
Plasma shaping
Encyclopedia
Magnetically confined
fusion plasma
s such as those generated in tokamak
s and stellarator
s are characterized by a typical shape. Plasma shaping is the study of the plasma shape in such devices, and is particularly important for next step fusion devices such as ITER
. This shape is conditioning partly the performance of the plasma. Tokamaks, in particular, are axisymmetric devices, and therefore one can completely define the shape of the plasma by its cross-section
.
- the plasma elongation,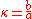 , where
, where  is the plasma minor radius, and
is the plasma minor radius, and  is the height of the plasma measured from the equatorial plane.
is the height of the plasma measured from the equatorial plane.
-the plasma triangularity, defined as the horizontal distance between the plasma major radius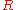 and the X point.
and the X point.
-the angle between the horizontal and the plasma last closed flux surface (LCFS) at the low field side.
-the angle between the horizontal and the plasma last closed flux surface (LCFS) at the high field side.
Magnetic confinement fusion
Magnetic confinement fusion is an approach to generating fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine the hot fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, the other being inertial confinement fusion. The magnetic approach is...
fusion plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
s such as those generated in tokamak
Tokamak
A tokamak is a device using a magnetic field to confine a plasma in the shape of a torus . Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that move around the torus in a helical shape...
s and stellarator
Stellarator
A stellarator is a device used to confine a hot plasma with magnetic fields in order to sustain a controlled nuclear fusion reaction. It is one of the earliest controlled fusion devices, first invented by Lyman Spitzer in 1950 and built the next year at what later became the Princeton Plasma...
s are characterized by a typical shape. Plasma shaping is the study of the plasma shape in such devices, and is particularly important for next step fusion devices such as ITER
ITER
ITER is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering project, which is currently building the world's largest and most advanced experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor at Cadarache in the south of France...
. This shape is conditioning partly the performance of the plasma. Tokamaks, in particular, are axisymmetric devices, and therefore one can completely define the shape of the plasma by its cross-section
Cross section (geometry)
In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
.
Cross-section
In the simple case of a plasma with up-down symmetry, the plasma cross-section is defined using a combination of four parameters:- the plasma elongation,
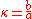 , where
, where  is the plasma minor radius, and
is the plasma minor radius, and  is the height of the plasma measured from the equatorial plane.
is the height of the plasma measured from the equatorial plane. -the plasma triangularity, defined as the horizontal distance between the plasma major radius
 and the X point.
and the X point. -the angle between the horizontal and the plasma last closed flux surface (LCFS) at the low field side.
-the angle between the horizontal and the plasma last closed flux surface (LCFS) at the high field side.

