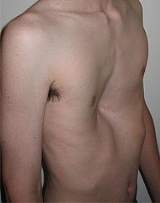
Pectus excavatum
Encyclopedia
Pectus excavatum is the most common congenital deformity of the anterior wall of the chest, in which several ribs and the sternum grow abnormally. This produces a caved-in or sunken appearance of the chest
. It can either be present at birth or not develop until puberty.
Pectus excavatum is sometimes considered to be cosmetic; however, depending on the severity, it can impair cardiac and respiratory function and cause pain in the chest and back. People with the abnormality may experience negative psychosocial
effects, and avoid
activities that expose the chest.
Pectus excavatum is sometimes referred to as cobbler's chest, sunken chest, funnel chest or simply a dent in the chest.
of the condition is a sunken appearance of the sternum. The heart can be displaced and/or rotated. Mitral valve prolapse
may also be present. Base lung capacity is decreased.
and increased traction on the sternum due to abnormalities of the diaphragm
have been postulated as specific mechanisms. Pectus excavatum is also a relatively common symptom of Marfan syndrome
. Many children with spinal muscular atrophy
develop pectus excavatum due to the diaphragmatic breathing
that is common with the disease. Pectus excavatum also occurs in about 1% of persons diagnosed with Celiac disease for unknown reasons.
is located behind the sternum, and because individuals with pectus excavatum have been shown to have visible deformities of the heart (seen both on radiological imaging and after autopsies), it has been hypothesized that there is impairment of function of the cardiovascular system in individuals with pectus excavatum. While some studies have demonstrated decreased cardiovascular function in pectus excavatum, there has been no consensus reached based on newer physiological tests (such as echocardiography
) of the presence or degree of impairment in cardiovascular function in people with pectus excavatum. Similarly, there is no consensus on the degree of functional improvement after corrective surgery.
of the chest can reveal displaced heart beat and valve prolapse. There can be a heart murmur
occurring during systole
caused by proximity between the sternum and the pulmonary artery
.
Lung sounds are usually clear yet diminished due to decreased base lung capacity.
Many scales have been developed to determine the degree of deformity in the chest wall. Most of these are variants on the distance between the sternum and the spine
. One such index is the Backer ratio which grades severity of deformity based on the ratio between the diameter of the vertebral body nearest to xiphosternal junction and the distance between the xiphosternal junction and the nearest vertebral body. More recently the Haller index
has been used based on CT scan measurements. An index over 3.25 is often defined as severe. The Haller index is the ratio between the horizontal distance of the inside of the ribcage and the shortest distance between the vertebrae and sternum.
Chest x-ray
s are also useful in the diagnosis. The chest x-ray in pectus excavatum can show an opacity in the right lung area that can be mistaken for an infiltrate (such as that seen with pneumonia
). Some studies also suggest that the Haller index
can be calculated based on chest x-ray as opposed to CT scanning in individuals who have no limitation in their function.
Pectus excavatum is differentiated from other disorders by a series of elimination of signs and symptoms. Pectus carinatum
is excluded by the simple observation of a collapsing of the sternum
rather than a protrusion. Kyphoscoliosis
is excluded by diagnostic imaging of the spine, where in pectus excavatum the spine usually appears normal in structure.
exams (such as auscultation and ECGs). After a CT scan is taken the Haller index
is measured. The patient's Haller is calculated by obtaining the ratio of the transverse diameter (the horizontal distance of the inside of the ribcage) and the anteroposterior diameter (the shortest distance between the vertebrae and sternum). A Haller Index of greater than 3.25 is generally considered severe, while normal chest has an index of 2.5. The cardiopulmonary tests are used to determine the lung capacity and to check for heart murmurs.

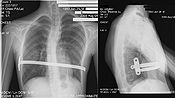 Since then, Dr. Donald Nuss, based at Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters
Since then, Dr. Donald Nuss, based at Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters
(CHKD) in Norfolk, Virginia
, has developed a technique that is minimally invasive. The Nuss procedure involves slipping in one or more concave steel bars into the chest, underneath the sternum. The bar is flipped to a convex position so as to push outward on the sternum, correcting the deformity. The bar usually stays in the body for about two years, although many surgeons are now moving toward leaving them in for up to five years. When the bones have solidified into place, the bar is removed through outpatient surgery
.
. However, as this does nothing to alleviate the actual deformity it will not prevent any physiological symptoms caused by the condition.
Mild cases have also reportedly been treated with corset
-like orthopedic support vests and exercise.
