
Patient registration
Encyclopedia
Patient registration is the concept and set of methods needed to correlate the reference position of a virtual
3D
dataset gathered by computer medical imaging
with the reference position of the patient. This procedure is crucial in computer assisted surgery
, in order to insure the reproducitibility of the preoperative registration and the clinical situation during surgery.
The use of the term "patient registration" out of this context can lead to a confusion with the procedure of registering a patient into the files of a medical institution.
, the first step is to gather a 3D dataset that reproduces with great accuracy the geometry of the normal and pathological tissues in the region that has to be operated on. This is mainly obtained by using CT
or MRI scans of that region. The role of patient registration is to obtain a close-to-ideal reference reproducitibility of the dataset – in order to correlate the position (offset) of the gathered dataset with the patient's position during the surgical intervention. Patient registration (1) eliminates the necessity of maintaining the same strict position of the patient during both preoperative scanning and surgery, and (2) provides the surgical robot the necessary reference information to act accurately on the patient, even if he has (been) moved during the intervention.
and R. Clarke in 1906. They have built a rectangular stereotactic headframe that had to be fixed to the head. It was based on cartesian principles and allowed them to accurately and reproductibly guide needle-like electrodes for neurophysiological experiments. They have experimented animals and were able to contribute to the mapping of the cerebellum. Improved versions of the Horsley–Clarke apparatus are still in used today in experimental neurosurgery.
The first stereotactic device for humans was also developed in neurosurgery, by E. Spiegel and H. Wycis in 1947. It was used for surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease
and, during time, its applicability was extended for the surgical treatment of tumors, vascular malformations, functional neurosurgery etc. The system was based both on headframes and X-ray images taken for all three planes of space.
Further development of stereotactic surgery was made by Brown, Roberts and Wells in 1980. They have developed a halo ring that was applied on the skull, during a CT
scan and neurosurgical interventions. This method provided improved surgical guidance and was in fact the first development of computer guided surgery.
Patient registration for the head area has developed for nearly two decades on the same principle of combining CT scans with mechanical reference devices such as headframes or halo rings. But the clinical experience showed that headgear is very uncomfortable to wear and even impossible to apply on little children, because their lack of cooperation; furthermore, the headframes can create artifacts in preoperative data gathering, or during surgery.

s – in dental prosthetics
, orthodontics
and orthognatic surgery. By applying several infrared markers on the splints and using an infrared camera, a better registration was obtained.
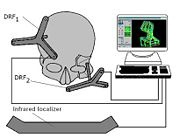
Based on this concept, several registration and navigation systems were built by the same team. The Surgical Segment Navigator (SSN and SSN++)
is such a system, developed for the first time for oral and maxillofacial surgery
. This system correlates three different coordinate sets: CT data set, surface laser scan data set and the dataset produced by a small guiding transmitter, placed on the patient's head. The Laboratory Unit for Computer-Assisted Surgery (LUCAS) is used for planning surgery in the laboratory. This technological and surgical advance has permitted the elimination of mechanical guidance systems and improved the accuracy of the determinations, and thus the surgical act.
Virtual
The term virtual is a concept applied in many fields with somewhat differing connotations, and also, differing denotations.The term has been defined in philosophy as "that which is not real" but may display the salient qualities of the real....
3D
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
dataset gathered by computer medical imaging
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
with the reference position of the patient. This procedure is crucial in computer assisted surgery
Computer assisted surgery
Computer assisted surgery represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for presurgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions...
, in order to insure the reproducitibility of the preoperative registration and the clinical situation during surgery.
The use of the term "patient registration" out of this context can lead to a confusion with the procedure of registering a patient into the files of a medical institution.
The larger context
In computer assisted surgeryComputer assisted surgery
Computer assisted surgery represents a surgical concept and set of methods, that use computer technology for presurgical planning, and for guiding or performing surgical interventions...
, the first step is to gather a 3D dataset that reproduces with great accuracy the geometry of the normal and pathological tissues in the region that has to be operated on. This is mainly obtained by using CT
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
or MRI scans of that region. The role of patient registration is to obtain a close-to-ideal reference reproducitibility of the dataset – in order to correlate the position (offset) of the gathered dataset with the patient's position during the surgical intervention. Patient registration (1) eliminates the necessity of maintaining the same strict position of the patient during both preoperative scanning and surgery, and (2) provides the surgical robot the necessary reference information to act accurately on the patient, even if he has (been) moved during the intervention.
