
Pipe insulation
Encyclopedia

Thermal insulation
Thermal insulation is the reduction of the effects of the various processes of heat transfer between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Heat transfer is the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature...
or acoustic insulation used on pipework.
Condensation control
Where pipes operate at below-ambient temperatures, the potential exists for water vapour to condenseCondensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
on the pipe surface. Moisture is known to contribute towards many different types of corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
, so preventing the formation of condensation on pipework is usually considered important.
Pipe insulation can prevent condensation forming, as the surface temperature of the insulation will vary from the surface temperature of the pipe. Condensation will not occur, provided that (a) the insulation surface is above the dewpoint temperature of the air; and (b) the insulation incorporates some form of water-vapour barrier or retarder that prevents water vapour from passing through the insulation to form on the pipe surface.
Pipe freezing
Since some water pipes are located either outside or in unheated areas where the ambient temperature may occasionally drop below the freezing point of water, any water in the pipework may potentially freeze. When water freezes, it expands due to negative thermal expansion, and this expansion can cause failure of a pipe system in any one of a number of ways.Pipe insulation cannot prevent the freezing of standing water in pipework, but it can increase the time required for freezing to occur—thereby reducing the risk of the water in the pipes freezing. For this reason, it is recommended to insulate pipework at risk of freezing, and local water-supply regulations may require pipe insulation be applied to pipework to reduce the risk of pipe freezing.
For a given length, a smaller-bore pipe holds a smaller volume of water than a larger-bore pipe, and therefore water in a smaller-bore pipe will freeze more easily (and more quickly) than water in a larger-bore pipe (presuming equivalent environments). Since smaller-bore pipes present a greater risk of freezing, insulation is typically used in combination with alternative methods of freeze prevention (e.g., modulating trace heating
Trace heating
Electric trace heating, also known as electric heat tracing, heat tape or surface heating, is a system used to maintain or raise the temperature of pipes and vessels. Trace heating takes the form of an electrical heating element run in physical contact along the length of a pipe. The pipe must...
cable, or ensuring a consistent flow of water through the pipe).
Energy saving
Since pipework can operate at temperatures far removed from the ambient temperature, and the rate of heat flow from a pipe is related to the temperature differential between the pipe and the surrounding ambient air, heat flow from pipework can be considerable. In many situations, this heat flow is undesirable. The application of thermal pipe insulation introduces thermal resistance and reduces the heat flow.Thicknesses of thermal pipe insulation used for saving energy vary, but as a general rule, pipes operating at more-extreme temperatures exhibit a greater heat flow and larger thicknesses are applied due to the greater potential savings.
The location of pipework also influences the selection of insulation thickness. For instance, in some circumstances, heating pipework within a well-insulated building might not require insulation, as the heat that's "lost" (i.e., the heat that flows from the pipe to the surrounding air) may be considered “useful” for heating the building, as such "lost" heat would be effectively trapped by the structural insulation
Building insulation
building insulation refers broadly to any object in a building used as insulation for any purpose. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation...
anyway. Conversely, such pipework may be insulated to prevent overheating or unnecessary cooling in the rooms through which it passes.
Protection against extreme temperatures
Where pipework is operating at extremely high or low temperatures, the potential exists for injury to occur should any person come into physical contact with the pipe surface. The threshold for human pain varies, but several international standards set recommended touch temperature limits.Since the surface temperature of insulation varies from the temperature of the pipe surface, typically such that the insulation surface has a "less extreme" temperature, pipe insulation can be used to bring surface touch temperatures into a safe range.
Control of noise
Pipework can operate as a conduit for noiseNoise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
to travel from one part of a building to another (a typical example of this can be seen with waste-water pipework routed within a building). Acoustic insulation can prevent this noise transfer by acting to damp
Damping
In physics, damping is any effect that tends to reduce the amplitude of oscillations in an oscillatory system, particularly the harmonic oscillator.In mechanics, friction is one such damping effect...
the pipe wall and performing an acoustic decoupling function wherever the pipe passes through a fixed wall or floor and wherever the pipe is mechanically fixed.
Pipework can also radiate mechanical noise. In such circumstances, the breakout of noise from the pipe wall can be achieved by acoustic insulation incorporating a high-density sound barrier
Noise barrier
A noise barrier is an exterior structure designed to protect sensitive land uses from noise pollution...
.
Factors influencing performance
The relative performance of different pipe insulation on any given application can be influenced by many factors. The principle factors are:- Thermal conductivityThermal conductivityIn physics, thermal conductivity, k, is the property of a material's ability to conduct heat. It appears primarily in Fourier's Law for heat conduction....
("k" or "λ" value) - Surface emissivityEmissivityThe emissivity of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit energy by radiation. It is the ratio of energy radiated by a particular material to energy radiated by a black body at the same temperature...
("ε" value) - Water-vapour resistance ("μ" value)
- Insulation thickness
- DensityDensityThe mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
Other factors, such as the level of moisture content and the opening of joints, can influence the overall performance of pipe insulation. Many of these factors are listed in the international standard EN ISO 23993.
Materials
Pipe insulation materials come in a large variety of forms, but most materials fall into one of the following categories.Mineral wool
Mineral woolsMineral wool
Mineral wool, mineral fibers or man-made mineral fibers are fibers made from natural or synthetic minerals or metal oxides. The latter term is generally used to refer solely to synthetic materials including fiberglass, ceramic fibers and stone wool...
