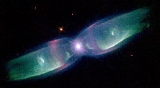
Planetary Nebula M2-9
Encyclopedia
Minkowski 2-9, abbreviated M2-9, (and also known as Minkowski's Butterfly, the Wings of a Butterfly Nebula or just Butterfly Nebula, and Twin Jet Nebula) is a planetary nebula
that was discovered by Rudolph Minkowski
in 1947. It is located about 2,100 light-years away from Earth in the direction of the constellation Ophiuchus
. This bipolar nebula
takes the peculiar form of twin lobes of material that emanate from a central star
. Astronomer
s have dubbed this object as the Twin Jet Nebula because of the polar jets believed to cause the shape of the lobes. Its form also resembles the wings of a butterfly
. The nebula was imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope
in the 1990s.
M2-9 represents the spectacular “last gasp” of a binary star system at the nebula's center. The primary component of this binary is the hot core of a star that reached the end of its main-sequence life cycle, ejected most of its outer layers and became a red giant
, and is now contracting into a white dwarf
. It is believed to have been a sun-like star early in its life. The second, smaller star of the binary orbits very closely and may even have been engulfed by the other's expanding stellar atmosphere with the resulting interaction creating the nebula. Astronomers theorize that the gravity of one star pulls some of the gas from the surface of the other and flings it into a thin, dense disk extending into space. Such a disk can successfully account for the jet-exhaust-like appearance of M2-9.
The nebula has inflated dramatically due to a fast stellar wind
, blowing out into the surrounding disk and inflating the large, wispy hourglass-shaped wings perpendicular to the disk. These wings produce the butterfly appearance when seen in projection. The outer shell is estimated to be about 1,200 years old .
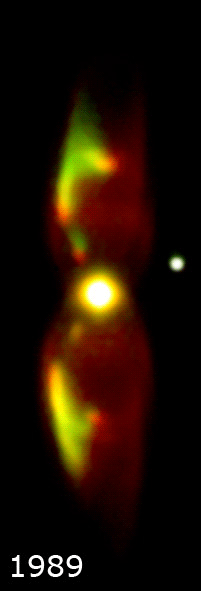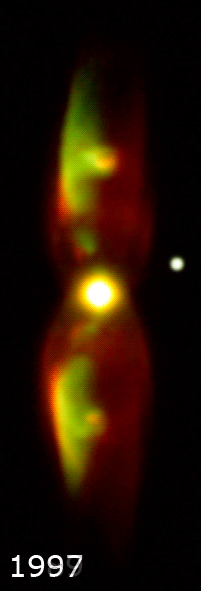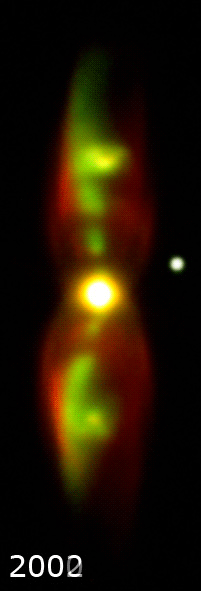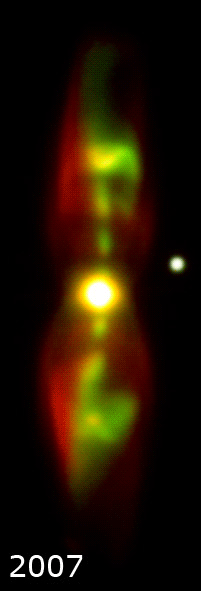 ]
]
Planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life...
that was discovered by Rudolph Minkowski
Rudolph Minkowski
Rudolph Minkowski was a German-American astronomer. His father was the physiologist Oskar Minkowski and his uncle was Hermann Minkowski....
in 1947. It is located about 2,100 light-years away from Earth in the direction of the constellation Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century...
. This bipolar nebula
Bipolar nebula
A bipolar nebula is a distinctive nebular formation characterized by an axially symmetric bi-lobed appearance.Many, but not all, planetary nebulae exhibit an observed bipolar structure...
takes the peculiar form of twin lobes of material that emanate from a central star
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
. Astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
s have dubbed this object as the Twin Jet Nebula because of the polar jets believed to cause the shape of the lobes. Its form also resembles the wings of a butterfly
Butterfly
A butterfly is a mainly day-flying insect of the order Lepidoptera, which includes the butterflies and moths. Like other holometabolous insects, the butterfly's life cycle consists of four parts: egg, larva, pupa and adult. Most species are diurnal. Butterflies have large, often brightly coloured...
. The nebula was imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
in the 1990s.
M2-9 represents the spectacular “last gasp” of a binary star system at the nebula's center. The primary component of this binary is the hot core of a star that reached the end of its main-sequence life cycle, ejected most of its outer layers and became a red giant
Red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5,000 K and lower...
, and is now contracting into a white dwarf
White dwarf
A white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored...
. It is believed to have been a sun-like star early in its life. The second, smaller star of the binary orbits very closely and may even have been engulfed by the other's expanding stellar atmosphere with the resulting interaction creating the nebula. Astronomers theorize that the gravity of one star pulls some of the gas from the surface of the other and flings it into a thin, dense disk extending into space. Such a disk can successfully account for the jet-exhaust-like appearance of M2-9.
The nebula has inflated dramatically due to a fast stellar wind
Stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of neutral or charged gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric.Different types of stars have...
, blowing out into the surrounding disk and inflating the large, wispy hourglass-shaped wings perpendicular to the disk. These wings produce the butterfly appearance when seen in projection. The outer shell is estimated to be about 1,200 years old .

See also
- Bipolar nebulaBipolar nebulaA bipolar nebula is a distinctive nebular formation characterized by an axially symmetric bi-lobed appearance.Many, but not all, planetary nebulae exhibit an observed bipolar structure...
- Bipolar outflowBipolar outflowA bipolar outflow represents two continuous flows of gas from the poles of a star. Bipolar outflows may be associated with protostars , or with evolved post-AGB stars ....
- Planetary nebulaPlanetary nebulaA planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life...
- Protoplanetary nebulaProtoplanetary nebulaA protoplanetary nebula or preplanetary nebula is an astronomical object which is at the short-lived episode during a star's rapid stellar evolution between the late asymptotic giant branch phase and the subsequent planetary nebula phase. A PPN emits strongly in infrared radiation, and is a...
- Mz 3
External links
- NASA APoD 1997-12-23 & APoD 1999-03-21 & APoD 2004-02-01 & APoD 2005-06-12 & APoD 2007-06-18 M2-9: Wings of a Butterfly Nebula

