
Polyunsaturated fat
Encyclopedia
In nutrition, polyunsaturated fat, or polyunsaturated fatty acid
, are fatty acids in which more than one carbon–carbon double bond
exists within the representative molecule
. That is, the molecule has two or more points on its structure capable of supporting hydrogen atoms not currently part of the structure. Polyunsaturated fatty acids can assume a cis or trans conformation
depending on the geometry of the double bond.
The lack of the extra hydrogen atoms on the molecule's surface typically reduces the strength of the compound's intermolecular force
s, thus causing the melting point
of the compound to be significantly lower. This property can be observed by comparing predominately unsaturated
vegetable oils, which remain liquid even at relatively low temperatures, to much more saturated
fats such as butter or lard
which are mainly solid at room temperature. Trans fat
s are more similar to saturated fat than are cis fats in many respects, including the fact that they solidify at a lower temperature than cis fats.
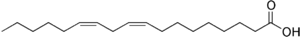
 A fatty acid has a carboxylic acid
A fatty acid has a carboxylic acid
at one end and a methyl group at the other end. Carbon
atoms in a fatty acid are identified by Greek letters
on the basis of their distance from the carboxylic acid. The carbon atom closest to the carboxylic acid is the alpha carbon, the next adjacent carbon is the beta carbon, etc. In a long-chain fatty acid the carbon atom in the methyl group is called the omega carbon because omega is the last letter of the Greek alphabet.
Omega-3 fatty acid
s have a double bond three carbons away from the methyl carbon, whereas omega-6 fatty acid
s have a double bond six carbons away from the methyl carbon. The illustration below shows the omega-6 fatty acid, linoleic acid
.
.. Omega-6 fatty acids in sunflower oil
and safflower oil may also reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Among n-3 fatty acids [Omega-3], neither long-chain nor short-chain forms were consistently associated with breast cancer risk. High levels of docosahexaenoic acid
(DHA), however, the most abundant n-3 PUFA [Omega-3] in erythrocyte (red blood cell
) membranes, were associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer. The DHA obtained through the consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids is positively associated with cognitive and behavioral performance. In addition DHA is vital for the grey matter structure of the human brain, as well as retinal stimulation and neurotransmission
.
Dietary intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids has been shown in several studies to decrease the risk of developing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
(ALS, a.k.a. Lou Gehrig
's Disease). Essential fatty acids (EFA) are shown to decrease the risk of depression
, hypertension
, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
There exist conflicting associations between dietary factors and incident atrial fibrillation
(AF). A 2010 study published in AJCN suggested that polyunsaturated fats were found to have no significant association with AF.
and retinal stimulation.
A study published in The Journal of Nutrition in 2007 found that the maternal diet of rats affects the brain DHA status of offspring. It suggests that a maternal diet containing insufficient amounts of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid
can lead to greater risk of decreased accretion of brain DHA in offspring.
At least one study in mice has shown that consuming high amounts of polyunsaturated fat (but not monounsaturated fat) may increase the risk of metastasis in cancer patients. The researchers found that linoleic acid in polyunsaturated fats produced increasing membrane phase separation, and thereby increased adherence of circulating tumor cell
s to blood vessel walls and remote organs. According to the report 'The new findings support earlier evidence from other research that consuming high amounts of polyunsaturated fat may increase the risk of cancer spreading'.The propensity for polyunsaturated fats to oxidize is another possible risk factor. This leads to the generation of free radicals
and eventually to rancidity
. Studies have shown that low dosages of Coenzyme Q10 reduce this oxidation, and a combination of a diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids and Coenzyme Q10 supplementation leads to a longer lifespan in rats. Studies on animals have shown a link between polyunsaturated fat and the incidence of tumours. In some of these studies the incidence of tumours increased with increasing intake of polyunsaturated fat, up to about 5% of total energy, near to the middle of the current dietary intake in humans. It is advised that the level of polyunsaturated fats in the diet be regulated if Coenzyme Q10 supplements are not being taken. However, even without Coenzyme Q10 supplementation, the effect on health might be considered by some to be more beneficial than harmful, due to the supposed cholesterol lowering effects of unsaturated fats compared to saturated fats; however, (a) monounsaturated fats have also been posited to lead to lower cholesterol levels; (and (b) it is no longer clear that saturated fats actually cause elevated blood cholesterol levels.
