
Plus-minus sign
Encyclopedia
The plus-minus sign is a mathematical symbol commonly used either
The sign is normally pronounced "plus or minus". In experimental sciences, the sign commonly indicates the confidence interval
or error
in a measurement, often the standard deviation
or standard error
. The sign may also represent an inclusive range of values that a reading might have. In mathematics, it may indicate two possible values: one positive, and one negative.
or its statistical margin of error
.
For example, "" denotes a quantity that is specified or estimated to be within 0.2 units of 5.7; it may be anywhere in the range from (i.e., 5.5) to (5.9). In scientific usage it sometimes refers to a probability of being within the stated interval, usually corresponding to either 1 or 2 standard deviation
s (a probability of 68.3% or 95.4% in a Normal distribution).
A percentage
may also be used to indicate the error margin. For example, refers to a voltage within 10% of either side of 230 V (207 V to 253 V). Separate values for the upper and lower bounds may also be used. For example, to indicate that a value is most likely 5.7 but may be as high as 5.9 or as low as 5.6, one could write .
For example, given the equation x2 = 1, one may give the solution as x = ±1, such that both x = +1 and x = −1 are valid solutions.
More generally we have the quadratic formula:
If ax2 + bx + c = 0 then
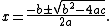
Written out in full, this states that there are two solutions to the equation, i.e. that
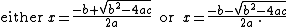
Another example is found in the trigonometric identity
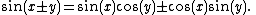
This stands for two identities: one with "+" on both sides of the equation, and one with "−" on both sides.
A somewhat different use is found in this presentation of the formula for the Taylor series
of the sine function:
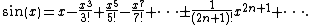
This mild abuse of notation
is intended to indicate that the signs of the terms alternate, where (starting the count at 0) the terms with an even index n are added while those with an odd index are subtracted. A more rigorous presentation would use the expression (−1)n, which gives +1 when n is even and −1 when n is odd.
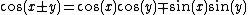
are most neatly written using the "" sign. The trigonometric equation above thus represents the two equations: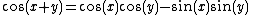
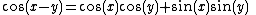
but never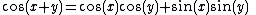
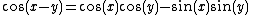
because the signs are exclusively alternating.
士, whereas the minus-plus sign resembles 干.
- to indicate the precisionAccuracy and precisionIn the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
of an approximationApproximationAn approximation is a representation of something that is not exact, but still close enough to be useful. Although approximation is most often applied to numbers, it is also frequently applied to such things as mathematical functions, shapes, and physical laws.Approximations may be used because...
, or - to indicate a value that can be of either sign.
The sign is normally pronounced "plus or minus". In experimental sciences, the sign commonly indicates the confidence interval
Confidence interval
In statistics, a confidence interval is a particular kind of interval estimate of a population parameter and is used to indicate the reliability of an estimate. It is an observed interval , in principle different from sample to sample, that frequently includes the parameter of interest, if the...
or error
Errors and residuals in statistics
In statistics and optimization, statistical errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of a sample from its "theoretical value"...
in a measurement, often the standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
or standard error
Standard error
Standard error can refer to:* Standard error , the estimated standard deviation or error of a series of measurements* Standard error stream, one of the standard streams in Unix-like operating systems...
. The sign may also represent an inclusive range of values that a reading might have. In mathematics, it may indicate two possible values: one positive, and one negative.
Precision indication
The use of for an approximation is most commonly encountered in presenting the numerical value of a quantity together with its toleranceTolerance (engineering)
Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in# a physical dimension,# a measured value or physical property of a material, manufactured object, system, or service,# other measured values ....
or its statistical margin of error
Margin of error
The margin of error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in a survey's results. The larger the margin of error, the less faith one should have that the poll's reported results are close to the "true" figures; that is, the figures for the whole population...
.
For example, "" denotes a quantity that is specified or estimated to be within 0.2 units of 5.7; it may be anywhere in the range from (i.e., 5.5) to (5.9). In scientific usage it sometimes refers to a probability of being within the stated interval, usually corresponding to either 1 or 2 standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
s (a probability of 68.3% or 95.4% in a Normal distribution).
A percentage
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100 . It is often denoted using the percent sign, “%”, or the abbreviation “pct”. For example, 45% is equal to 45/100, or 0.45.Percentages are used to express how large/small one quantity is, relative to another quantity...
may also be used to indicate the error margin. For example, refers to a voltage within 10% of either side of 230 V (207 V to 253 V). Separate values for the upper and lower bounds may also be used. For example, to indicate that a value is most likely 5.7 but may be as high as 5.9 or as low as 5.6, one could write .
