
Phosphorane
Encyclopedia
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
in organophosphorus chemistry with pentavalent phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
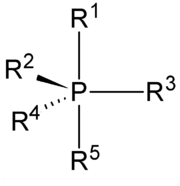
. It has the general formula PR5. The parent hydride
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is the anion of hydrogen, H−, or, more commonly, a compound in which one or more hydrogen centres have nucleophilic, reducing, or basic properties. In compounds that are regarded as hydrides, hydrogen is bonded to a more electropositive element or group...
compound is the unstable molecule PH5. The derivative pentaphenylphosphorane (Ph5P) is stable.
Phosphoranes adopt a trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry with the two apical bonds longer than the three equatorial bonds. Bonding is described by three-center, 4-electron bonds
Hypervalent molecule
A hypervalent molecule is a molecule that contains one or more main group elements formally bearing more than eight electrons in their valence shells...
, as also invoked for the closely related molecule phosphorus pentafluoride
Phosphorus pentafluoride
Phosphorus pentafluoride, PF5, is a phosphorus halide. It's a colourless gas at room temperature and pressure.-Structure:Single-crystal X-ray studies indicate PF5 molecule has two distinct P−F bonds : P−Fax = 158.0 pm and P−Feq = 152.2 pm...
.
Phosphoranes of the type R3P=CR2 are more common and more important. These compounds feature a tetrahedral phosphorus center including a phosphorus carbon double bond or ylide
Ylide
An ylide or ylid is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom directly attached to a hetero atom with a formal positive charge , and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds...
. These compounds are used as reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
s in the Wittig reaction
Wittig reaction
The Wittig reaction is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide to give an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide....
, for instance methylenetriphenylphosphorane or Ph3P=CH2.