, including rock and slag wools, are inorganic strands of mineral fibre bonded together using organic binders. Mineral wools are capable of operating at high temperatures and exhibit good fire performance ratings when tested.
Mineral wools are used on all types of pipework, particularly industrial pipework operating at higher temperatures.
Glass wool
Glass wool is a high-temperature fibrous insulation material, similar to mineral wool, where inorganic strands of glass fibre are bound together using a binder.As with other forms of mineral wool, glass-wool insulation can be used for thermal and acoustic applications.
Flexible elastomeric foams
These are flexible, closed-cell, rubber foams based on NBRNitrile rubber
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N, Perbunan, or NBR, is a synthetic rubber copolymer of acrylonitrile and butadiene. Trade names include Nipol, Krynac and Europrene....
or EPDM rubber
EPDM rubber
EPDM rubber , a type of synthetic rubber, is an elastomer which is characterized by a wide range of applications. The E refers to ethylene, P to propylene, D to diene and M refers to its classification in ASTM standard D-1418. The M class includes rubbers having a saturated chain of the...
. Flexible elastomeric foams exhibit such a high resistance to the passage of water vapour that they do not generally require additional water-vapour barriers. Such high vapour resistance, combined with the high surface emissivity of rubber, allows flexible elastomeric foams to prevent surface condensation formation with comparatively small thicknesses.
As a result, flexible elastomeric foams are widely used on refrigeration and air-conditioning pipework. Flexible elastomeric foams are also used on heating and hot-water systems.
Rigid foam
Pipe insulation made from rigid Phenolic, PIR, or PUR foam insulation is common in some countries. Rigid-foam insulation has minimal acoustic performance but can exhibit low thermal-conductivity values of 0.021 W/(m·K) or lower, allowing energy-saving legislation to be met whilst using reduced insulation thicknessess.Polyethylene
PolyethylenePolyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons...
is a semi-flexible plastic foamed insulation that is widely used to prevent freezing of domestic water supply pipes and to reduce heat loss from domestic heating pipes.
The fire performance of Polyethylene usually prohibits its use in commercial buildings.
Aerogel
Silica AerogelAerogel
Aerogel is a synthetic porous material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component of the gel has been replaced with a gas. The result is a solid with extremely low density and thermal conductivity...
insulation has the lowest thermal conductivity of any commercially produced insulation. Although no manufacturer currently manufactures Aerogel pipe sections, it is possible to wrap Aerogel blanket around pipework, allowing it to function as pipe insulation.
The usage of Aerogel for pipe insulation is currently limited.
Heat flow calculations and R-value
Heat flow passing through pipe insulation can be calculated by following the equations set out in either the ASTM C 680 or EN ISO 12241 standards. Heat flow is given by the following equation: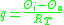
Where:
-
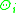 is the internal pipe temperature,
is the internal pipe temperature, -
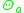 is the external ambient temperature, and
is the external ambient temperature, and -
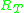 is the sum total thermal resistance of all insulation layers and the internal- and external-surface heat-transfer resistances.
is the sum total thermal resistance of all insulation layers and the internal- and external-surface heat-transfer resistances.
In order to calculate heat flow, it is first necessary to calculate the thermal resistance ("R-value
R-value (insulation)
The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance used in the building and construction industry. Under uniform conditions it is the ratio of the temperature difference across an insulator and the heat flux through it or R = \Delta T/\dot Q_A.The R-value being discussed is the unit thermal resistance...
") for each layer of insulation.
For pipe insulation, the R-value
R-value (insulation)
The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance used in the building and construction industry. Under uniform conditions it is the ratio of the temperature difference across an insulator and the heat flux through it or R = \Delta T/\dot Q_A.The R-value being discussed is the unit thermal resistance...
varies not only with the insulation thickness and thermal conductivity ("k-value") but also with the pipe outer diameter and the average material temperature. For this reason, it is more common to use the thermal conductivity value when comparing the effectiveness of pipe insulation, and R-values
R-value (insulation)
The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance used in the building and construction industry. Under uniform conditions it is the ratio of the temperature difference across an insulator and the heat flux through it or R = \Delta T/\dot Q_A.The R-value being discussed is the unit thermal resistance...
of pipe insulation are not covered by the US FTC R-value rule.
The thermal resistance of each insulation layer is calculated using the following equation:
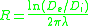
Where:
-
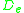 represents the insulation outer diameter,
represents the insulation outer diameter, -
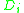 represents the insulation inner diameter, and
represents the insulation inner diameter, and -
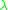 represents the thermal conductivity ("k-value") at the average insulation temperature (for accurate results iterative calculations are necessary).
represents the thermal conductivity ("k-value") at the average insulation temperature (for accurate results iterative calculations are necessary).
Calculating the heat transfer resistance of the inner- and outer-insulation surfaces is more complex and requires the calculation of the internal- and external-surface coefficients of heat transfer. Equations for calculating this are based on empirical results and vary from standard to standard (both ASTM C 680 and EN ISO 12241 contain equations for estimating surface coefficients of heat transfer).
A number of organisations such as the North American Insulation Manufacturers Association and Firo Insulation offer free programs that allow the calculation of heat flow through pipe insulation.
External links
- Mechanical Insulation Design Guide - National Insulation Association
- Insulating Cold Pipe Systems - Thermaxx Jackets
- R-Values by Insulation Material - InspectAPedia
- Pipe Insulation Products - Advanced Insulation

