Phosphole
Encyclopedia
Phosphole is the organic compound
with the chemical formula
C4H4PH; it is the phosphorus
analog of pyrrole
. The term phosphole also refers to substituted derivatives of the parent heterocycle. These compounds are of theoretical interest but also serve as ligand
s for transition metals and as precursors to more complex organophosphorus compounds.
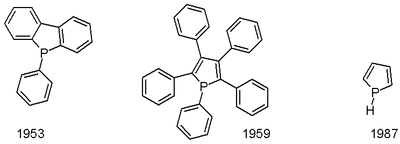
The first phosphole, pentaphenylphosphole, was reported in 1953, and the parent phosphole itself was first described in 1987. The usual route to phospholes is via the McCormack reaction
, involving the addition of a 1,3-diene
to a phosphonous chloride followed by dehydrohalogenation
. Phenylphospholes can be prepared via zirconacyclopentadienes by reaction with PhPCl2
.
Unlike the related 5-membered heterocycles pyrrole
, thiophene
, and furan
, the aromaticity of phospholes is diminished, reflecting the reluctance of phosphorus to delocalize its lone pair
. For example, phospholes undergo Diels-Alder reaction
s with electrophilic alkyne
s.
2,5-diphenyl phospholes can be functionalised by deprotonation followed by P-acylation then a 1H, 2H, 3H phospholide equilibrium resulting in a 1:3 shift of the acyl group.
Phospholes can also be turned in to β-functional phosphabenzenes (phosphinines, or phosphorine
) via functionalisaiton by imidoyl chloride and insertion.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with the chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C4H4PH; it is the phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
analog of pyrrole
Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3...
. The term phosphole also refers to substituted derivatives of the parent heterocycle. These compounds are of theoretical interest but also serve as ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s for transition metals and as precursors to more complex organophosphorus compounds.
The first phosphole, pentaphenylphosphole, was reported in 1953, and the parent phosphole itself was first described in 1987. The usual route to phospholes is via the McCormack reaction
McCormack reaction
The McCormack reaction is a method for the synthesis of organophosphorus compounds. In this reaction a 1,3-diene and a source of R2P+ are combined to give phospholenium cation. The reaction is named after W. B. McCormack, a research chemist at duPont....
, involving the addition of a 1,3-diene
Diene
In organic chemistry a diene or diolefin is a hydrocarbon that contains two carbon double bonds.Conjugated dienes are functional groups, with a general formula of CnH2n-2. Dienes and alkynes are functional isomers...
to a phosphonous chloride followed by dehydrohalogenation
Dehydrohalogenation
Dehydrohalogenation is an organic reaction from which an alkene is obtained from an alkyl halide . It is also called a β-Elimination reaction and is a type of elimination reaction....
. Phenylphospholes can be prepared via zirconacyclopentadienes by reaction with PhPCl2
Dichlorophenylphosphine
Dichlorophenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula C6H5PCl2. This colourless viscous liquid is commonly used in the synthesis of phosphine ligands....
.
Unlike the related 5-membered heterocycles pyrrole
Pyrrole
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4NH. It is a colourless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., N-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3...
, thiophene
Thiophene
Thiophene is a heterocyclic compound with the formula C4H4S. Consisting of a flat five-membered ring, it is aromatic as indicated by its extensive substitution reactions. Related to thiophene are benzothiophene and dibenzothiophene, containing the thiophene ring fused with one and two benzene...
, and furan
Furan
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen. The class of compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans....
, the aromaticity of phospholes is diminished, reflecting the reluctance of phosphorus to delocalize its lone pair
Lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
. For example, phospholes undergo Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
s with electrophilic alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
s.
Reactivity
Phosphole chemistry is hampered by its sensitivity to moisture.2,5-diphenyl phospholes can be functionalised by deprotonation followed by P-acylation then a 1H, 2H, 3H phospholide equilibrium resulting in a 1:3 shift of the acyl group.
Phospholes can also be turned in to β-functional phosphabenzenes (phosphinines, or phosphorine
Phosphorine
Phosphorine is a heavier element analog of pyridine, containing a phosphorus atom instead of an aza- moiety. It is also called phosphabenzene and belongs to the phosphaalkene class. Phosphorine is a planar aromatic compound with 88% of the aromaticity of that of benzene...
) via functionalisaiton by imidoyl chloride and insertion.