Palladin
Encyclopedia
Palladin is a protein
that in humans is encoded by the PALLD gene
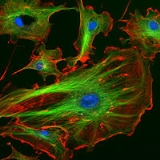
. Palladin is a component of actin
-containing microfilaments that control cell shape, adhesion
, and contraction.
cytoskeleton
. Palladin, in contrast to myotilin
and myopalladin
, which are expressed only in striated muscle
, is expressed ubiquitously in cells of mesenchymal
origin.
Palladin was named after the Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio
, reflecting its localization to architectural elements of the cell.
. In mice, three major isoforms of palladin arise from a single gene. These isoforms contain between three and five copies (depending on the isoform) of an Ig-like domain and between one and two copies of a polyproline domain.
is overexpressed in patients with pancreatic
neoplasia
, and that palladin is both overexpressed and mutated in an inherited form of pancreatic cancer
. The palladin mutation identified in familial pancreatic cancer may be unique to a single North American family, as this same mutation has not been found in any other European or North American populations, respectively, in two other genetic studies.
Further, Salaria et al. have shown that palladin is overexpressed in the non-neoplastic stroma of pancreatic cancer, but only rarely in the cancer cells per se, suggesting that palladin's role in this disease may involve changes in the tumor microenvironmment. More research is clearly required before this protein and its role in neoplasia can be fully understood.
Disease-causing mutations have also been identified in the two other members of this gene family. Myotilin
mutations cause a form of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and mutations in myopalladin
cause an inherited form of heart disease (dilated cardiomyopathy
).
with EZR.
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that in humans is encoded by the PALLD gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
. Palladin is a component of actin
Actin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
-containing microfilaments that control cell shape, adhesion
Cell adhesion
Cellular adhesion is the binding of a cell to a surface, extracellular matrix or another cell using cell adhesion molecules such as selectins, integrins, and cadherins. Correct cellular adhesion is essential in maintaining multicellular structure...
, and contraction.
Discovery
Palladin was characterised independently by two research groups, first in the lab of Carol Otey (in 2000) and then in the lab of Olli Carpén (in 2001). It is a part of the myotilin-myopalladin-palladin family and may play an important role in modulating the actinActin
Actin is a globular, roughly 42-kDa moonlighting protein found in all eukaryotic cells where it may be present at concentrations of over 100 μM. It is also one of the most highly-conserved proteins, differing by no more than 20% in species as diverse as algae and humans...
cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a cellular "scaffolding" or "skeleton" contained within a cell's cytoplasm and is made out of protein. The cytoskeleton is present in all cells; it was once thought to be unique to eukaryotes, but recent research has identified the prokaryotic cytoskeleton...
. Palladin, in contrast to myotilin
MYOT
Myotilin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYOT gene.Myotilin also known as TTID is a skeletal muscle protein that is found within the Z-disc of sarcomeres...
and myopalladin
MYPN
Myopalladin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYPN gene.-Interactions:MYPN has been shown to interact with Actinin, alpha 2, ANKRD23 and ANKRD1.-Further reading:...
, which are expressed only in striated muscle
Striated muscle
Striated muscle tissue is a form of fibers that are combined into parallel fibers. More specifically, it can refer to:* Cardiac muscle .* Skeletal muscle* Branchiomeric muscles...
, is expressed ubiquitously in cells of mesenchymal
Mesenchymal stem cell
Mesenchymal stem cells, or MSCs, are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including: osteoblasts , chondrocytes and adipocytes...
origin.
Palladin was named after the Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio was an architect active in the Republic of Venice. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily by Vitruvius, is widely considered the most influential individual in the history of Western architecture...
, reflecting its localization to architectural elements of the cell.
 |
Isoforms
In humans, it appears that seven different isoforms exist, some of which arise through alternative splicingAlternative splicing
Alternative splicing is a process by which the exons of the RNA produced by transcription of a gene are reconnected in multiple ways during RNA splicing...
. In mice, three major isoforms of palladin arise from a single gene. These isoforms contain between three and five copies (depending on the isoform) of an Ig-like domain and between one and two copies of a polyproline domain.
Function
Palladin's precise biological role is poorly understood, but it has been shown to play a role in cytoskeletal organization, embryonic development, cell motility, scar formation in the skin, and nerve cell development.Disease linkage
Recently, it has been demonstrated that palladin RNARNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
is overexpressed in patients with pancreatic
Pancreas
The pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
neoplasia
Neoplasia
Neoplasm is an abnormal mass of tissue as a result of neoplasia. Neoplasia is the abnormal proliferation of cells. The growth of neoplastic cells exceeds and is not coordinated with that of the normal tissues around it. The growth persists in the same excessive manner even after cessation of the...
, and that palladin is both overexpressed and mutated in an inherited form of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
. The palladin mutation identified in familial pancreatic cancer may be unique to a single North American family, as this same mutation has not been found in any other European or North American populations, respectively, in two other genetic studies.
Further, Salaria et al. have shown that palladin is overexpressed in the non-neoplastic stroma of pancreatic cancer, but only rarely in the cancer cells per se, suggesting that palladin's role in this disease may involve changes in the tumor microenvironmment. More research is clearly required before this protein and its role in neoplasia can be fully understood.
Disease-causing mutations have also been identified in the two other members of this gene family. Myotilin
MYOT
Myotilin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYOT gene.Myotilin also known as TTID is a skeletal muscle protein that is found within the Z-disc of sarcomeres...
mutations cause a form of limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and mutations in myopalladin
MYPN
Myopalladin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYPN gene.-Interactions:MYPN has been shown to interact with Actinin, alpha 2, ANKRD23 and ANKRD1.-Further reading:...
cause an inherited form of heart disease (dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy or DCM is a condition in which the heart becomes weakened and enlarged and cannot pump blood efficiently. The decreased heart function can affect the lungs, liver, and other body systems....
).
Interactions
PALLD has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with EZR.

