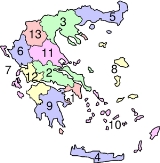
Peripheries of Greece
Encyclopedia
The current official regional administrative division
s of Greece
were instituted in 1987. Although best translated into English as "regions", the transcription peripheries is sometimes used, perhaps to distinguish them from the traditional regions which they replaced. The English word 'periphery' is derived from the , which in Greek (but not in English) also means 'region'. There are 13 regions (nine on the mainland and four island groups), which (until 2010) were further subdivided into the now abolished 54 prefectures
.
Traditionally, Greece was divided into 10 regions, which are still sometimes referred to in popular discourse. These are not to be confused with the new regions, even though the latter are largely based on the former, because there are areas of divergence. For example, the new region of the Peloponnese does not include all of the landmass traditionally known as the Peloponnese; the excluded part now finds itself in the region of Western Greece.
The first seven regions were established by the then-ruling military regime in 1971, but they were abolished after the fall of Georgios Papadopoulos in November 1973. The current regions were created by Law 1622/1986 and Presidential Decree 51/1987, and were conceived as an auxiliary regional level of the central government. With ongoing decentralization, they were accorded more powers in the 1997 Kapodistrias reform of local and regional government, and were finally transformed into fully separate entities by the 2010 Kallikratis plan (Law 3852/2010), which entered into effect on 1 January 2011. The government-appointed general secretary was replaced with a popularly elected regional governor and a regional council with 5-year terms, while many powers of the abolished prefectures
were transferred to the regions. As regional organs of the central government, the new regions were in turn replaced by seven decentralized administrations, which group from one to three regions under a government-appointed general secretary.
Bordering the region of Central Macedonia
there is one autonomous region, Mount Athos
(Agion Oros, or "Holy Mountain"), a monastic
community under Greek sovereignty. It is located on the easternmost of the three large peninsulas jutting into the Aegean
from the Chalcidice Peninsula.
Through the administrative reform of 2011, known as the Kallikratis plan, seven new administrative divisions (διοικήσεις) have been created:
Administrative division
An administrative division, subnational entity, or country subdivision is a portion of a country or other political division, established for the purpose of government. Administrative divisions are each granted a certain degree of autonomy, and are required to manage themselves through their own...
s of Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
were instituted in 1987. Although best translated into English as "regions", the transcription peripheries is sometimes used, perhaps to distinguish them from the traditional regions which they replaced. The English word 'periphery' is derived from the , which in Greek (but not in English) also means 'region'. There are 13 regions (nine on the mainland and four island groups), which (until 2010) were further subdivided into the now abolished 54 prefectures
Prefectures of Greece
During the first administrative division of independent Greece in 1833–1836 and then again from 1845 until their abolition with the Kallikratis reform in 2010, the prefectures were the country's main administrative unit...
.
Traditionally, Greece was divided into 10 regions, which are still sometimes referred to in popular discourse. These are not to be confused with the new regions, even though the latter are largely based on the former, because there are areas of divergence. For example, the new region of the Peloponnese does not include all of the landmass traditionally known as the Peloponnese; the excluded part now finds itself in the region of Western Greece.
The first seven regions were established by the then-ruling military regime in 1971, but they were abolished after the fall of Georgios Papadopoulos in November 1973. The current regions were created by Law 1622/1986 and Presidential Decree 51/1987, and were conceived as an auxiliary regional level of the central government. With ongoing decentralization, they were accorded more powers in the 1997 Kapodistrias reform of local and regional government, and were finally transformed into fully separate entities by the 2010 Kallikratis plan (Law 3852/2010), which entered into effect on 1 January 2011. The government-appointed general secretary was replaced with a popularly elected regional governor and a regional council with 5-year terms, while many powers of the abolished prefectures
Prefectures of Greece
During the first administrative division of independent Greece in 1833–1836 and then again from 1845 until their abolition with the Kallikratis reform in 2010, the prefectures were the country's main administrative unit...
were transferred to the regions. As regional organs of the central government, the new regions were in turn replaced by seven decentralized administrations, which group from one to three regions under a government-appointed general secretary.
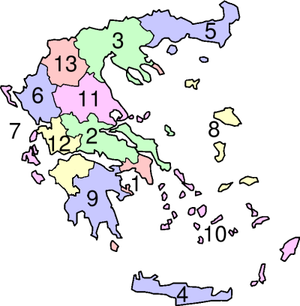 |
|
Bordering the region of Central Macedonia
Central Macedonia
Central Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
there is one autonomous region, Mount Athos
Mount Athos
Mount Athos is a mountain and peninsula in Macedonia, Greece. A World Heritage Site, it is home to 20 Eastern Orthodox monasteries and forms a self-governed monastic state within the sovereignty of the Hellenic Republic. Spiritually, Mount Athos comes under the direct jurisdiction of the...
(Agion Oros, or "Holy Mountain"), a monastic
Monasticism
Monasticism is a religious way of life characterized by the practice of renouncing worldly pursuits to fully devote one's self to spiritual work...
community under Greek sovereignty. It is located on the easternmost of the three large peninsulas jutting into the Aegean
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
from the Chalcidice Peninsula.
Through the administrative reform of 2011, known as the Kallikratis plan, seven new administrative divisions (διοικήσεις) have been created:
See also
- ISO 3166-2:GRISO 3166-2:GRISO 3166-2:GR is the entry for Greece in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Greece, ISO 3166-2 codes are...

