Peltephilus
Encyclopedia
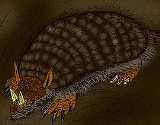
Peltephilus ferox, the Horned Armadillo, was a species of dog-sized, armadillo
-like xenarthran mammal
which first inhabited Argentina
during the Oligocene
epoch
, and became extinct in the Miocene
epoch. Notably, the scute
s on its head were so developed that they formed horn
s protecting its eyes. Aside from the horned gopher
s of North America
, it is the only known fossorial
horned mammal.
Although it had traditionally been perceived as a carnivore
because of its large, triangular-shaped teeth, Vizcaino and Farina argued in 1997 that Peltephilus was a herbivore
.
Armadillo
Armadillos are New World placental mammals, known for having a leathery armor shell. Dasypodidae is the only surviving family in the order Cingulata, part of the superorder Xenarthra along with the anteaters and sloths. The word armadillo is Spanish for "little armored one"...
-like xenarthran mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
which first inhabited Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
during the Oligocene
Oligocene
The Oligocene is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 34 million to 23 million years before the present . As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the period are slightly...
epoch
Epoch (reference date)
In the fields of chronology and periodization, an epoch is an instance in time chosen as the origin of a particular era. The "epoch" then serves as a reference point from which time is measured...
, and became extinct in the Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
epoch. Notably, the scute
Scute
A scute or scutum is a bony external plate or scale, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, the feet of some birds or the anterior portion of the mesonotum in insects.-Properties:...
s on its head were so developed that they formed horn
Horn (anatomy)
A horn is a pointed projection of the skin on the head of various animals, consisting of a covering of horn surrounding a core of living bone. True horns are found mainly among the ruminant artiodactyls, in the families Antilocapridae and Bovidae...
s protecting its eyes. Aside from the horned gopher
Horned gopher
Horned gophers are rodents from the genus Ceratogaulus, a member of the extinct fossorial rodent family Mylagaulidae. Ceratogaulus is the only known rodent genus with horns, and is the smallest known horned mammal...
s of North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, it is the only known fossorial
Fossorial
A fossorial organism is one that is adapted to digging and life underground such as the badger, the naked mole rat, and the mole salamanders Ambystomatidae...
horned mammal.
Although it had traditionally been perceived as a carnivore
Carnivore
A carnivore meaning 'meat eater' is an organism that derives its energy and nutrient requirements from a diet consisting mainly or exclusively of animal tissue, whether through predation or scavenging...
because of its large, triangular-shaped teeth, Vizcaino and Farina argued in 1997 that Peltephilus was a herbivore
Herbivore
Herbivores are organisms that are anatomically and physiologically adapted to eat plant-based foods. Herbivory is a form of consumption in which an organism principally eats autotrophs such as plants, algae and photosynthesizing bacteria. More generally, organisms that feed on autotrophs in...
.

