Photoacoustic Doppler effect
Encyclopedia
The photoacoustic Doppler effect, as its name implies, is one specific kind of Doppler effect, which occurs when an intensity modulated light wave induces a photoacoustic wave on moving particles with a specific frequency. The observed frequency shift is a good indicator of the velocity of the illuminated moving particles. A potential biomedical application is measuring blood flow.
Specifically, when an intensity modulated light wave is exerted on a localized medium, the resulting heat can induce an alternating and localized pressure change. This periodic pressure change generates an acoustic wave with a specific frequency. Among various factors that determine this frequency, the velocity of the heated area and thus the moving particles in this area can induce a frequency shift proportional to the relative motion. Thus, from the perspective of an observer, the observed frequency shift can be used to derive the velocity of illuminated moving particles..
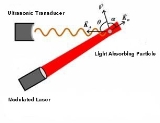
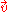 . The absorbers are irradiated by a laser with intensity modulated at frequency
. The absorbers are irradiated by a laser with intensity modulated at frequency 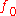 .
.
Thus, the intensity of the laser
could be described by:
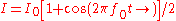
 When
When  is zero, an acoustic wave
is zero, an acoustic wave
with the same frequency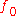 as the light intensity wave is induced. Otherwise, there is a frequency shift in the induced acoustic wave. The magnitude of the frequency shift depends on the relative velocity
as the light intensity wave is induced. Otherwise, there is a frequency shift in the induced acoustic wave. The magnitude of the frequency shift depends on the relative velocity 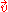 , the angle
, the angle  between the velocity and the photon density wave propagation direction, and the angle
between the velocity and the photon density wave propagation direction, and the angle 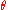 between the velocity and the ultrasonic wave propagation direction.
between the velocity and the ultrasonic wave propagation direction.
The frequency shift is given by:
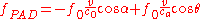
Where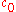 is the speed of light in the medium and
is the speed of light in the medium and  is the speed of sound. The first term on the right side of the expression represents the frequency shift in the photon density wave observed by the absorber acting as a moving receiver. The second term represents the frequency shift in the photoacoustic wave due to the motion of the absorbers observed by the ultrasonic transducer.
is the speed of sound. The first term on the right side of the expression represents the frequency shift in the photon density wave observed by the absorber acting as a moving receiver. The second term represents the frequency shift in the photoacoustic wave due to the motion of the absorbers observed by the ultrasonic transducer.
In practice, since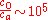 and
and 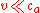 , only the second term is detectable. Therefore, the above equation reduces to:
, only the second term is detectable. Therefore, the above equation reduces to:
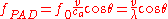
In this approximation, the frequency shift is not affected by the direction of the optical radiation. It is only affected by the magnitude of velocity and the angle between the velocity and the acoustic wave propagation direction.
This equation also holds for a scattering medium. In this case, the photon density wave becomes diffusive due to light scattering. Although the diffusive photon density wave has a slower phase velocity than the speed of light, its wavelength is still much longer than the acoustic wave.
 In the first demonstration of the Photoacoustic Doppler effect, a continuous wave diode laser
In the first demonstration of the Photoacoustic Doppler effect, a continuous wave diode laser
was used in a photoacoustic microscopy setup with an ultrasonic transducer as the detector. The sample was a solution of absorbing particles moving through a tube. The tube was in a water bath containing scattering particles
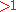
Figure 2 shows a relationship between average flow velocity and the experimental photoacoustic Doppler frequency shift. In a scattering medium, such as the experimental phantom, fewer photons reach the absorbers than in an optically clear medium. This affects the signal intensity but not the magnitude of the frequency shift. Another demonstrated feature of this technique is that it is capable of measuring flow direction relative to the detector based on the sign of the frequency shift. The reported minimum detected flow rate is 0.027 mm/s in the scattering medium.
.However, a particular difficulty of measuring flow velocity in capillaries is caused by the low blood flow rate and micrometre-scale diameter.Photoacoustic Doppler effect based imaging is a promising method for blood flow measurement in capillaries.
or light there are several techniques currently being used to measure blood
velocity in a clinical setting or other types of flow velocities.
 cm/s) generally found in large vessels due to the high background ultrasound signal from biological tissue.
cm/s) generally found in large vessels due to the high background ultrasound signal from biological tissue.
to detect flow velocity. The much shorter optical wavelength means this technology is able to detect low flow velocities out of the range of Doppler ultrasound. But this technique is limited by high background noise and low signal due to multiple scattering. Laser Doppler flowmetry can measure only the averaged blood speed within 1mm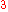 without information about flow direction.
without information about flow direction.