There are also prosthetic implants available to fill the depressed area. Solid silicone implants have been successfully used for many years with acceptable results in some cases. More recently a porex implant has been used which is a similar material used to replace skull
in brain surgery and severe head injuries.
(T) in order to slowly move the sternum outwards over a number of years. The maximum magnetic field
that can be applied to the body safely is around 4 T, making this technique safe from a magnetic viewpoint. The 3MP technique's main advantages are that it is more cost-effective than major surgical approaches such as the Nuss procedure and it is considerably less painful postoperatively. One potential adverse effect of 3MP is inactivation of implanted devices such as an artificial pacemaker
. Since the 3MP is still in a trial period it is unknown whether long term wearing of the magnet will affect the skin or other vital organs.
breed of cat. Some procedures used to treat the condition in animals have not been used in humans, such as the use of a cast with sutures wrapped around the sternum and the use of internal and external splints
. These techniques are generally used in immature animals with flexible cartilage.
Chest
The chest is a part of the anatomy of humans and various other animals. It is sometimes referred to as the thorax or the bosom.-Chest anatomy - Humans and other hominids:...
. It can either be present at birth or not develop until puberty.
Pectus excavatum is sometimes considered to be cosmetic; however, depending on the severity, it can impair cardiac and respiratory function and cause pain in the chest and back. People with the abnormality may experience negative psychosocial
Psychosocial
For a concept to be psychosocial means it relates to one's psychological development in, and interaction with, a social environment. The individual needs not be fully aware of this relationship with his or her environment. It was first commonly used by psychologist Erik Erikson in his stages of...
effects, and avoid
Body dysmorphic disorder
Body Dysmorphic Disorder is a type of mental illness, a somatoform disorder, wherein the affected person is exclusively concerned with body image, manifested as excessive concern about and preoccupation with a perceived defect of his or her physical features...
activities that expose the chest.
Pectus excavatum is sometimes referred to as cobbler's chest, sunken chest, funnel chest or simply a dent in the chest.
Signs and symptoms
The hallmarkHallmark
A hallmark is an official mark or series of marks struck on items made of precious metals — platinum, gold, silver and in some nations, palladium...
of the condition is a sunken appearance of the sternum. The heart can be displaced and/or rotated. Mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the left atrium during systole. There are various types of MVP, broadly classified as classic and nonclassic. In its nonclassic form, MVP carries a low risk of...
may also be present. Base lung capacity is decreased.
Causes
Researchers are currently unsure as to the actual cause of pectus excavatum but hypothesize genetic defect. Approximately 37% of individuals with pectus excavatum have a first degree family member with the condition. Physiologically, increased pressure in utero, ricketsRickets
Rickets is a softening of bones in children due to deficiency or impaired metabolism of vitamin D, magnesium , phosphorus or calcium, potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries...
and increased traction on the sternum due to abnormalities of the diaphragm
Thoracic diaphragm
In the anatomy of mammals, the thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm , is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle that extends across the bottom of the rib cage. The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and performs an important function in respiration...
have been postulated as specific mechanisms. Pectus excavatum is also a relatively common symptom of Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a genetic disorder of the connective tissue. People with Marfan's tend to be unusually tall, with long limbs and long, thin fingers....
. Many children with spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal Muscular Atrophy is a neuromuscular disease characterized by degeneration of motor neurons, resulting in progressive muscular atrophy and weakness. The clinical spectrum of SMA ranges from early infant death to normal adult life with only mild weakness...
develop pectus excavatum due to the diaphragmatic breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, abdominal breathing, belly breathing or deep breathing is breathing that is done by contracting the diaphragm, a muscle located horizontally between the chest cavity and stomach cavity...
that is common with the disease. Pectus excavatum also occurs in about 1% of persons diagnosed with Celiac disease for unknown reasons.
Pathophysiology
Because the heartHeart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
is located behind the sternum, and because individuals with pectus excavatum have been shown to have visible deformities of the heart (seen both on radiological imaging and after autopsies), it has been hypothesized that there is impairment of function of the cardiovascular system in individuals with pectus excavatum. While some studies have demonstrated decreased cardiovascular function in pectus excavatum, there has been no consensus reached based on newer physiological tests (such as echocardiography
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram, often referred to in the medical community as a cardiac ECHO or simply an ECHO, is a sonogram of the heart . Also known as a cardiac ultrasound, it uses standard ultrasound techniques to image two-dimensional slices of the heart...
