
Planetshine
Encyclopedia

Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
from a planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
illuminates the night side of one of its moon
Natural satellite
A natural satellite or moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet or smaller body, which is called its primary. The two terms are used synonymously for non-artificial satellites of planets, of dwarf planets, and of minor planets....
s. Typically, this results in the moon's night side being bathed in a soft, faint light. The best known example of planetshine is earthshine, which can be seen from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
when the Moon is a thin crescent. Planetshine has been observed elsewhere in the solar system: in particular, it has recently been used by the Cassini space probe to image portions of the moons of Saturn even when they are not lit by the Sun.
Diagram of planetshine
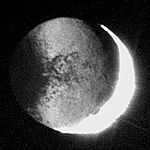
Earthshine
Earthshine is reflected earthlightEarthlight (astronomy)
Earthlight is the partial illumination of the dark portion of the moon's surface by light reflected from the earth. It is also known as earthshine, the Moon's ashen glow or the old Moon in the new Moon's arms....
visible on the Moon's
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
night side. It is also known as the Moon's ashen glow or as the old Moon in the new Moon's arms.

New moon
In astronomical terminology, the new moon is the lunar phase that occurs when the Moon, in its monthly orbital motion around Earth, lies between Earth and the Sun, and is therefore in conjunction with the Sun as seen from Earth...
, during the waxing or waning crescent phase. When the Moon is new as viewed from Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
, the Earth is nearly fully lit up as viewed from the Moon. Sunlight
Sunlight
Sunlight, in the broad sense, is the total frequency spectrum of electromagnetic radiation given off by the Sun. On Earth, sunlight is filtered through the Earth's atmosphere, and solar radiation is obvious as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon.When the direct solar radiation is not blocked...
is reflected from the Earth to the night side of the Moon. The night side appears to glow faintly and the entire orb of the Moon is dimly visible.

Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
explained the phenomenon in the early 16th century when he realized that both Earth and the Moon reflect sunlight. Light is reflected from the Earth to the Moon and back to the Earth as earthshine.
Earthshine is used to help determine the current albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
of the Earth. The data are used to analyze global cloud cover, a climate factor. Oceans reflect the least amount of light, roughly 10%. Land reflects anywhere from 10-25% of the Sun's light, and clouds reflect around 50%. So, the part of the Earth where it is daytime and from which the Moon is visible determines how bright the Moon's earthshine appears at any given time.

Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
. Some clouds have a net warming effect because they trap heat, while others have a net cooling effect because they increase albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
, so the overall effect on global temperature remains unclear. http://skyandtelescope.com/news/article_1287_1.asp
See also: André-Louis Danjon
André Danjon
André-Louis Danjon was a French astronomer born in Caen.Danjon devised a method to measure "Earthshine" on the Moon using a telescope in which a prism split the Moon's image into two identical side-by-side images...
, Danjon scale
Danjon scale
The Danjon Scale of lunar eclipse brightness is a five-point scale useful for measuring the appearance and luminosity of the Moon during a lunar eclipse. It was proposed by André-Louis Danjon when he was measuring the Earthshine on the Moon...
.
Ringshine
Ringshine is when sunlight is reflected by a planet's ring system onto the planet or onto the moons of the planet. This has been observed in many of the photos from the Cassini–Huygens probe.Search for terrestrial planets
Scientists at NASANASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's Navigator Program, which specializes in the detection of terrestrial planets, have backed the launch of a Terrestrial Planet Finder
Terrestrial Planet Finder
The Terrestrial Planet Finder was a proposed project by NASA to construct a system of telescopes for detecting extrasolar terrestrial planets. TPF was postponed several times and finally cancelled...
(TPF) mission. http://planetquest.jpl.nasa.gov/TPF/tpf_index.cfm TPF would detect planetshine from planets orbiting stars to investigate whether they could harbor life. It would use advanced telescope technologies to look for life-marks in the light reflected from the planets, including water, oxygen and methane.
The European Space Agency
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
has a similar mission, named Darwin
Darwin (ESA)
Darwin was a suggested ESA Cornerstone mission which would have involved a constellation of four to nine spacecraft designed to directly detect Earth-like planets orbiting nearby stars and search for evidence of life on these planets...
, under consideration. This will also study the earthshine of planets to detect the signatures of life. http://www.esa.int/esaSC/120382_index_0_m.html
Unlike many traditional astronomical challenges, the most serious challenge for these missions is not gathering enough photons from the faint planet, but rather detecting a faint planet that is extremely close to a very bright star. For a terrestrial planet, the contrast ratio of planet to its host stars is approximately ~10−6-10−7 in the thermal infrared or ~10−9-10−10 in the optical/near infrared. For this reason, Darwin and Terrestrial Planet Finder-I will work in the thermal infrared. However, searching for terrestrial planets in the optical/near infrared has the advantage that the diffraction limit corresponds to a smaller angle for a given size telescope. Therefore, NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
is also pursuing an Terrestrial Planet Finder-C mission that will search for and study terrestrial planets using the optical (and near infrared) wavelengths. While Terrestrial Planet Finder-C aims to study the planetshine of extrasolar planets, Darwin and Terrestrial Planet Finder-I will search for thermal infrared light that is reradiated (rather than scattered) by the planet, and most astronomers would not consider that to be planetshine.
In preparation for these missions, astronomers have performed detailed earthshine observations. Astronomers have paid particular attention to whether earthshine measurement can detect the red edge
Red edge
Red edge refers to the region of rapid change in reflectance of chlorophyll in the near infrared range. Vegetation absorbs most of the light in the visible part of the spectrum but is strongly reflective at wavelengths greater than 700 nm. The change can be from 5% to 50% reflectance between 680 nm...
, a spectral feature that is due to the plants. The detection of a similar spectral feature in light from an extrasolar planet would be particularly interesting, since it might be due to a light-harvesting organism. While the red edge
Red edge
Red edge refers to the region of rapid change in reflectance of chlorophyll in the near infrared range. Vegetation absorbs most of the light in the visible part of the spectrum but is strongly reflective at wavelengths greater than 700 nm. The change can be from 5% to 50% reflectance between 680 nm...
is almost certainly the easiest way to directly detect life on earth
Life on Earth
Life on Earth: A Natural History by David Attenborough is a television natural history series made by the BBC in association with Warner Bros. and Reiner Moritz Productions...
via earthshine observations, it could be extremely difficult to interpret a similar feature due to life on another planet, since the wavelength of the spectral feature is not known in advance (unlike most atomic or molecular spectral features).
External links
- Science@NASA: Earthshine
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day, 19 April 2002
- Earthshine' Linked to Solar Cycle, Climate Change, Space.com
- Scientists Watch Dark Side of the Moon to Monitor Earth's Climate, American Geophysical Union
- Earthshine picture gallery on SkyTrip.de

