
Paracrystalline
Encyclopedia
Paracrystalline materials are defined as having short and medium range ordering in their lattice (similar to the liquid crystal
phases) but lacking long-range ordering at least in one direction.
Ordering is the regularity in which atoms appear in a predictable lattice, as measured from one point. In a highly ordered, perfectly crystalline material, or single crystal
, the location of every atom in the structure can be described exactly measuring out from a single origin. Conversely, in a disordered structure such as a liquid or amorphous solid
, the location of the first and perhaps second nearest neighbors can be described from an origin (with some degree of uncertainty) and the ability to predict locations decreases rapidly from there out. The distance at which atom locations can be predicted is referred to as the correlation
length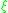 . A paracrystalline material exhibits correlation somewhere between the fully amorphous and fully crystalline.
. A paracrystalline material exhibits correlation somewhere between the fully amorphous and fully crystalline.
The primary, most accessible source of crystallinity
information is X-ray diffraction
and Electron Cryomicroscopy
, although other techniques may be needed to observe the complex structure of paracrystalline materials, such as fluctuation electron microscopy in combination with Density of states
modeling of electronic and vibrational states.
An example of a paracrystalline, or partially disordered lattice is showin in the following figure.
Liquid crystal
Liquid crystals are a state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal. For instance, an LC may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. There are many different types of LC phases, which can be...
phases) but lacking long-range ordering at least in one direction.
Ordering is the regularity in which atoms appear in a predictable lattice, as measured from one point. In a highly ordered, perfectly crystalline material, or single crystal
Single crystal
A single crystal or monocrystalline solid is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no grain boundaries...
, the location of every atom in the structure can be described exactly measuring out from a single origin. Conversely, in a disordered structure such as a liquid or amorphous solid
Amorphous solid
In condensed matter physics, an amorphous or non-crystalline solid is a solid that lacks the long-range order characteristic of a crystal....
, the location of the first and perhaps second nearest neighbors can be described from an origin (with some degree of uncertainty) and the ability to predict locations decreases rapidly from there out. The distance at which atom locations can be predicted is referred to as the correlation
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
length
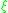 . A paracrystalline material exhibits correlation somewhere between the fully amorphous and fully crystalline.
. A paracrystalline material exhibits correlation somewhere between the fully amorphous and fully crystalline.The primary, most accessible source of crystallinity
Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal, the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, transparency and diffusion. In a gas, the relative positions of the atoms or...
information is X-ray diffraction
X-ray scattering techniques
X-ray scattering techniques are a family of non-destructive analytical techniques which reveal information about the crystallographic structure, chemical composition, and physical properties of materials and thin films...
and Electron Cryomicroscopy
Cryo-electron microscopy
Cryo-electron microscopy , or electron cryomicroscopy, is a form of transmission electron microscopy where the sample is studied at cryogenic temperatures...
, although other techniques may be needed to observe the complex structure of paracrystalline materials, such as fluctuation electron microscopy in combination with Density of states
Density of states
In solid-state and condensed matter physics, the density of states of a system describes the number of states per interval of energy at each energy level that are available to be occupied by electrons. Unlike isolated systems, like atoms or molecules in gas phase, the density distributions are not...
modeling of electronic and vibrational states.
Paracrystalline Model
The paracrystalline model is a revision of the Continuous Random Network model first proposed by W. H. Zachariasen in 1932. The paracrystal model is defined as highly strained, microcrystalline grains surrounded by fully amorphous material. This is a higher energy state then the continuous random network model. The important distinction between this model and the microcrystalline phases is the lack of defined grain boundaries and highly strained lattice parameters, which makes calculations of molecular and lattice dynamics difficult. A general theory of paracrystals has been formulated in a basic textbook, and then further developed/refined by various authors.An example of a paracrystalline, or partially disordered lattice is showin in the following figure.
Applications
The paracrystal model has been useful, for example, in describing the state of partially amorphous semiconductor materials after deposition. It has also been successfully applied to synthetic polymers, liquid crystals, biopoloymers, and biomembranes.See also
- X-ray scattering
- Amorphous solidAmorphous solidIn condensed matter physics, an amorphous or non-crystalline solid is a solid that lacks the long-range order characteristic of a crystal....
- Single CrystalSingle crystalA single crystal or monocrystalline solid is a material in which the crystal lattice of the entire sample is continuous and unbroken to the edges of the sample, with no grain boundaries...
- PolycrystallinePolycrystallinePolycrystalline materials are solids that are composed of many crystallites of varying size and orientation. The variation in direction can be random or directed, possibly due to growth and processing conditions. Fiber texture is an example of the latter.Almost all common metals, and many ceramics...
- CrystallographyCrystallographyCrystallography is the experimental science of the arrangement of atoms in solids. The word "crystallography" derives from the Greek words crystallon = cold drop / frozen drop, with its meaning extending to all solids with some degree of transparency, and grapho = write.Before the development of...
- DNADNADeoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
- X-ray pattern of a B-DNA Paracrystal