10% of a person’s daily caloric intake should be consumed from polyunsaturated fats.
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids that contain more than one double bond in their backbone. This class includes many important compounds, such as essential fatty acids and those that give drying oils their characteristic property....
, are fatty acids in which more than one carbon–carbon double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
exists within the representative molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
. That is, the molecule has two or more points on its structure capable of supporting hydrogen atoms not currently part of the structure. Polyunsaturated fatty acids can assume a cis or trans conformation
Conformational isomerism
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted exclusively by rotations about formally single bonds...
depending on the geometry of the double bond.
The lack of the extra hydrogen atoms on the molecule's surface typically reduces the strength of the compound's intermolecular force
Intermolecular force
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles: atoms, molecules or ions. They are weak compared to the intramolecular forces, the forces which keep a molecule together...
s, thus causing the melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
of the compound to be significantly lower. This property can be observed by comparing predominately unsaturated
Saturated fat
Saturated fat is fat that consists of triglycerides containing only saturated fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between the individual carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain. That is, the chain of carbon atoms is fully "saturated" with hydrogen atoms...
vegetable oils, which remain liquid even at relatively low temperatures, to much more saturated
Saturated fat
Saturated fat is fat that consists of triglycerides containing only saturated fatty acids. Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between the individual carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain. That is, the chain of carbon atoms is fully "saturated" with hydrogen atoms...
fats such as butter or lard
Lard
Lard is pig fat in both its rendered and unrendered forms. Lard was commonly used in many cuisines as a cooking fat or shortening, or as a spread similar to butter. Its use in contemporary cuisine has diminished because of health concerns posed by its saturated-fat content and its often negative...
which are mainly solid at room temperature. Trans fat
Trans fat
Trans fat is the common name for unsaturated fat with trans-isomer fatty acid. Because the term refers to the configuration of a double carbon-carbon bond, trans fats are sometimes monounsaturated or polyunsaturated, but never saturated....
s are more similar to saturated fat than are cis fats in many respects, including the fact that they solidify at a lower temperature than cis fats.


Carboxylic acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group...
at one end and a methyl group at the other end. Carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
atoms in a fatty acid are identified by Greek letters
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
on the basis of their distance from the carboxylic acid. The carbon atom closest to the carboxylic acid is the alpha carbon, the next adjacent carbon is the beta carbon, etc. In a long-chain fatty acid the carbon atom in the methyl group is called the omega carbon because omega is the last letter of the Greek alphabet.
Omega-3 fatty acid
Omega-3 fatty acid
N−3 fatty acids are essential unsaturated fatty acids with a double bond starting after the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain....
s have a double bond three carbons away from the methyl carbon, whereas omega-6 fatty acid
Omega-6 fatty acid
n−6 fatty acids are a family of unsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the n−6 position, that is, the sixth bond, counting from the methyl end.The biological effects of the n−6 fatty acids are largely mediated by their conversion to n-6 eicosanoids...
s have a double bond six carbons away from the methyl carbon. The illustration below shows the omega-6 fatty acid, linoleic acid
Linoleic acid
Linoleic acid is an unsaturated n-6 fatty acid. It is a colorless liquid at room temperature. In physiological literature, it has a lipid number of 18:2...
.