) of the presence or degree of impairment in cardiovascular function in people with pectus excavatum. Similarly, there is no consensus on the degree of functional improvement after corrective surgery.
Diagnosis
Pectus excavatum is initially suspected from visual examination of the anterior chest. AuscultationAuscultation
Auscultation is the term for listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope...
of the chest can reveal displaced heart beat and valve prolapse. There can be a heart murmur
Heart murmur
Murmurs are extra heart sounds that are produced as a result of turbulent blood flow that is sufficient to produce audible noise. Most murmurs can only be heard with the assistance of a stethoscope ....
occurring during systole
Systole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
caused by proximity between the sternum and the pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery
The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
.
Lung sounds are usually clear yet diminished due to decreased base lung capacity.
Many scales have been developed to determine the degree of deformity in the chest wall. Most of these are variants on the distance between the sternum and the spine
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
. One such index is the Backer ratio which grades severity of deformity based on the ratio between the diameter of the vertebral body nearest to xiphosternal junction and the distance between the xiphosternal junction and the nearest vertebral body. More recently the Haller index
Haller index
The Haller index, created in 1987 by Dr. Haller, Dr. Kramer, and Dr. Lietman, is a mathematical relationship that exists in a human chest section observed with a CT scan. It is defined as the ratio of the transverse diameter and the anteroposterior diameter...
has been used based on CT scan measurements. An index over 3.25 is often defined as severe. The Haller index is the ratio between the horizontal distance of the inside of the ribcage and the shortest distance between the vertebrae and sternum.
Chest x-ray
Chest X-ray
In medicine, a chest radiograph, commonly called a chest X-ray , is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures...
s are also useful in the diagnosis. The chest x-ray in pectus excavatum can show an opacity in the right lung area that can be mistaken for an infiltrate (such as that seen with pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
). Some studies also suggest that the Haller index
Haller index
The Haller index, created in 1987 by Dr. Haller, Dr. Kramer, and Dr. Lietman, is a mathematical relationship that exists in a human chest section observed with a CT scan. It is defined as the ratio of the transverse diameter and the anteroposterior diameter...
can be calculated based on chest x-ray as opposed to CT scanning in individuals who have no limitation in their function.
Pectus excavatum is differentiated from other disorders by a series of elimination of signs and symptoms. Pectus carinatum
Pectus carinatum
Pectus carinatum, , also called pigeon chest, is a deformity of the chest characterized by a protrusion of the sternum and ribs. It is the opposite of pectus excavatum.-Causes:...
is excluded by the simple observation of a collapsing of the sternum
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bony plate shaped like a capital "T" located anteriorly to the heart in the center of the thorax...
rather than a protrusion. Kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both a coronal and sagittal plane. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. Kyphoscoliosis is a musculoskeletal disorder causing chronic underventilation of the lungs and may be one of the major causes of pulmonary hypertension...
is excluded by diagnostic imaging of the spine, where in pectus excavatum the spine usually appears normal in structure.
Treatment
Treatment for pectus excavatum can involve either invasive or non-invasive techniques or a combination of both. Before an operation proceeds several tests are usually to be performed. These include, but are not limited to, a CT scan, pulmonary function tests, and cardiologyCardiology
Cardiology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the heart . The field includes diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology...
exams (such as auscultation and ECGs). After a CT scan is taken the Haller index
Haller index
The Haller index, created in 1987 by Dr. Haller, Dr. Kramer, and Dr. Lietman, is a mathematical relationship that exists in a human chest section observed with a CT scan. It is defined as the ratio of the transverse diameter and the anteroposterior diameter...
is measured. The patient's Haller is calculated by obtaining the ratio of the transverse diameter (the horizontal distance of the inside of the ribcage) and the anteroposterior diameter (the shortest distance between the vertebrae and sternum). A Haller Index of greater than 3.25 is generally considered severe, while normal chest has an index of 2.5. The cardiopulmonary tests are used to determine the lung capacity and to check for heart murmurs.
Surgery
Surgical correction has been shown to repair any functional symptoms that may occur in the condition, such as respiratory problems or heart murmurs, provided that permanent damage has not already arisen from an extremely severe case.Ravitch technique
The Ravitch technique is an invasive surgery that was introduced in 1949, and developed in the 1950s to treat the condition. This procedure involves creating an incision along the chest through which the cartilage is removed and the sternum detached. A small bar is then inserted underneath the sternum to hold it up in the desired position. The bar is left implanted until the cartilage grows back, typically about 6 months. The bar is subsequently removed in a simple out-patient procedure. The Ravitch technique is not widely practiced because it is so invasive. It is often used in older patients, where the sternum has calcified, when the deformity is asymmetrical, or when the less invasive Nuss procedure has proven unsuccessful.Nuss procedure


Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters
Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters , located in Norfolk, Virginia, is the only freestanding children's hospital in Virginia and the home to one of the nation's top pediatric residency programs....
