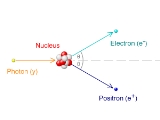
Pair production
Overview
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle not known to have substructure; that is, it is not known to be made up of smaller particles. If an elementary particle truly has no substructure, then it is one of the basic building blocks of the universe from which...
and its antiparticle
Antiparticle
Corresponding to most kinds of particles, there is an associated antiparticle with the same mass and opposite electric charge. For example, the antiparticle of the electron is the positively charged antielectron, or positron, which is produced naturally in certain types of radioactive decay.The...
, usually from a photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
(or another neutral boson
Boson
In particle physics, bosons are subatomic particles that obey Bose–Einstein statistics. Several bosons can occupy the same quantum state. The word boson derives from the name of Satyendra Nath Bose....
). For example an electron and its antiparticle, the positron, may be created. This is allowed, provided there is enough energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
available to create the pair at least the total rest mass energy of the two particles and that the situation allows both energy and momentum to be conserved. Other pairs produced could be a muon and anti-muon or a tau and anti-tau.

