
Plastic Moment
Encyclopedia
The plastic moment is a property of a structural section. It is defined as the moment at which the entire cross section has reached its yield stress. This is theoretically the maximum bending moment that the section can resist - when this point is reached a plastic hinge
is formed and any load beyond this point will result in theoretically infinite plastic deformation. In practice most materials work harden resulting in increased stiffness and moment resistance until the material fails. This is of little significance in structural mechanics
as the deflection prior to this occurring is considered to be an earlier failure point in the member.
Mp for a rectangular section can be calculated with the following formula:
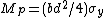
For other sections it is normal to calculate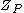 then substitute it into the formula as follows:
then substitute it into the formula as follows:
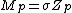
The plastic moment for a given section will always be larger than the yield moment (the bending moment at which the first part of the sections reaches the yield stress)
Plastic hinge
In structural engineering beam theory the term, plastic hinge, is used to describe the deformation of a section of a beam where plastic bending occurs...
is formed and any load beyond this point will result in theoretically infinite plastic deformation. In practice most materials work harden resulting in increased stiffness and moment resistance until the material fails. This is of little significance in structural mechanics
Structural mechanics
Structural mechanics or Mechanics of structures is the computation of deformations, deflections, and internal forces or stresses within structures, either for design or for performance evaluation of existing structures. It is one subset of structural analysis...
as the deflection prior to this occurring is considered to be an earlier failure point in the member.
Mp for a rectangular section can be calculated with the following formula:
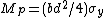
For other sections it is normal to calculate
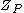 then substitute it into the formula as follows:
then substitute it into the formula as follows: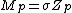
The plastic moment for a given section will always be larger than the yield moment (the bending moment at which the first part of the sections reaches the yield stress)

