
Pneumonic plague
Encyclopedia
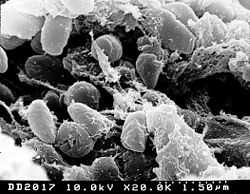
Yersinia pestis
Yersinia pestis is a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium. It is a facultative anaerobe that can infect humans and other animals....
. It is more virulent and rare than bubonic plague
Bubonic plague
Plague is a deadly infectious disease that is caused by the enterobacteria Yersinia pestis, named after the French-Swiss bacteriologist Alexandre Yersin. Primarily carried by rodents and spread to humans via fleas, the disease is notorious throughout history, due to the unrivaled scale of death...
. The difference between the versions of plague is simply the location of the infection in the body; the bubonic plague is an infection of the lymphatic system, the pneumonic plague is an infection of the respiratory system, and the septicemic plague is an infection in the blood stream.
Typically, pneumonic form is due to a secondary spread from advanced infection of an initial bubonic form. Primary pneumonic plague results from inhalation of fine infective droplets and can be transmitted from human to human without involvement of fleas or animals. Untreated pneumonic plague has a very high fatality rate.
Epidemiology
Since 2002, the World Health OrganizationWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) has reported six plague outbreaks, though some may go unreported because they often happen in remote areas. Between 1998 and 2009, nearly 24,000 cases have been reported, including about 2,000 deaths, in Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, the Americas and Eastern Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. 98% of the world's cases occur in Africa.
Pathology and transmission
Pneumonic plague can be caused in two ways: primary, which results from the inhalation of aerosolised plague bacteriaBacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, or secondary, when septicemic plague
Septicemic plague
Septicemic plague is a deadly blood infection, one of the three main forms of plague. It is caused by Yersinia pestis, a gram-negative bacterium....
spreads into lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
tissue from the bloodstream. Pneumonic plague is not exclusively vector-borne like bubonic plague; instead it can be spread from person to person. There have been cases of pneumonic plague resulting from the dissection or handling of contaminated animal tissue. This is one type of the formerly known Black Death
Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have...
. It could kill 90%–95% of a population if the victims coughed and passed on the bacteria.
Symptoms
The most apparent symptom of pneumonic plague is coughing, often with hemoptysisHemoptysis
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the expectoration of blood or of blood-stained sputum from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the expectoration (coughing up) of blood or of blood-stained sputum from the bronchi, larynx, trachea, or lungs Hemoptysis or haemoptysis ...
(coughing up blood). With pneumonic plague, the first signs of illness are fever, headache, weakness, and rapidly developing pneumonia with shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, and sometimes bloody or watery sputum. The pneumonia progresses for two to four days and may cause respiratory failure and shock. Patients will die without early treatment, some within 36 hours.
Initial pneumonic plague symptoms can often include:
- FeverFeverFever is a common medical sign characterized by an elevation of temperature above the normal range of due to an increase in the body temperature regulatory set-point. This increase in set-point triggers increased muscle tone and shivering.As a person's temperature increases, there is, in...
- WeaknessMuscle weaknessMuscle weakness or myasthenia is a lack of muscle strength. The causes are many and can be divided into conditions that have true or perceived muscle weakness...
- HeadacheHeadacheA headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
- NauseaNauseaNausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
Rapidly developing pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
with:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest painChest painChest pain may be a symptom of a number of serious conditions and is generally considered a medical emergency. Even though it may be determined that the pain is non-cardiac in origin, this is often a diagnosis of exclusion made after ruling out more serious causes of the pain.-Differential...
- CoughCoughA cough is a sudden and often repetitively occurring reflex which helps to clear the large breathing passages from secretions, irritants, foreign particles and microbes...
- Bloody or watery sputumSputumSputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways. It is usually used for microbiological investigations of respiratory infections....
(saliva and discharge from respiratory passages).
Prognosis and treatment
Pneumonic plague is a very aggressive infection requiring early treatment. Antibiotics must be given within 24 hours of first symptoms to reduce the risk of death,. StreptomycinStreptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic drug, the first of a class of drugs called aminoglycosides to be discovered, and was the first antibiotic remedy for tuberculosis. It is derived from the actinobacterium Streptomyces griseus. Streptomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic. Streptomycin cannot be given...
, gentamicin
Gentamicin
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic, used to treat many types of bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Gram-negative organisms. However, gentamicin is not used for Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis or Legionella pneumophila...
, tetracyclines
Tetracycline antibiotics
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotics whose general usefulness has been reduced with the onset of bacterial resistance. Despite this, they remain the treatment of choice for some specific indications....
, and chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic antimicrobial that became available in 1949. It is considered a prototypical broad-spectrum antibiotic, alongside the tetracyclines, and as it is both cheap and easy to manufacture it is frequently found as a drug of choice in the third world.Chloramphenicol is...
are all effective against pneumonic plague.
Antibiotic treatment for 7 days will protect people who have had direct, close contact with infected patients. Wearing a close-fitting surgical mask also protects against infection.
The mortality rate from untreated pneumonic plague approaches 100%.
