
Pentahedron
Encyclopedia
In geometry
, a pentahedron (plural: pentahedra) is a polyhedron
with five faces. Since there are no face-transitive polyhedra with five sides and there are two distinct topological types, this term is less frequently used than tetrahedron
or octahedron
.
With regular polygon
faces, the two topological forms types are the square pyramid
and triangular prism
. Geometric variations with irregular faces can also be constructed.
The square pyramid can be seen as a degenerate triangular prism where one edge of its side edges is collapsed into a point, losing one edge and one vertex, and changing two squares into triangles.
faces, called a pentagonal hosohedron with Schläfli symbol {2,5}. It has 2 (antipodal point
) vertices, 5 edges, and 5 digonal faces.
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a pentahedron (plural: pentahedra) is a polyhedron
Polyhedron
In elementary geometry a polyhedron is a geometric solid in three dimensions with flat faces and straight edges...
with five faces. Since there are no face-transitive polyhedra with five sides and there are two distinct topological types, this term is less frequently used than tetrahedron
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids...
or octahedron
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex....
.
With regular polygon
Regular polygon
A regular polygon is a polygon that is equiangular and equilateral . Regular polygons may be convex or star.-General properties:...
faces, the two topological forms types are the square pyramid
Square pyramid
In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it will have C4v symmetry.- Johnson solid :...
and triangular prism
Triangular prism
In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides....
. Geometric variations with irregular faces can also be constructed.
| Name | Picture | Vertices | Edges | Faces | Faces by type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Square pyramid Square pyramid In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it will have C4v symmetry.- Johnson solid :... (Pyramid family Pyramid (geometry) In geometry, a pyramid is a polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point, called the apex. Each base edge and apex form a triangle. It is a conic solid with polygonal base.... ) |
 |
5 | 8 | 5 | 4 triangles 1 square |
| Triangular prism Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... (Prism family Prism (geometry) In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron with an n-sided polygonal base, a translated copy , and n other faces joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All cross-sections parallel to the base faces are the same. Prisms are named for their base, so a prism with a pentagonal base is called a... ) |
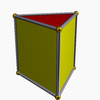 |
6 | 9 | 5 | 2 triangles 3 squares |
The square pyramid can be seen as a degenerate triangular prism where one edge of its side edges is collapsed into a point, losing one edge and one vertex, and changing two squares into triangles.
Hosohedron
There is a third topological polyhedral figure with 5 faces, degenerate as a polyhedron, it exists as a spherical tiling of digonDigon
In geometry, a digon is a polygon with two sides and two vertices. It is degenerate in a Euclidean space, but may be non-degenerate in a spherical space.A digon must be regular because its two edges are the same length...
faces, called a pentagonal hosohedron with Schläfli symbol {2,5}. It has 2 (antipodal point
Antipodal point
In mathematics, the antipodal point of a point on the surface of a sphere is the point which is diametrically opposite to it — so situated that a line drawn from the one to the other passes through the centre of the sphere and forms a true diameter....
) vertices, 5 edges, and 5 digonal faces.

