
Poynting effect
Encyclopedia
The Poynting effect may refer to two unrelated physical phenomena. Neither should be confused with the Poynting–Robertson effect. All of these effects are named after John Henry Poynting
, an English physicist.
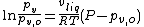
where
As a common example, the ability to combine nitrous oxide
and oxygen
at high pressure
while remaining in the gaseous form is due to the Poynting effect.
Entonox
is a 50:50 combination of the anesthetic gas nitrous oxide
and oxygen
. This combination is useful because it can provide a sufficient concentration of nitrous oxide to provide analgesia (pain relief) in sufficient oxygen so that the risk of hypoxemia
is eliminated. This makes it safe to use by para-medical staff such as ambulance officers. However the ability to combine these two gases at the temperature and pressure in the cylinder while remaining in the gaseous form is unexpected based on the known properties of the two gases.
The Poynting effect involves the dissolution of gaseous O2 when bubbled through liquid N2O, with vaporisation of the liquid to form a gaseous O2/N2O mixture.
John Henry Poynting
John Henry Poynting was an English physicist. He was a professor of physics at Mason Science College from 1880 until his death....
, an English physicist.
Chemistry / Thermodynamics
The Poynting effect generally refers to the change in the vapor pressure of a liquid when a non-condensable gas in mixed with the vapor at saturated conditions. If one assumes that the vapor and the non-condensable gas behave as ideal gases and an ideal mixture, it can be shown that :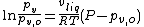
where
- pv is the modified vapor pressure
- pv,o is the unmodified vapor pressure
- vliq is the liquid specific volume
- R is the liquid/vapor's gas constant
- T is the temperature
- P is the total pressure (vapor pressure + non-condensable gas)
As a common example, the ability to combine nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
at high pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
while remaining in the gaseous form is due to the Poynting effect.
Entonox
Entonox
A mix of nitrous oxide 50% and oxygen 50% is a medical anaesthesia gas, commonly known as Entonox or Nitronox, or colloquially as gas and air, and is frequently used in pre-hospital care, childbirth and emergency medicine situations by medical professionals such as doctors, nurses, midwives and...
is a 50:50 combination of the anesthetic gas nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or sweet air, is a chemical compound with the formula . It is an oxide of nitrogen. At room temperature, it is a colorless non-flammable gas, with a slightly sweet odor and taste. It is used in surgery and dentistry for its anesthetic and analgesic...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. This combination is useful because it can provide a sufficient concentration of nitrous oxide to provide analgesia (pain relief) in sufficient oxygen so that the risk of hypoxemia
Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is generally defined as decreased partial pressure of oxygen in blood, sometimes specifically as less than or causing hemoglobin oxygen saturation of less than 90%.-Distinction from anemia and hypoxia:...
is eliminated. This makes it safe to use by para-medical staff such as ambulance officers. However the ability to combine these two gases at the temperature and pressure in the cylinder while remaining in the gaseous form is unexpected based on the known properties of the two gases.
The Poynting effect involves the dissolution of gaseous O2 when bubbled through liquid N2O, with vaporisation of the liquid to form a gaseous O2/N2O mixture.