Shorthand
In mathematical equations, the use of may be found as shorthand, to present two equations in one formula: + or −, represented with .For example, given the equation x2 = 1, one may give the solution as x = ±1, such that both x = +1 and x = −1 are valid solutions.
More generally we have the quadratic formula:
If ax2 + bx + c = 0 then
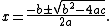
Written out in full, this states that there are two solutions to the equation, i.e. that
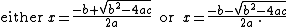
Another example is found in the trigonometric identity
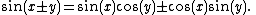
This stands for two identities: one with "+" on both sides of the equation, and one with "−" on both sides.
A somewhat different use is found in this presentation of the formula for the Taylor series
Taylor series
In mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
of the sine function:
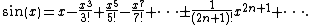
This mild abuse of notation
Abuse of notation
In mathematics, abuse of notation occurs when an author uses a mathematical notation in a way that is not formally correct but that seems likely to simplify the exposition or suggest the correct intuition . Abuse of notation should be contrasted with misuse of notation, which should be avoided...
is intended to indicate that the signs of the terms alternate, where (starting the count at 0) the terms with an even index n are added while those with an odd index are subtracted. A more rigorous presentation would use the expression (−1)n, which gives +1 when n is even and −1 when n is odd.
Minus-plus sign
There is another character, the minus-plus sign . It is generally used in conjunction with the "" sign, in such expressions as "x y z", which can be interpreted as meaning "x + y − z" or/and "x − y + z", but not "x + y + z" nor "x − y − z". The upper "−" in "" is considered to be associated to the "+" of "" (and similarly for the two lower symbols) even though there is no visual indication of the dependency. The original expression can be rewritten as "x (y − z)" to avoid confusion, but cases such as the trigonometric identity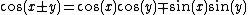
are most neatly written using the "" sign. The trigonometric equation above thus represents the two equations:
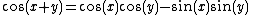
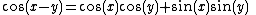
but never
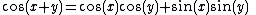
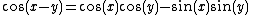
because the signs are exclusively alternating.
Other uses
and are used in chess notation to denote an advantage for white and black respectively.Encodings
- In ISO 8859-1, -7, -8, -9, -13, -15, and -16, the plus-minus symbol is given by the code 0xB1hexHexadecimalIn mathematics and computer science, hexadecimal is a positional numeral system with a radix, or base, of 16. It uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols 0–9 to represent values zero to nine, and A, B, C, D, E, F to represent values ten to fifteen...
Since the first 256 code points of Unicode are identical to the contents of ISO-8859-1 this symbol is also at UnicodeUnicodeUnicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
code point U+00B1. - The symbol also has a HTML entityCharacter entity referenceIn the markup languages SGML, HTML, XHTML and XML, a character entity reference is a reference to a particular kind of named entity that has been predefined or explicitly declared in a Document Type Definition . The "replacement text" of the entity consists of a single character from the Universal...
representation of±. - On WindowsMicrosoft WindowsMicrosoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
systems, it may be entered by means of Alt codes, by holding the ALT key while typing the numbers 0177 on the numeric keypadNumeric keypadA numeric keypad, numpad or tenkey for short, is the small, palm-sized, seventeen key section of a computer keyboard, usually on the very far right. The numeric keypad features digits 0 to 9, addition , subtraction , multiplication and division symbols, a decimal point and Num Lock and Enter keys...
. - On Unix-like systems, it can be entered by typing the sequence composeCompose keyA compose key, available on some computer keyboards, is a special kind of modifier key designated to signal the software to interpret the following sequence of two keystrokes as a combination in order to produce a character not found directly on the keyboard...
+ -. - On Macintosh systems, it may be entered by pressing option shift = (on the non-numeric keypad).
- The rarer minus-plus sign is not generally found in legacy encodings and does not have a named HTML entity but is available in Unicode with codepoint U+2213 and so can be used in HTML using
∓or∓. - In TeXTeXTeX is a typesetting system designed and mostly written by Donald Knuth and released in 1978. Within the typesetting system, its name is formatted as ....
'plus-or-minus' and 'minus-or-plus' symbols are denoted\pmand\mp, respectively. - These characters are also seen written as a (rather untidy) underlined or overlined + symbol. ( + or ).
Similar characters
The plus-minus sign resembles the Chinese characterChinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
士, whereas the minus-plus sign resembles 干.

