
Phase retrieval
Encyclopedia
Phase retrieval concerns the solution to the phase problem
. Given a complex signal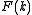 , of amplitude
, of amplitude 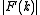 , and phase
, and phase 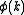 :
:
phase retrieval consists in finding the phase that for a measured amplitude satisfies a set of constraints.
For example if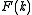 is the Fourier transform
is the Fourier transform
of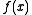 , a typical constraint would be that
, a typical constraint would be that 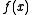 is a bounded real and positive function.
is a bounded real and positive function.
Important applications of phase retrieval include X-ray crystallography
and transmission electron microscopy
.
Phase problem
In physics the phase problem is the name given to the problem of loss of information concerning the phase that can occur when making a physical measurement. The name itself comes from the field of x-ray crystallography, where the phase problem has to be solved for the determination of a structure...
. Given a complex signal
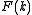 , of amplitude
, of amplitude 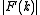 , and phase
, and phase 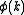 :
:
-
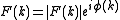 ,
,
phase retrieval consists in finding the phase that for a measured amplitude satisfies a set of constraints.
For example if
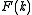 is the Fourier transform
is the Fourier transformFourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
of
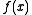 , a typical constraint would be that
, a typical constraint would be that 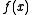 is a bounded real and positive function.
is a bounded real and positive function.Important applications of phase retrieval include X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...
and transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy is a microscopy technique whereby a beam of electrons is transmitted through an ultra thin specimen, interacting with the specimen as it passes through...
.
See also
- Phase problemPhase problemIn physics the phase problem is the name given to the problem of loss of information concerning the phase that can occur when making a physical measurement. The name itself comes from the field of x-ray crystallography, where the phase problem has to be solved for the determination of a structure...
- CrystallographyCrystallographyCrystallography is the experimental science of the arrangement of atoms in solids. The word "crystallography" derives from the Greek words crystallon = cold drop / frozen drop, with its meaning extending to all solids with some degree of transparency, and grapho = write.Before the development of...
- X-ray crystallographyX-ray crystallographyX-ray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and causes the beam of light to spread into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a...

