
Pondage
Encyclopedia
Pondage usually refers to the comparably small water storage behind the weir
of a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power plant. It is considerably less storage than the reservoirs of large dams and conventional hydroelectric stations which can store water for long periods such as a dry season or year. It is usually stored during periods of low electricity demand and days when the power plant is inactive, enabling its use as a peaking power plant
in dry seasons and a base load power plant
during wet seasons. Ample pondage allows a power plant meet hourly load fluctuations
for a period of a week or more.
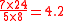
24-hour inflows and plant operation would have a pondage factor of one.
If power is used for twelve hours per day and during the inactive hours, relatively all inflows can be stored, then power can be doubled during active hours. In 12 hours there are 43,200 seconds and in 1 acre.ft there are 43560 ft3. This gives an estimation and guide that for twelve hours of pondage, there must be as much storage available in the pond as cubic feet per section received.
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
of a run-of-the-river hydroelectric power plant. It is considerably less storage than the reservoirs of large dams and conventional hydroelectric stations which can store water for long periods such as a dry season or year. It is usually stored during periods of low electricity demand and days when the power plant is inactive, enabling its use as a peaking power plant
Peaking power plant
Peaking power plants, also known as peaker plants, and occasionally just "peakers," are power plants that generally run only when there is a high demand, known as peak demand, for electricity.-Peak hours:...
in dry seasons and a base load power plant
Base load power plant
Baseload is the minimum amount of power that a utility or distribution company must make available to its customers, or the amount of power required to meet minimum demands based on reasonable expectations of customer requirements...
during wet seasons. Ample pondage allows a power plant meet hourly load fluctuations
Load balancing (electrical power)
Load balancing refers to the use of various techniques by electrical power stations to store excess electrical power during low demand periods for release as demand rises....
for a period of a week or more.
Calculation
Because of the possibility of limited pondage, calculating its effect on power generation is important in determining how often the plant can be operated. The pondage factor is a rough index of the amount pondage needed when the stream flow is constant and the plant is operational during specific periods. It is calculated by the ratio of total inflow hours per week to the hours the power plant will be operated in that same period. For example, if a river has an inflow for seven days a week and the plant operates for five of those days for eight hours: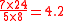
24-hour inflows and plant operation would have a pondage factor of one.
If power is used for twelve hours per day and during the inactive hours, relatively all inflows can be stored, then power can be doubled during active hours. In 12 hours there are 43,200 seconds and in 1 acre.ft there are 43560 ft3. This gives an estimation and guide that for twelve hours of pondage, there must be as much storage available in the pond as cubic feet per section received.