Dietary Sources
Polyunsaturated fat can be found mostly in Nuts, Seeds, Fish, Algae, Leafy Greens, and Krill. Whole food sources are always best, as processing and heating may damage polyunsaturated fats.Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids in algal oil, fish oil, fish and seafood have been shown to lower the risk of heart attacksMyocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
.. Omega-6 fatty acids in sunflower oil
Sunflower oil
Sunflower oil is the non-volatile oil expressed from sunflower seeds. Sunflower oil is commonly used in food as a frying oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient. Sunflower oil was first industrially produced in 1835 in the Russian Empire.- Composition :Sunflower oil is mainly a...
and safflower oil may also reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Among n-3 fatty acids [Omega-3], neither long-chain nor short-chain forms were consistently associated with breast cancer risk. High levels of docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain and retina. In chemical structure, DHA is a carboxylic acid with a 22-carbon chain and six cis double bonds; the first double bond is located at the third carbon from the omega end...
(DHA), however, the most abundant n-3 PUFA [Omega-3] in erythrocyte (red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
) membranes, were associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer. The DHA obtained through the consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids is positively associated with cognitive and behavioral performance. In addition DHA is vital for the grey matter structure of the human brain, as well as retinal stimulation and neurotransmission
Neurotransmission
Neurotransmission , also called synaptic transmission, is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by a neuron , and bind to and activate the receptors of another neuron...
.
Dietary intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids has been shown in several studies to decrease the risk of developing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
(ALS, a.k.a. Lou Gehrig
Lou Gehrig
Henry Louis "Lou" Gehrig , nicknamed "The Iron Horse" for his durability, was an American Major League Baseball first baseman. He played his entire 17-year baseball career for the New York Yankees . Gehrig set several major league records. He holds the record for most career grand slams...
's Disease). Essential fatty acids (EFA) are shown to decrease the risk of depression
Clinical depression
Major depressive disorder is a mental disorder characterized by an all-encompassing low mood accompanied by low self-esteem, and by loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities...
, hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
There exist conflicting associations between dietary factors and incident atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia . It is a common cause of irregular heart beat, identified clinically by taking a pulse. Chaotic electrical activity in the two upper chambers of the heart result in the muscle fibrillating , instead of achieving coordinated contraction...
(AF). A 2010 study published in AJCN suggested that polyunsaturated fats were found to have no significant association with AF.
Consumption during pregnancy
Consumption of omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy is critical to fetal development. They are required during the prenatal period for the formation of synapses and cell membranes. These processes are also essential in postnatal human development for injury response of the central nervous systemCentral nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
and retinal stimulation.
A study published in The Journal of Nutrition in 2007 found that the maternal diet of rats affects the brain DHA status of offspring. It suggests that a maternal diet containing insufficient amounts of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids that contain more than one double bond in their backbone. This class includes many important compounds, such as essential fatty acids and those that give drying oils their characteristic property....
can lead to greater risk of decreased accretion of brain DHA in offspring.
Relation to cancer
A 2010 study of 3,081 women suffering from breast cancer was done to research the effects of polyunsaturated fats on breast cancer. It demonstrated that the consumption of high amounts of long chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fats from food produced a 25% reduced risk of additional breast cancer events. These women were also shown to have reduced risk of “all-cause mortality.” Consumption of polyunsaturated fats through fish oil supplements was not shown to decrease risk of recurring breast cancer events.At least one study in mice has shown that consuming high amounts of polyunsaturated fat (but not monounsaturated fat) may increase the risk of metastasis in cancer patients. The researchers found that linoleic acid in polyunsaturated fats produced increasing membrane phase separation, and thereby increased adherence of circulating tumor cell
Circulating Tumor Cell
Circulating tumor cells are cells that have detached from a primary tumor and circulate in the bloodstream. CTCs may constitute seeds for subsequent growth of additional tumors in different tissues....
s to blood vessel walls and remote organs. According to the report 'The new findings support earlier evidence from other research that consuming high amounts of polyunsaturated fat may increase the risk of cancer spreading'.The propensity for polyunsaturated fats to oxidize is another possible risk factor. This leads to the generation of free radicals
Radical (chemistry)
Radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons on an open shell configuration. Free radicals may have positive, negative, or zero charge...
and eventually to rancidity
Rancidification
Rancidification is the chemical decomposition of fats, oils and other lipids . When these processes occur in food, undesirable odors and flavors can result. In some cases, however, the flavors can be desirable . In processed meats, these flavors are collectively known as "warmed over flavor"...