Evolution of the concept
Patient registration was used mostly in head surgery – oral and maxillofacial surgery, neurosurgery, otolaryngology. With the advent of marker- and markerless-registration, the concept has been extended for abdominal surgery.Patient registration using headframes
The first attempts in 3D mapping of human tissues were made by V. HorsleyVictor Horsley
Sir Victor Alexander Haden Horsley was an accomplished scientist and professor. He was born in Kensington, London. He was educated at Cranbrook School, Kent and studied medicine at University College London and in Berlin, Germany , and in the same year started his career as a house surgeon and...
and R. Clarke in 1906. They have built a rectangular stereotactic headframe that had to be fixed to the head. It was based on cartesian principles and allowed them to accurately and reproductibly guide needle-like electrodes for neurophysiological experiments. They have experimented animals and were able to contribute to the mapping of the cerebellum. Improved versions of the Horsley–Clarke apparatus are still in used today in experimental neurosurgery.
The first stereotactic device for humans was also developed in neurosurgery, by E. Spiegel and H. Wycis in 1947. It was used for surgical treatment of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
and, during time, its applicability was extended for the surgical treatment of tumors, vascular malformations, functional neurosurgery etc. The system was based both on headframes and X-ray images taken for all three planes of space.
Further development of stereotactic surgery was made by Brown, Roberts and Wells in 1980. They have developed a halo ring that was applied on the skull, during a CT
Computed tomography
X-ray computed tomography or Computer tomography , is a medical imaging method employing tomography created by computer processing...
scan and neurosurgical interventions. This method provided improved surgical guidance and was in fact the first development of computer guided surgery.
Patient registration for the head area has developed for nearly two decades on the same principle of combining CT scans with mechanical reference devices such as headframes or halo rings. But the clinical experience showed that headgear is very uncomfortable to wear and even impossible to apply on little children, because their lack of cooperation; furthermore, the headframes can create artifacts in preoperative data gathering, or during surgery.
Patient registration using skin markers
In 1986, a different approach was developed by Roberts und Strohbehn. They have used as landmarks several markers on the patient's skin both preoperative CT registration, and intraoperatively. This was a new current of the time in patient registration. Still, the method is time-consuming, and the exact reproducitibility of the marker positions is questionable.Patient registration using bone markers
The bony structures can provide a much better stability and reproducibility of the landmarks for patient registration. Based on this concept, a further technique was used: to implant temporary markers into bone structures that are superficial to the skin, under local anestesia. This was also combined with surface markers and CT registration. The technique has the disadvantage of a further minimal surgical procedure of placing the bone implants, with some risk of infection for the patient.
Patient registration using markers on a dental splint
Dental splints have been traditionally used for transferring and reproducing 3D reference landmarks for positioning cast models in articulatorArticulator
An articulator is a mechanical device used in dentistry to which casts of the maxillary and mandibular teeth are fixed, reproducing recorded positions of the mandible in relation to the maxilla...
s – in dental prosthetics
Prosthodontics
Prosthodontics, also known as dental prosthetics or prosthetic dentistry, is one of nine dental specialties recognized by the American Dental Association, Royal College of Dentists of Canada, and Royal Australasian College of Dental Surgeons...
, orthodontics
Orthodontics
Orthodontics, orthodontia, or orthodonture is the first specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the study and treatment of malocclusions , which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both...
and orthognatic surgery. By applying several infrared markers on the splints and using an infrared camera, a better registration was obtained.
Markerless patient registration using anatomical landmarks
The first attempts, based on the identification of anatomical landmarks were made by Caversaccio and Zulliger. The method was based on identifying certain antropometrical points and other anatomical landmarks on the skull, in correlation with the CT registration. But the landmarks cannot be exactly pointed out and reproduced during patient dataset registration and surgery, therefore the method is not precise enough.

Markerless patient registration using surface registration
Since 1998, new procedures have been developed by Marmulla and co-workers, using a different approach to the problem. Both during CT dataset gathering and surgical intervention, the patient registration was made by registering complete areas and surfaces, instead of distinctive surface markers. This was achieved by using laser scanners and a small guiding transmitter. The precision of the patient registration was significantly improved with this method.Based on this concept, several registration and navigation systems were built by the same team. The Surgical Segment Navigator (SSN and SSN++)
Surgical Segment Navigator
The Surgical Segment Navigator is a computer-based system for use in surgical navigation. It is integrated into a common platform, together with the Surgical Tool Navigator , the Surgical Microscope Navigator and the 6DOF Manipulator , developed by Carl Zeiss.- SSN :The SSN has been developed as...
is such a system, developed for the first time for oral and maxillofacial surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is surgery to correct a wide spectrum of diseases, injuries and defects in the head, neck, face, jaws and the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial region. It is an internationally recognized surgical specialty...
. This system correlates three different coordinate sets: CT data set, surface laser scan data set and the dataset produced by a small guiding transmitter, placed on the patient's head. The Laboratory Unit for Computer-Assisted Surgery (LUCAS) is used for planning surgery in the laboratory. This technological and surgical advance has permitted the elimination of mechanical guidance systems and improved the accuracy of the determinations, and thus the surgical act.

