
Photochemical reflectance Index
Encyclopedia
The Photochemical Reflectance Index or PRI is a reflectance measurement developed by Dr. John Gamon
. The PRI is sensitive to changes in carotenoid
pigments (e.g. xanthophyll
pigments) in live foliage. Carotenoid pigments are indicative of photosynthetic light use efficiency, or the rate of carbon dioxide
uptake by foliage per unit energy absorbed. As such, it is used in studies of vegetation productivity and stress. Because the PRI measures plant responses to stress, it can be used to assess general ecosystem health using satellite data or other forms of remote sensing. Applications include vegetation health in evergreen shrubland
s, forests, and agricultural crops prior to senescence
. PRI is defined by the following equation:
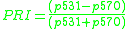
Some authors use
p531
p750
The values range from -1 to 1.
[2] John Gamon
, Penuelas, J. and Field, C.B. (1992). A narrow-waveband spectral index that tracks diurnal changes in photosynthetic efficiency. Remote Sensing of environment, 41, 35-44.
[3] Drolet, G.G. Heummrich, K.F. Hall, F.G., Middleton, E.M., Black, T.A., Barr, A.G. and Margolis, H.A. (2005). A MODIS-derived photochemical reflectance index to detect inter-annual variations in the photosynthetic light-use efficiency of a boreal deciduous forest. Remote Sensing of environment, 98, 212-224.
John Gamon
- Background :Dr. John Gamon, a prolific researcher overseeing numerous field research projects, pioneered the use of the relationship between leaf xanthophyll cycle pigment content and spectral reflectance to improve satellite monitoring of photosynthesis. Gamon's seminal work resulted in the...
. The PRI is sensitive to changes in carotenoid
Carotenoid
Carotenoids are tetraterpenoid organic pigments that are naturally occurring in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some other photosynthetic organisms like algae, some bacteria, and some types of fungus. Carotenoids can be synthesized fats and other basic organic metabolic building...
pigments (e.g. xanthophyll
Xanthophyll
Xanthophylls are yellow pigments that form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group. The name is from Greek xanthos + phyllon , due to their formation of the yellow band seen in early chromatography of leaf pigments...
pigments) in live foliage. Carotenoid pigments are indicative of photosynthetic light use efficiency, or the rate of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
uptake by foliage per unit energy absorbed. As such, it is used in studies of vegetation productivity and stress. Because the PRI measures plant responses to stress, it can be used to assess general ecosystem health using satellite data or other forms of remote sensing. Applications include vegetation health in evergreen shrubland
Shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub or brush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity...
s, forests, and agricultural crops prior to senescence
Senescence
Senescence or biological aging is the change in the biology of an organism as it ages after its maturity. Such changes range from those affecting its cells and their function to those affecting the whole organism...
. PRI is defined by the following equation:
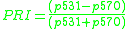
Some authors use

p531
p750
The values range from -1 to 1.
Sources
[1] ENVI Users Guide[2] John Gamon
John Gamon
- Background :Dr. John Gamon, a prolific researcher overseeing numerous field research projects, pioneered the use of the relationship between leaf xanthophyll cycle pigment content and spectral reflectance to improve satellite monitoring of photosynthesis. Gamon's seminal work resulted in the...
, Penuelas, J. and Field, C.B. (1992). A narrow-waveband spectral index that tracks diurnal changes in photosynthetic efficiency. Remote Sensing of environment, 41, 35-44.
[3] Drolet, G.G. Heummrich, K.F. Hall, F.G., Middleton, E.M., Black, T.A., Barr, A.G. and Margolis, H.A. (2005). A MODIS-derived photochemical reflectance index to detect inter-annual variations in the photosynthetic light-use efficiency of a boreal deciduous forest. Remote Sensing of environment, 98, 212-224.

