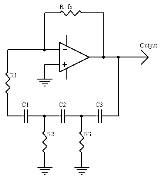
Phase-shift oscillator
Encyclopedia
A phase-shift oscillator is a simple electronic oscillator
. It contains an inverting amplifier, and a feedback
filter
which 'shifts' the phase
of the amplifier output by 180 degrees at a specific oscillation frequency.
The filter produces a phase shift that increases with frequency
. It must have a maximum phase shift of considerably greater than 180° at high frequencies, so that the phase shift at the desired oscillation frequency is 180°.
The most common way of achieving this kind of filter is using three identical cascaded resistor-capacitor filters, which together produce a phase shift of zero at low frequencies, and 270 degrees at high frequencies. At the oscillation frequency each filter produces a phase shift of 60 degrees and the whole filter circuit produces a phase shift of 180 degrees.
(op-amp), three capacitor
s and four resistor
s, as shown in the diagram.
The mathematics for calculating the oscillation frequency and oscillation criterion for this circuit are surprisingly complex, due to each R-C stage loading the previous ones. The calculations are greatly simplified by setting all the resistors (except the negative feedback
resistor) and all the capacitors to the same values. In the diagram, if R1 = R2 = R3 = R, and C1 = C2 = C3 = C, then:
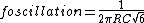
and the oscillation criterion is:
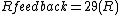
Without the simplification of all the resistors and capacitors having the same values, the calculations become more complex:
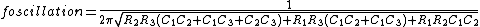
Oscillation criterion:
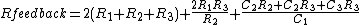
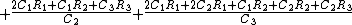
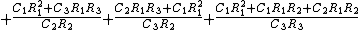
A version of this circuit can be made by putting an op-amp buffer between each R-C stage which simplifies the calculations. Тhe voltage gain of the inverting channel is always unity.
When the oscillation frequency is high enough to be near the amplifier's cutoff frequency
, the amplifier will contribute significant phase shift itself, which will add to the phase shift of the feedback network. Therefore the circuit will oscillate at a frequency at which the phase shift of the feedback filter is less than 180 degrees.
Electronic oscillator
An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices...
. It contains an inverting amplifier, and a feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
filter
Electronic filter
Electronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
which 'shifts' the phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of the amplifier output by 180 degrees at a specific oscillation frequency.
The filter produces a phase shift that increases with frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
. It must have a maximum phase shift of considerably greater than 180° at high frequencies, so that the phase shift at the desired oscillation frequency is 180°.
The most common way of achieving this kind of filter is using three identical cascaded resistor-capacitor filters, which together produce a phase shift of zero at low frequencies, and 270 degrees at high frequencies. At the oscillation frequency each filter produces a phase shift of 60 degrees and the whole filter circuit produces a phase shift of 180 degrees.
Op-amp implementation
One of the simplest implementations for this type of oscillator uses an operational amplifierOperational amplifier
An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
(op-amp), three capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s and four resistor
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
s, as shown in the diagram.
The mathematics for calculating the oscillation frequency and oscillation criterion for this circuit are surprisingly complex, due to each R-C stage loading the previous ones. The calculations are greatly simplified by setting all the resistors (except the negative feedback
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when the output of a system acts to oppose changes to the input of the system, with the result that the changes are attenuated. If the overall feedback of the system is negative, then the system will tend to be stable.- Overview :...
resistor) and all the capacitors to the same values. In the diagram, if R1 = R2 = R3 = R, and C1 = C2 = C3 = C, then:
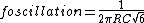
and the oscillation criterion is:
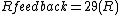
Without the simplification of all the resistors and capacitors having the same values, the calculations become more complex:
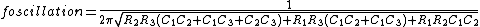
Oscillation criterion:
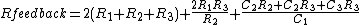
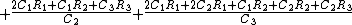
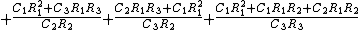
A version of this circuit can be made by putting an op-amp buffer between each R-C stage which simplifies the calculations. Тhe voltage gain of the inverting channel is always unity.
When the oscillation frequency is high enough to be near the amplifier's cutoff frequency
Cutoff frequency
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced rather than passing through.Typically in electronic systems such as filters and...
, the amplifier will contribute significant phase shift itself, which will add to the phase shift of the feedback network. Therefore the circuit will oscillate at a frequency at which the phase shift of the feedback filter is less than 180 degrees.

