
Potential Determining Ion
Encyclopedia
In a colloid
al dispersed system, ion
dissolution arises, where the dispersed particles exist in equilibrium with their saturated counterpart, i.e.

The behavior of this system is characterised by the components activity coefficient
s and solubility product, i.e.
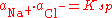
The ability of an ion to preferentially dissolve (as a result of unequal activities) over its counterion is classified as the Potential Determining Ion. This in turn results in the remaining particle possessing either a net positive/negative surface charge.One way in which surface charge can develop is by adsorption of an ion where the solid acts as an electrode. (e.g., H+ and OH− on the surfaces of clays).
In clay-aqueous systems the potential of the surface is determined by the activity of ions which react with the mineral surface. Frequently this is the hydrogen ion
H+ in which case the pertinent activity is determined by the pH
.
The simultaneous adsorption of protons and hydroxyls as well as other potential determining cations and anions, leads to the concept of zero point of charge or ZPC, where the total charge from the cations and anions at the surface is equal to zero.
The charge must be zero and this does not necessarily mean the number of cations versus anions in the solution are equal. For clay minerals the potential determining ions are H+ and OH− and complex ions formed by bonding with H+ and OH−.
Colloid
A colloid is a substance microscopically dispersed evenly throughout another substance.A colloidal system consists of two separate phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase . A colloidal system may be solid, liquid, or gaseous.Many familiar substances are colloids, as shown in the chart below...
al dispersed system, ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
dissolution arises, where the dispersed particles exist in equilibrium with their saturated counterpart, i.e.

The behavior of this system is characterised by the components activity coefficient
Activity coefficient
An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed...
s and solubility product, i.e.
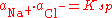
The ability of an ion to preferentially dissolve (as a result of unequal activities) over its counterion is classified as the Potential Determining Ion. This in turn results in the remaining particle possessing either a net positive/negative surface charge.One way in which surface charge can develop is by adsorption of an ion where the solid acts as an electrode. (e.g., H+ and OH− on the surfaces of clays).
In clay-aqueous systems the potential of the surface is determined by the activity of ions which react with the mineral surface. Frequently this is the hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion
Hydrogen ion is recommended by IUPAC as a general term for all ions of hydrogen and its isotopes.Depending on the charge of the ion, two different classes can be distinguished: positively charged ions and negatively charged ions....
H+ in which case the pertinent activity is determined by the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
.
The simultaneous adsorption of protons and hydroxyls as well as other potential determining cations and anions, leads to the concept of zero point of charge or ZPC, where the total charge from the cations and anions at the surface is equal to zero.
The charge must be zero and this does not necessarily mean the number of cations versus anions in the solution are equal. For clay minerals the potential determining ions are H+ and OH− and complex ions formed by bonding with H+ and OH−.