. Studies have shown that low dosages of Coenzyme Q10 reduce this oxidation, and a combination of a diet rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids and Coenzyme Q10 supplementation leads to a longer lifespan in rats. Studies on animals have shown a link between polyunsaturated fat and the incidence of tumours. In some of these studies the incidence of tumours increased with increasing intake of polyunsaturated fat, up to about 5% of total energy, near to the middle of the current dietary intake in humans. It is advised that the level of polyunsaturated fats in the diet be regulated if Coenzyme Q10 supplements are not being taken. However, even without Coenzyme Q10 supplementation, the effect on health might be considered by some to be more beneficial than harmful, due to the supposed cholesterol lowering effects of unsaturated fats compared to saturated fats; however, (a) monounsaturated fats have also been posited to lead to lower cholesterol levels; (and (b) it is no longer clear that saturated fats actually cause elevated blood cholesterol levels.
Food sources of polyunsaturated fat
| Food source (100g) | Polyunsaturated fat (g) |
|---|---|
| Walnuts | 47 |
| Sunflower Seeds | 33 |
| Sesame Seeds | 26 |
| Unsalted Peanuts | 16 |
| Peanut Butter | 14.2 |
| Olive Oil | 11 |
| Seaweed | 11 |
| Sardines | 5 |
| Soybeans | 5 |
| Tuna | 3 |
| Wild Salmon | 2.5 |
| Whole Grain Wheat | 0.8 |
10% of a person’s daily caloric intake should be consumed from polyunsaturated fats.
See also
- Monounsaturated fatMonounsaturated fatIn biochemistry and nutrition, monounsaturated fats or MUFA are fatty acids that have one double bond in the fatty acid chain and all of the remainder of the carbon atoms in the chain are single-bonded...
- For listings of particular classes, see
- Polyunsaturated fatty acidPolyunsaturated fatty acidPolyunsaturated fatty acids are fatty acids that contain more than one double bond in their backbone. This class includes many important compounds, such as essential fatty acids and those that give drying oils their characteristic property....
- Omega-3 fatty acidOmega-3 fatty acidN−3 fatty acids are essential unsaturated fatty acids with a double bond starting after the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain....
- Omega-6 fatty acidOmega-6 fatty acidn−6 fatty acids are a family of unsaturated fatty acids that have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the n−6 position, that is, the sixth bond, counting from the methyl end.The biological effects of the n−6 fatty acids are largely mediated by their conversion to n-6 eicosanoids...
- Omega-9 fatty acidOmega-9 fatty acidn−9 fatty acids are a family of unsaturated fatty acids which have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the n−9 position; that is, the ninth bond from the end of the fatty acid.-Background:Some n−9s are common components of animal fat and vegetable oil...
- Conjugated linoleic acidConjugated linoleic acidConjugated linoleic acids are a family of at least 28 isomers of linoleic acid found mainly in the meat and dairy products derived from ruminants. As the name implies, the double bonds of CLAs are conjugated, with only one single bond between them....
- Polyunsaturated fatty acid
- Essential fatty acidEssential fatty acidEssential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them...
– for biochemistry of most polyunsaturated fats - Essential fatty acid interactionsEssential fatty acid interactionsThe actions of the ω-3 and ω-6 essential fatty acids are best characterized by their interactions; they cannot be understood separately.Arachidonic acid is a 20-carbon ω-6 conditionally essential fatty acid...
– for the interactions between ω-6 and ω-3 fatty acids - Unsaturated fatUnsaturated fatAn unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fat molecule is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double bond. Where double bonds are formed, hydrogen atoms are...

