
Praxis intervention
Encyclopedia
Praxis Intervention is a form of participatory action research
. Where other forms of participatory action research emphasize the collective modification of the external world, the praxis intervention model emphasizes working on the Praxis potential (phronesis
) of its participants . "Praxis Potential" means the 'members' potential to reflexively work on their respective 'mentalities'; by 'participant' it is not just meant the clientele beneficiaries of the praxis intervention project alone, but also the organizers and experts participating in such a project. The praxis intervention aims at leading its members through a "participant objectivation". The praxis intervention method prioritizes unsettling the settled mentalities, especially where the settled mindsets prevalent in the social world or individuals is suspected to have sustained or contributed to their suffering or marginality http://www.sef.org.pk/educatewebsite/educate2fol/glosiconedu2.asp.
To state it as it is explained by , moments of praxis include creativity instead of sameness, autonomy instead of subordination, sociality instead of massification, rationality instead of blind reaction and intentionality rather than compliance.
Praxis Intervention helps respondents to come out with answers which they would not have otherwise expressed. Questionnaire based surveys, formal interviews, and even focus group discussions are not useful to help respondents to come out with genuine answers to the questions posed at them. Praxis Intervention as it helps groups of people probing their own conditions phase by phase through prolonged discussions, experiments and conscious explorations is capable of coming out with better quality data that could be useful for the group to challenge existing epistemic structures and work out their own well being.
Praxis intervention is useful wherever reflexivity
is a major component in a research project.
is carried out but also it is intervention on the praxis intervention practitioners habitus. In this respect the practice of praxis intervention is also a systematic participant objectivation.
Participatory objectivation is ‘objectifying the act of objectification.’ By ‘objectifying the objectification’ it is meant the researcher, while observing and objectifying, taking a similar critical distance towards the objectification itself. It is being sensitive to the immensely possible biases from the researcher’s social coordinates, field and intellectual orientation and self-critically problematising them to reduce the impact of the biases .
According to Bourdieu, within the sociological analysis, the participant objectivation is the essential but difficult exercise of all because it requires the break with the deepest and most conscious adherence and adhesions, those quite often give the object its very interest for those who study it- i.e., everything about their relation to the object they try to know that they least want to know . It is through the participant objectivation the practical relation to practice is substituted with the observer’s relation to practice . Through the practice of participant objectivation, Bourdieu aims to make the critical and political activity of social research the ‘solvent of doxa.
Though the practice of reflexive participant objectivation, the practitioner re-looks the taken for granted assumptions in order to wake up from her epistemic sleep and helps her clients too to help them to wake up from theirs.
In practice it involves the clientele and the researchers collectively probing into a problem that affects the clientele and helping the clientele to find solutions to their problem through reflexive probing with the experts belonging to relevant fields. The project aims at the clientele and the researchers work together and collectively learn from each other.
Praxis Intervention can be carried out in phased manner. The first phase could involve orienting the clientele (and experts as well) of the problem under focus. The problem under focus could be anything like existing status of marginality, gender relation, health condition or status of present technology etc. Once the problem could properly be oriented from as much angles as possible the clientele , experts and others could involve discussing appropriate method to probe the issue under discussion. They could also decide on the phases through which the collective probing to be undertaken. The second phase could be clientele exploring the issue themselves through the methods collectively agreed. They could maintain a journal to record their experiences and reflexive probing. The third phase could be the clientele coming together with experts and sharing their experience with their fellow clients and experts. After discussing all the observations and experiences the method of enquiry can be further fine-tuned for better understanding. Gradually the clientele could be guided to intervene on the issue concerned and document their experience. Their action and reflexion could be discussed and fine tuned for further interventions. The phases and intervention strategies could be decided as it could be appropriate for different problems.
Praxis intervention method focuses on what happens to mindsets. In the community work situation it could be a project helping the community participants to undertake a systematic research on themselves in the areas such as history of their social relationships, land ownership patterns, critically exploring gender relations, studying the ecological changes happening in their habitat, learning historically and comparatively on their health status, nutrition status etc. The research undertook by the local residents can be converted into social actions or welfare projects.
The practice of praxis intervention can be used in many fields such as post positivist research, social work research, participatory action research
, Local history research, Social action and social work projects, Clinical health research, Community Health research Projects, Participatory technology development
projects, and many other projects where people's participation and their critical reflexivity is crucial.
The method can be used in the field of education
. Educational process can be re constituted in accordance to the learning capabilities of the sets of students. Students going under the process of praxis intervention would listen to the expert opinions and explanations of the phenomenon under discussion and they would carry out experiments in the laboratory or in appropriate practical field relevant to the phenomenon under focus individually, collectively and collaboratively as they are guided by the expert teachers. They would bring back the results of experiments to the classroom setting and clarify with each other and also with the expert teachers. In this process syllabus can be indicative negotiable taking into consideration of the advancement of knowledge creation. In this process knowledge becomes creative appropriation rather than indoctrination.This may help students to gain great quantity of quality knowledge within short periods of time. The method could be effectively used in pre-primary to Higher schools of education.The method could be used in development of professional skills such as engineering, medicine, nursing, law, agricultural science, social work, management
, career guidance, expertise development, teaching and other such fields.