is an optical flow measurement technique that improves on the spatial resolution of laser Doppler flowmetry by rejecting multiple scattering light
with coherent gating. This technique is able to detect flow velocity as low as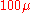 m/s with the spatial resolution of
m/s with the spatial resolution of 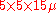 m
m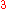 . The detection depth is usually limited by the high optical scattering coefficient of biological tissue to
. The detection depth is usually limited by the high optical scattering coefficient of biological tissue to 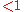 mm.
mm.
imaging with the contrast of optical absorption in deep biological tissue. Ultrasound
has good spatial resolution
in deep biological tissue since ultrasonic scattering is much weaker than optical scattering, but it is insensitive to biochemical properties. Conversely, optical imaging is able to achieve high contrast
in biological tissue via high sensitivity to small molecular optical absorbers, such as hemoglobin
found in red blood cells, but its spatial resolution is compromised by the strong scattering
of light in biological tissue. By combining the optical imaging with ultrasound, it is possible to achieve both high contrast and spatial resolution.
The photoacoustic Doppler flowmetry could use the power of photoacoustics to measure flow velocities that are usually inaccessible to pure light-based or ultrasound techniques. The high spatial resolution could make it possible to pinpoint only a few absorbing particles localized to a single capillary. High contrast from the strong optical absorbers make it possible to clearly resolve the signal from the absorbers over the background.
Specifically, when an intensity modulated light wave is exerted on a localized medium, the resulting heat can induce an alternating and localized pressure change. This periodic pressure change generates an acoustic wave with a specific frequency. Among various factors that determine this frequency, the velocity of the heated area and thus the moving particles in this area can induce a frequency shift proportional to the relative motion. Thus, from the perspective of an observer, the observed frequency shift can be used to derive the velocity of illuminated moving particles..
Theory
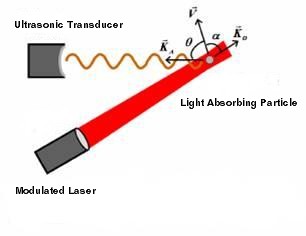
To be simple, consider a clear medium firstly. The medium contains small optical absorbers moving with velocity vector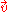 . The absorbers are irradiated by a laser with intensity modulated at frequency
. The absorbers are irradiated by a laser with intensity modulated at frequency 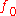 .
.Thus, the intensity of the laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
could be described by:
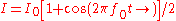

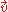 is zero, an acoustic wave
is zero, an acoustic waveAcoustic wave
Acoustic waves are a type of longitudinal waves that propagate by means of adiabatic compression and decompression. Longitudinal waves are waves that have the same direction of vibration as their direction of travel. Important quantities for describing acoustic waves are sound pressure, particle...
with the same frequency
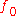 as the light intensity wave is induced. Otherwise, there is a frequency shift in the induced acoustic wave. The magnitude of the frequency shift depends on the relative velocity
as the light intensity wave is induced. Otherwise, there is a frequency shift in the induced acoustic wave. The magnitude of the frequency shift depends on the relative velocity 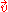 , the angle
, the angle  between the velocity and the photon density wave propagation direction, and the angle
between the velocity and the photon density wave propagation direction, and the angle 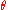 between the velocity and the ultrasonic wave propagation direction.
between the velocity and the ultrasonic wave propagation direction.The frequency shift is given by:
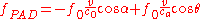
Where
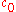 is the speed of light in the medium and
is the speed of light in the medium and  is the speed of sound. The first term on the right side of the expression represents the frequency shift in the photon density wave observed by the absorber acting as a moving receiver. The second term represents the frequency shift in the photoacoustic wave due to the motion of the absorbers observed by the ultrasonic transducer.
is the speed of sound. The first term on the right side of the expression represents the frequency shift in the photon density wave observed by the absorber acting as a moving receiver. The second term represents the frequency shift in the photoacoustic wave due to the motion of the absorbers observed by the ultrasonic transducer.In practice, since
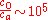 and
and  , only the second term is detectable. Therefore, the above equation reduces to:
, only the second term is detectable. Therefore, the above equation reduces to: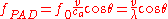
In this approximation, the frequency shift is not affected by the direction of the optical radiation. It is only affected by the magnitude of velocity and the angle between the velocity and the acoustic wave propagation direction.
This equation also holds for a scattering medium. In this case, the photon density wave becomes diffusive due to light scattering. Although the diffusive photon density wave has a slower phase velocity than the speed of light, its wavelength is still much longer than the acoustic wave.
