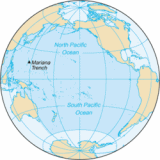
's ocean
ic divisions. It extends from the Arctic
in the north to the Southern Ocean
(or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, bounded by Asia
and Australia
in the west, and the Americas
in the east.
At 165.2 million square kilometres (64.1 million square miles) in area, this largest division of the World Ocean
– and, in turn, the hydrosphere
– covers about 46% of the Earth's water surface and about one-third of its total surface area, making it larger than all of the Earth's land area combined.
1513 Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa reaches what would become known as the Pacific Ocean.
1520 The Strait of Magellan, the passage immediately south of mainland South America, connecting the Pacific and the Atlantic Oceans, is first navigated by Ferdinand Magellan during his global circumnavigation voyage.
1520 After navigating through the South American strait, three ships under the command of Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan reach the Pacific Ocean, becoming the first Europeans to sail from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific.
1610 Henry Hudson sails into what it is now known as Hudson Bay thinking he had made it through the Northwest Passage and reached the Pacific Ocean.
1793 Alexander Mackenzie reaches the Pacific Ocean becoming the first Euro-American to complete a transcontinental crossing of Canada.
1806 After traveling through the Louisiana Purchase and reaching the Pacific Ocean, explorers Lewis and Clark and their "Corps of Discovery" begin their arduous journey home.
1855 The first locomotive runs from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean on the Panama Railway.
1899 The United States takes possession of Wake Island in the Pacific Ocean.
1902 The Commercial Pacific Cable Company lays the first Pacific telegraph cable, from Ocean Beach, San Francisco to Honolulu, Hawaii.
1914 World War I: the first British Royal Navy defeat of the war with Germany, the Battle of Coronel, is fought off of the western coast of Chile, in the Pacific, with the loss of HMS Good Hope and HMS Monmouth.