For instance, students of various technology oriented courses can be guided to develop and enhance technology by going under a praxis intervention experiment with users, experts and other relevant stakeholders. This could be appropriate for development and promotion of free software
.
Similarly praxis intervention can be used in helping patients to undergo a participatory diagnostic and experience sharing research with the medical professionals and other experts on their health conditions and take necessary action. Group of Patients suffering from similar diseases, their family members, and their significant others, medical practitioners and relevant experts can sit together and be guided through informed dialogue, systematic corrective measures, and experience sharing. . In this process both the facilitating professionals and the patients can overcome their respective personal and professional bias.
The Praxis Intervention method could be extended to the professional social work
practice in facilitating the social workers themselves and their clients overcoming personal or social mindsets that induce suffering or marginality. The praxis mode of social work depends on the sensibility that could be provoked in a given context: sensible towards one’s own biography, historical locatedness, spatial positioning and the interaction setting. The praxis intervention practice has its implications for social work education. A social work education based on praxis model could shape the students and teachers self-reflexive, sensible. Through this method, it may be possible for students gaining theoretical and practical skills. The method can be used in other branches of education and training like the management education, medical education, agriculture extension and other fields where the clientele really matter. However, the praxis model would be yielding better results if sufficient flexibility is maintained. It could be a model for providing companionship to people in need of self-exploration. Praxis intervention as a practice can be carried on to the extent it is possible for people to take care of themselves and to the extent people require professional companionship of the social work practice. Praxis intervention practice requires the professionals and the client participants to be self-reflexive and self-critical. The model provides opportunity for the social worker to undertake a reflexive inward journey to get rid of biases that affect her practice. The context that is not suitable for self-reflexivity or self-criticism is not suitable for praxis intervention practice either.
The praxis practice could also be extended to social work practice in the medical setting, AIDS care, psychiatric social work, management of juvenile delinquency, school social work, correctional administration practices in prison social work, gender related social work practice, geriatric social work, etc.
 The method could be fruitful in working with the marginalized people as marginalisation is usually a historical phenomenon. This would avoid people losing self-respect and dignity under the conditions of marginalisation. The method could be applied in other conditions of marginalisation such as working with people discriminated on the basis of gender. It can also serve as a model for opportunity scanning. The praxis intervention can be used as a method to initiate and implement participatory project provided the project has sufficient flexibility inbuilt for effecting a change from its pre-designs. A project management from praxis perspective should not have full-fledged blue print before hand, rather the projects should be flexible enough to wait till the participants themselves research and come out with a project plan. In the new practice, the experts could be facilitated to work with the participants. While a project is designed and carried out with this method, there should be options to change the course of project or even to suspend some projects according to the collective findings and evaluations of the collaborative research. Similarly the praxis method could be used in the planning process provided sufficient flexibility is allowed and reflexivity is tolerated. It has to be further tested whether the model works with socially, economically, and culturally heterogeneous set of people.
The method could be fruitful in working with the marginalized people as marginalisation is usually a historical phenomenon. This would avoid people losing self-respect and dignity under the conditions of marginalisation. The method could be applied in other conditions of marginalisation such as working with people discriminated on the basis of gender. It can also serve as a model for opportunity scanning. The praxis intervention can be used as a method to initiate and implement participatory project provided the project has sufficient flexibility inbuilt for effecting a change from its pre-designs. A project management from praxis perspective should not have full-fledged blue print before hand, rather the projects should be flexible enough to wait till the participants themselves research and come out with a project plan. In the new practice, the experts could be facilitated to work with the participants. While a project is designed and carried out with this method, there should be options to change the course of project or even to suspend some projects according to the collective findings and evaluations of the collaborative research. Similarly the praxis method could be used in the planning process provided sufficient flexibility is allowed and reflexivity is tolerated. It has to be further tested whether the model works with socially, economically, and culturally heterogeneous set of people.
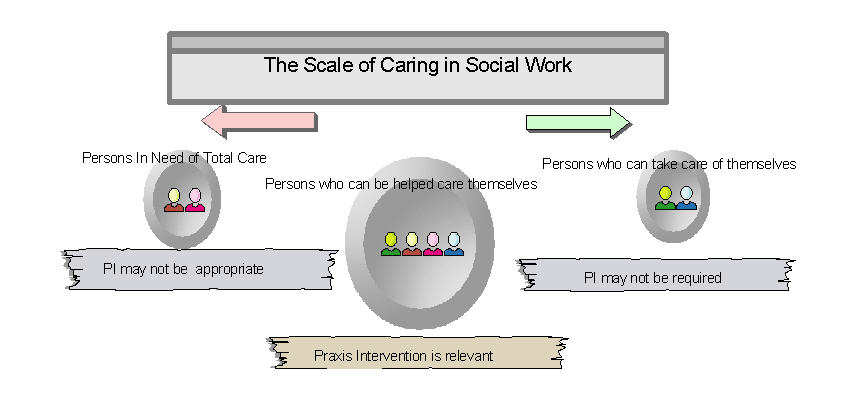
The praxis intervention model of social intervention may not be applicable in all contexts. There are sections of people who cannot take care of themselves and hence require absolute external care. For example, persons suffering from progressive, irreversible diseases characterised by degeneration of the brain cells such as Alzheimer’s disease would require complete external care. The praxis practice would be inappropriate for the people who do not need care. The approach could be helpful in accompanying people who can be helped to care for themselves. Praxis intervention practice is appropriate for working with the people who can be helped to care themselves with in a scale of caring.
