
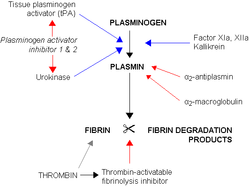
Plasminogen activator
Encyclopedia
Serine protease
Serine proteases are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins, in which serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the active site.They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes...
which converts plasminogen to plasmin, thus promoting fibrinolysis
Fibrinolysis
Fibrinolysis is a process that prevents blood clots from growing and becoming problematic. This process has two types: primary fibrinolysis and secondary fibrinolysis...
.
Types include:
- Tissue plasminogen activatorTissue plasminogen activatorTissue plasminogen activator is a protein involved in the breakdown of blood clots. It is a serine protease found on endothelial cells, the cells that line the blood vessels. As an enzyme, it catalyzes the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin, the major enzyme responsible for clot breakdown...
- UrokinaseUrokinaseUrokinase , also called urokinase-type plasminogen activator , is a serine protease . Urokinase was originally isolated from human urine, but is present in several physiological locations, such as blood stream and the extracellular matrix...
It is inhibited by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 also known as endothelial plasminogen activator inhibitor or serpin E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINE1 gene....
and plasminogen activator inhibitor-2
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-2
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 is a coagulation factor that inactivates tPA and urokinase. It is present in most cells, especially monocytes/macrophages...
.

