
Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and polypeptide, whereas its two products
are UDP
and N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-polypeptide.
This enzyme belongs to the family of glycosyltransferase
s, specifically the hexosyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyl-transferase. Other names in common use include protein-UDP acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:kappa-casein polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, uridine diphosphoacetylgalactosamine-glycoprotein, acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, glycoprotein acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, polypeptide-N-acetylgalactosamine transferase, UDP-acetylgalactosamine-glycoprotein, acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-acetylgalactosamine:peptide-N-galactosaminyltransferase, UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine-glycoprotein, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine-protein N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, and UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:protein N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase. This enzyme participates in o-glycan biosynthesis and glycan structures - biosynthesis 1. It has 2 cofactors
: manganese
, and Calcium
.
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
accession codes , , , , and .
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine + polypeptide
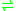 UDP + N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-polypeptide
UDP + N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-polypeptide
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine and polypeptide, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are UDP
Uridine diphosphate
Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.-See also:* Nucleoside...
and N-acetyl-D-galactosaminyl-polypeptide.
This enzyme belongs to the family of glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that act as a catalyst for the transfer of a monosaccharide unit from an activated nucleotide sugar to a glycosyl acceptor molecule, usually an alcohol....
s, specifically the hexosyltransferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyl-transferase. Other names in common use include protein-UDP acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:kappa-casein polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, uridine diphosphoacetylgalactosamine-glycoprotein, acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, glycoprotein acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, polypeptide-N-acetylgalactosamine transferase, UDP-acetylgalactosamine-glycoprotein, acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-acetylgalactosamine:peptide-N-galactosaminyltransferase, UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosamine:polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine-glycoprotein, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine-protein N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:polypeptide, N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, and UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine:protein N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferase. This enzyme participates in o-glycan biosynthesis and glycan structures - biosynthesis 1. It has 2 cofactors
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
: manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
, and Calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 5 structuresTertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank is a repository for the 3-D structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids....
accession codes , , , , and .