China
The People's Republic of ChinaPeople's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
has eradicated the pneumonic plague from most parts of the country, but still reports occasional cases in remote Western
Western China
Western China , refers to the western part of China. In the definition of the Chinese government, Western China covers six provinces: Gansu, Guizhou, Qinghai, Shaanxi, Sichuan, and Yunnan; one municipality: Chongqing; and three autonomous regions: Ningxia, Tibet, and Xinjiang.-Administrative...
areas where the disease is carried by rat
Rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents of the superfamily Muroidea. "True rats" are members of the genus Rattus, the most important of which to humans are the black rat, Rattus rattus, and the brown rat, Rattus norvegicus...
s and the marmot
Marmot
The marmots are a genus, Marmota, of squirrels. There are 14 species in this genus.Marmots are generally large ground squirrels. Those most often referred to as marmots tend to live in mountainous areas such as the Alps, northern Apennines, Eurasian steppes, Carpathians, Tatras, and Pyrenees in...
s that live across the Himalayan plateau. Outbreaks can be caused when a person eats an infected marmot or comes into contact with fleas carried by rats. A 2006 WHO report from an international meeting on plague cited a Chinese government disease expert as saying that most cases of the plague in China's northwest occur when hunters are contaminated while skinning infected animals. The expert said at the time that due to the region's remoteness, the disease killed more than half the infected people. The report also said that since the 1990s, there was a rise in plague cases in humans—from fewer than 10 in the 1980s to nearly 100 cases in 1996 and 254 in 2000. Official statistics posted on the Chinese Health Ministry's Web site showed no cases of plague in 2007 and 2008. In September 2008, two persons in east Tibet died of pneumonic plague.
A recent outbreak of the disease in China began in August 2009 in Ziketan Town
Ziketan Town
Ziketan Town is a farming town in Xinghai County of Hainan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai province, People's Republic of China. Ziketan town covers approximately and has a population of 10,000....
located in Qinghai Province. The town was sealed off and several people died as a result of the disease. According to spokesperson Vivian Tan of the WHO office in Beijing
Beijing
Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's...
, "In cases like this [in August 2009], we encourage the authorities to identify cases, to investigate any suspicious symptoms among close contacts, and to treat confirmed cases as soon as possible. So far, they have done exactly that. There have been sporadic cases reported around the country in the last few years so the authorities do have the experience to deal with this."
In September 2010, there were 5 reported cases of pneumonic plague in Tibet.
Peru
Peru's health minister says an outbreak of plague has killed a 14-year-old boy and infected at least 31 people in a northern coastal province.Health Minister Oscar Ugarte says authorities are screening sugar and fish meal exports from Ascope province, located about 325 miles (520 km) northwest of Lima. Popular Chicama beach isn't far away.
Ugarte says the boy, who had Down syndrome, died of bubonic plague July 26, 2010.
He said August 1 that most of the infections are bubonic plague, with four cases of pneumonic plague. The former is transmitted by flea bites, the latter by airborne contagion. The disease is curable if treated early with antibiotics.
The first recorded plague outbreak in Peru was in 1903. The last, in 1994, killed 35 people.
Recent notable cases
On November 2, 2007, wildlife biologist Eric York died of pneumonic plague in Grand Canyon National Park. York was exposed to the bacteria while conducting a necropsy on a mountain lion carcass.In popular culture
Pneumonic plague has occasionally been depicted in popular culture. Elia Kazan'sElia Kazan
Elia Kazan was an American director and actor, described by the New York Times as "one of the most honored and influential directors in Broadway and Hollywood history". Born in Istanbul, the capital of the Ottoman Empire, to Greek parents originally from Kayseri in Anatolia, the family emigrated...
1950 film Panic in the Streets, starring Richard Widmark
Richard Widmark
Richard Weedt Widmark was an American film, stage and television actor.He was nominated for an Academy Award for his role as the villainous Tommy Udo in his debut film, Kiss of Death...
and Jack Palance
Jack Palance
Jack Palance , was an American actor. During half a century of film and television appearances, Palance was nominated for three Academy Awards, all as Best Actor in a Supporting Role, winning in 1991 for his role in City Slickers.-Early life:Palance, one of five children, was born Volodymyr...
, concerns an attempt by New Orleans health authorities to suppress an outbreak of pneumonic plague. An episode of "NCIS
NCIS (TV series)
NCIS, formerly known as NCIS: Naval Criminal Investigative Service, is an American police procedural drama television series revolving around a fictional team of special agents from the Naval Criminal Investigative Service, which conducts criminal investigations involving the U.S...
", entitled "SWAK", depicts Special Agent
Special agent
Special agent is usually the title for a detective or investigator for a state, county, municipal, federal or tribal government. An agent is a worker for any federal agency, and a secret agent is one who works for an intelligence agency....
Anthony DiNozzo
Anthony DiNozzo
Anthony "Tony" D. DiNozzo Jr. is a fictional character from the CBS TV series NCIS. He is portrayed by Michael Weatherly.-Background:Tony comes from a wealthy family from Long Island, New York. He is an only child, but has been cut off from his family's fortune. His mother, maiden name Paddington,...
becoming infected with the plague. In "Royal Pains
Royal Pains
Royal Pains is a USA Network television series that premiered on June 4, 2009, starring Mark Feuerstein, Paulo Costanzo, Jill Flint and Reshma Shetty. The series is based in part on actual concierge medicine practices of independent doctors and companies...
", Divya and her fiancee Raj are quarantined for it when their tango instructor is diagnosed with the illness. The film Cassandra Crossing
The Cassandra Crossing
The Cassandra Crossing is a 1976 British disaster film directed by George Pan Cosmatos and starring Richard Harris, Ava Gardner, Sophia Loren, Martin Sheen, Burt Lancaster, Lee Strasberg and O. J. Simpson.-Plot:...
involves a terrorist who is accidentally infected with the illness and subsequently infects nearly everyone aboard a train. In an episode of S.W.A.T.
S.W.A.T. (TV series)
----S.W.A.T. is a 1970s American television series about the adventures of the WCPD's Olympic Division Special Weapons And Tactics team operating in an unidentified California city....
, a man hired to kill a U.S. senator contracts the virus in New Delhi
New Delhi
New Delhi is the capital city of India. It serves as the centre of the Government of India and the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. New Delhi is situated within the metropolis of Delhi. It is one of the nine districts of Delhi Union Territory. The total area of the city is...
.
External links
- Facts about Pneumonic Plague. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

