heart...
es helps distinguish various cardiac arrhythmias:
- A prolonged P wave may indicate left atrial enlargementLeft atrial enlargementLeft atrial enlargement or left atrial dilation is a form of cardiomegaly.In the general population, obesity appears to be the most important risk factor for LAE. Also, a study found that LAE can occur as a consequence of atrial fibrillation , although another study found that AF by itself does...
. Left atrial enlargement can accompany mitral stenosisMitral stenosisMitral stenosis is a valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the orifice of the mitral valve of the heart.-Signs and symptoms:Symptoms of mitral stenosis include:...
. - A P wave with increased amplitude can indicate hypokalemiaHypokalemiaHypokalemia or hypokalaemia , also hypopotassemia or hypopotassaemia , refers to the condition in which the concentration of potassium in the blood is low...
. It can also indicate right atrial enlargementRight atrial enlargementRight atrial enlargement is a form of cardiomegaly.It is characterized by a P wave height greater than 2.5 mm....
. - A P wave with decreased amplitude can indicate hyperkalemiaHyperkalemiaHyperkalemia refers to the condition in which the concentration of the electrolyte potassium in the blood is elevated...
. - Absence of the P wave may indicate atrial fibrillationAtrial fibrillationAtrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia . It is a common cause of irregular heart beat, identified clinically by taking a pulse. Chaotic electrical activity in the two upper chambers of the heart result in the muscle fibrillating , instead of achieving coordinated contraction...
. - A saw tooth formed P wave may indicate atrial flutterAtrial flutterAtrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm that occurs in the atria of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate or tachycardia , and falls into the category of supra-ventricular tachycardias. While this rhythm occurs most often in individuals with...
.
If P waves are not clearly delineated in the surface ECG, Lewis lead
Lewis lead
A Lewis Lead is a modified EKG lead used to detect atrial flutter waves when atrial flutter is suspected clinically but not definitely demonstrated on the standard 12 lead EKG. In order to create the Lewis Lead, the right arm electrode is moved to the right, second intercostal space adjacent to the...
may be used to better visualize P waves.

