
Patellar reflex
Encyclopedia
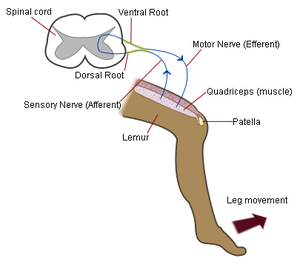
Mechanism
Striking the patellar tendon with a tendon hammer just below the patella stretches the sensory nerve fiber of the femoral nerveFemoral nerve
The femoral nerve, the largest branch of the lumbar plexus, arises from the dorsal divisions of the ventral rami of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves...
which synapses (without interneurons) at the level of L4 in the spinal cord, completely independent of higher centres. From there, an alpha-motor neuron
Motor neuron
In vertebrates, the term motor neuron classically applies to neurons located in the central nervous system that project their axons outside the CNS and directly or indirectly control muscles...
conducts an efferent impulse back to the quadriceps femoris muscle, triggering contraction. This contraction, coordinated with the relaxation of the antagonistic flexor hamstring muscle causes the leg to kick. This reflex helps maintain posture
Neutral spine
A neutral spine or good posture refers to the "three natural curves [that] are present in a healthy spine."- Posture :The word "posture" comes from the Latin verb "ponere" which is defined as "to put or place." The general concept of human posture refers to "the carriage of the body as a whole, the...
and balance
Balance (ability)
In biomechanics, balance is an ability to maintain the center of gravity of a body within the base of support with minimal postural sway. When exercising the ability to balance, one is said to be balancing....
, allowing one to walk without consciously thinking about each step.
The patellar reflex is a clinical and classic example of the monosynaptic reflex arc
Reflex arc
A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls an action reflex. In higher animals, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord...
. There is no interneuron
Interneuron
An interneuron is a multipolar neuron which connects afferent neurons and efferent neurons in neural pathways...
in the pathway leading to contraction of the quadriceps muscle. Instead the bipolar sensory neuron synapses directly on a motor neuron in the spinal cord. However, there is an inhibitory interneuron used to relax the antagonistic hamstring muscle.
It tests L2, L3, and L4.
Purpose of Testing
After the tap of a hammer, the leg is normally extended once and comes to rest. The absence or decrease of this reflex is known as Westphal's signWestphal's sign
Westphal's sign is the clinical correlate of the absence or decrease of patellar reflex or knee jerk. Patellar reflex or knee jerk is a kind of deep or stretch reflex where an application of a stimulus to the patellar tendon such as strike by a solid object or hammer caused the leg to extend due to...
. On the other hand, multiple oscillation of the leg following the tap may be a sign of a cerebellar disease.
History
The term knee-jerk was recorded by Sir Michael FosterMichael Foster (physiologist)
Sir Michael Foster was an English physiologist.He was born in Huntingdon, Cambridgeshire and educated at University College School, London....
in his Textbook of physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
in 1877: "Striking the tendon below the patella gives rise to a sudden extension of the leg, known as the knee-jerk."
Popular culture
The term began to be used figuratively from the early 20th century onwards. O. O. McIntyreO. O. McIntyre
Oscar Odd McIntyre was a famed New York newspaper columnist of the 1920s and 1930s who cleverly combined a small town point of view with urban sophistication...
, in his New York Day-By-Day column in The Coshocton Tribune, October 1921, wrote: "Itinerant preacher stemming Broadway on a soap box. And gets only an occasional knee-jerk."
See also
- Tonic vibration reflexTonic vibration reflexTonic vibration reflex is a sustained contraction of a muscle subjected to vibration. This reflex is caused by vibratory activation of muscle spindles — muscle receptors sensitive to stretch....
- Motor controlMotor controlMotor control are information processing related activities carried out by the central nervous system that organize the musculoskeletal system to create coordinated movements and skilled actions...
- Jendrassik maneuverJendrassik maneuverThe Jendrassik maneuver is a medical maneuver wherein the patient flexes both sets of fingers into a hook-like form and interlocks those sets of fingers together. The tendon below the patient's knee is then hit with a reflex hammer to elicit the patellar reflex. The elicited response is compared...

