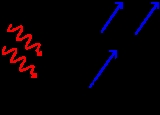
Photoelectric effect
Overview
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s are emitted from matter (metals and non-metallic solids, liquids or gases) as a consequence of their absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation of very short wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
, such as visible or ultraviolet light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
. Electrons emitted in this manner may be referred to as photoelectrons. First observed by Heinrich Hertz in 1887, the phenomenon is also known as the Hertz effect, although the latter term has fallen out of general use.
Unanswered Questions