(CHKD) in Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. With a population of 242,803 as of the 2010 Census, it is Virginia's second-largest city behind neighboring Virginia Beach....
, has developed a technique that is minimally invasive. The Nuss procedure involves slipping in one or more concave steel bars into the chest, underneath the sternum. The bar is flipped to a convex position so as to push outward on the sternum, correcting the deformity. The bar usually stays in the body for about two years, although many surgeons are now moving toward leaving them in for up to five years. When the bones have solidified into place, the bar is removed through outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory surgery, same-day surgery or day surgery, is surgery that does not require an overnight hospital stay. The term “outpatient” arises from the fact that surgery patients may go home and do not need an overnight hospital bed...
.
Vacuum bell
A relatively new alternative to surgery is the vacuum bell. It consists of a bowl shaped device which fits over the caved-in area; the air is then removed by the use of a hand pump. The vacuum created by this lifts the sternum upwards, lessening the severity of the deformity. As it is such a recent device there is currently no information as to whether it is effective in the long term.Cosmetic and light treatments
The cosmetic appearance of pectus excavatum can be treated with a dermal filler called Bio-AlcamidPolyalkylimide
Polyalkylimide is a polymer which belongs to the family of acryl derivatives. Its polymeric structure does not contain free monomers.It is also the active ingredient in a permanent dermal filler called Bio-Alcamid which is a three percent polyalkylimide suspension in water used medically to treat...
. However, as this does nothing to alleviate the actual deformity it will not prevent any physiological symptoms caused by the condition.
Mild cases have also reportedly been treated with corset
Corset
A corset is a garment worn to hold and shape the torso into a desired shape for aesthetic or medical purposes...
-like orthopedic support vests and exercise.
There are also prosthetic implants available to fill the depressed area. Solid silicone implants have been successfully used for many years with acceptable results in some cases. More recently a porex implant has been used which is a similar material used to replace skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
in brain surgery and severe head injuries.
Magnetic mini-mover procedure
This procedure is not available to adults. The magnetic mini-mover procedure (3MP) is a technique used to correct pectus excavatum by using two magnets to realign the sternum with the rest of the chest and ribcage. One magnet is inserted 1 cm into the patients body on the lower end of the sternum, the other is placed externally onto a custom fitted brace. These two magnets generate around 0.04 teslaTesla (unit)
The tesla is the SI derived unit of magnetic field B . One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter, and it was defined in 1960 in honour of the inventor, physicist, and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla...
(T) in order to slowly move the sternum outwards over a number of years. The maximum magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
that can be applied to the body safely is around 4 T, making this technique safe from a magnetic viewpoint. The 3MP technique's main advantages are that it is more cost-effective than major surgical approaches such as the Nuss procedure and it is considerably less painful postoperatively. One potential adverse effect of 3MP is inactivation of implanted devices such as an artificial pacemaker
Artificial pacemaker
A pacemaker is a medical device that uses electrical impulses, delivered by electrodes contacting the heart muscles, to regulate the beating of the heart...
. Since the 3MP is still in a trial period it is unknown whether long term wearing of the magnet will affect the skin or other vital organs.
Epidemiology
Pectus excavatum occurs in an estimated 1 in 150-1000 births, with male predominance (male-to-female ratio of 3:1). Occurrences of the condition in family members have been reported in 35% to 45% of cases.In animals
Pectus excavatum is also known to occur in animals, e.g. the MunchkinMunchkin (cat)
The Munchkin is a cat breed created by a naturally occurring genetic mutation that results in cats with abnormally short legs. However, the shortness of their legs does not seem to interfere with their running and leaping abilities...
breed of cat. Some procedures used to treat the condition in animals have not been used in humans, such as the use of a cast with sutures wrapped around the sternum and the use of internal and external splints
Splint (medicine)
A splint is a device used for support or immobilization of limbs or of the spine.It can be used:* By the emergency medical services or by volunteer first responders, to immobilize a fractured limb before the transportation; it is then a temporary immobilization;* By allied health professionals such...
. These techniques are generally used in immature animals with flexible cartilage.