Experiment

Laser diode
The laser diode is a laser where the active medium is a semiconductor similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The most common type of laser diode is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current...
was used in a photoacoustic microscopy setup with an ultrasonic transducer as the detector. The sample was a solution of absorbing particles moving through a tube. The tube was in a water bath containing scattering particles
Figure 2 shows a relationship between average flow velocity and the experimental photoacoustic Doppler frequency shift. In a scattering medium, such as the experimental phantom, fewer photons reach the absorbers than in an optically clear medium. This affects the signal intensity but not the magnitude of the frequency shift. Another demonstrated feature of this technique is that it is capable of measuring flow direction relative to the detector based on the sign of the frequency shift. The reported minimum detected flow rate is 0.027 mm/s in the scattering medium.
Application
One promising application is the non-invasive measurement of flow. This is related to an important problem in medicine: the measurement of blood flow through arteries, capillaries, and veins. Measuring blood velocity in capillaries is an important component to clinically determining how much oxygen is delivered to tissues and is potentially important to the diagnosis of a variety of diseases including diabetes and cancerCancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
.However, a particular difficulty of measuring flow velocity in capillaries is caused by the low blood flow rate and micrometre-scale diameter.Photoacoustic Doppler effect based imaging is a promising method for blood flow measurement in capillaries.
Existing techniques
Based on either ultrasoundUltrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
or light there are several techniques currently being used to measure blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
velocity in a clinical setting or other types of flow velocities.
Doppler ultrasound
The Doppler ultrasound technique uses Doppler frequency shifts in ultrasound wave. This technique is currently used in biomedicine to measure blood flow in arteries and veins. It is limited to high flow rates ( cm/s) generally found in large vessels due to the high background ultrasound signal from biological tissue.
cm/s) generally found in large vessels due to the high background ultrasound signal from biological tissue.Laser doppler flowmetry
Laser Doppler Flowmetry utilizes light instead of ultrasoundUltrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
to detect flow velocity. The much shorter optical wavelength means this technology is able to detect low flow velocities out of the range of Doppler ultrasound. But this technique is limited by high background noise and low signal due to multiple scattering. Laser Doppler flowmetry can measure only the averaged blood speed within 1mm
 without information about flow direction.
without information about flow direction.Doppler optical coherence tomography
Doppler Optical coherence tomographyOptical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography is an optical signal acquisition and processing method. It captures micrometer-resolution, three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media . Optical coherence tomography is an interferometric technique, typically employing near-infrared light...
is an optical flow measurement technique that improves on the spatial resolution of laser Doppler flowmetry by rejecting multiple scattering light
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
with coherent gating. This technique is able to detect flow velocity as low as
 m/s with the spatial resolution of
m/s with the spatial resolution of 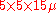 m
m . The detection depth is usually limited by the high optical scattering coefficient of biological tissue to
. The detection depth is usually limited by the high optical scattering coefficient of biological tissue to  mm.
mm.Photoacoustic doppler flowmetry
Photoacoustic Doppler effect can be used to measure the blood flow velocity with the advantages of Photoacoustic imaging. Photoacoustic imaging combines the spatial resolution of ultrasoundUltrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
imaging with the contrast of optical absorption in deep biological tissue. Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
has good spatial resolution
Image resolution
Image resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
in deep biological tissue since ultrasonic scattering is much weaker than optical scattering, but it is insensitive to biochemical properties. Conversely, optical imaging is able to achieve high contrast
Contrast (vision)
Contrast is the difference in visual properties that makes an object distinguishable from other objects and the background. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the color and brightness of the object and other objects within the same field of view...
in biological tissue via high sensitivity to small molecular optical absorbers, such as hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
found in red blood cells, but its spatial resolution is compromised by the strong scattering
Scattering
Scattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
of light in biological tissue. By combining the optical imaging with ultrasound, it is possible to achieve both high contrast and spatial resolution.
The photoacoustic Doppler flowmetry could use the power of photoacoustics to measure flow velocities that are usually inaccessible to pure light-based or ultrasound techniques. The high spatial resolution could make it possible to pinpoint only a few absorbing particles localized to a single capillary. High contrast from the strong optical absorbers make it possible to clearly resolve the signal from the absorbers over the background.
See also
- Photoacoustic spectroscopyPhotoacoustic spectroscopyPhotoacoustic spectroscopy is the measurement of the effect of absorbed electromagnetic energy on matter by means of acoustic detection. The discovery of the photoacoustic effect dates to 1880 when Alexander Graham Bell showed that thin discs emitted sound when exposed to a beam of sunlight that...
- Photoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
- Photoacoustic tomographyPhotoacoustic tomographyPhotoacoustic tomography , or photoacoustic computed tomography , is a materials analysis technique based on the reconstruction of an internal photoacoustic source distribution from measurements acquired by scanning ultrasound detectors over a surface that encloses the source under...
- Doppler effectDoppler effectThe Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...