We also witness from the current literature that the method is used in development of bottom-up organizational ethics, generating participatory forms of art and music and also in transformative nursing
practices.
Participatory action research
Participatory action research – or action research – is a recognized form of experimental research that focuses on the effects of the researcher's direct actions of practice within a participatory community with the goal of improving the performance quality of the community or an area of...
. Where other forms of participatory action research emphasize the collective modification of the external world, the praxis intervention model emphasizes working on the Praxis potential (phronesis
Phronesis
Phronēsis is an Ancient Greek word for wisdom or intelligence which is a common topic of discussion in philosophy. In Aristotelian Ethics, for example in the Nicomachean Ethics it is distinguished from other words for wisdom as the virtue of practical thought, and is usually translated "practical...
) of its participants . "Praxis Potential" means the 'members' potential to reflexively work on their respective 'mentalities'; by 'participant' it is not just meant the clientele beneficiaries of the praxis intervention project alone, but also the organizers and experts participating in such a project. The praxis intervention aims at leading its members through a "participant objectivation". The praxis intervention method prioritizes unsettling the settled mentalities, especially where the settled mindsets prevalent in the social world or individuals is suspected to have sustained or contributed to their suffering or marginality http://www.sef.org.pk/educatewebsite/educate2fol/glosiconedu2.asp.
Reflexive and routine praxis
Praxis is conceptualized in its reflexive as well as non-reflexive variety in Marx . The reflexive praxis is understood as the moment in the dialectic change, and the non-reflexive one as the routinising mechanism operating within the ideologies as a reproductive or status quo maintaining. It is, for Marx, the non-reflexive habituating praxis, which leads to False consciousness and alienation.To state it as it is explained by , moments of praxis include creativity instead of sameness, autonomy instead of subordination, sociality instead of massification, rationality instead of blind reaction and intentionality rather than compliance.
Reasons for praxis intervention
Praxis Intervention makes research, creative expression or technology development into a bottom up process. It democratizes making of art, science, technology and critical conscience. The Praxis intervention method aims at provoking members to unsettle their settled mindsets and to have a fresh look at the world around and intervene. For instance, members may take a fresh critical look on the gender relations existing, if the praxis intervention method is applied to study gender relations. They would be unsettling their biographically and structurally ingrained perceptions of gender relations and freshly look at it. A gradual process by which members are helped to reflexively recognize the arbitrary and discriminating mindsets within themselves and the world around and working towards correcting it is praxis intervention. The Praxis intervention method helps members to struggle against structurally ingrained discrimination.Praxis Intervention helps respondents to come out with answers which they would not have otherwise expressed. Questionnaire based surveys, formal interviews, and even focus group discussions are not useful to help respondents to come out with genuine answers to the questions posed at them. Praxis Intervention as it helps groups of people probing their own conditions phase by phase through prolonged discussions, experiments and conscious explorations is capable of coming out with better quality data that could be useful for the group to challenge existing epistemic structures and work out their own well being.
Praxis intervention is useful wherever reflexivity
Reflexivity (social theory)
Reflexivity refers to circular relationships between cause and effect. A reflexive relationship is bidirectional with both the cause and the effect affecting one another in a situation that does not render both functions causes and effects...
is a major component in a research project.
Systematic participant objectivation in praxis intervention
Praxis intervention is not just a method in which one interferes with the habitus of the persons with whom the Action researchAction research
Action research or participatory action research – is a reflective process of progressive problem solving led by individuals working with others in teams or as part of a "community of practice" to improve the way they address issues and solve problems. Action research is done simply by action,...
is carried out but also it is intervention on the praxis intervention practitioners habitus. In this respect the practice of praxis intervention is also a systematic participant objectivation.
Participatory objectivation is ‘objectifying the act of objectification.’ By ‘objectifying the objectification’ it is meant the researcher, while observing and objectifying, taking a similar critical distance towards the objectification itself. It is being sensitive to the immensely possible biases from the researcher’s social coordinates, field and intellectual orientation and self-critically problematising them to reduce the impact of the biases .
According to Bourdieu, within the sociological analysis, the participant objectivation is the essential but difficult exercise of all because it requires the break with the deepest and most conscious adherence and adhesions, those quite often give the object its very interest for those who study it- i.e., everything about their relation to the object they try to know that they least want to know . It is through the participant objectivation the practical relation to practice is substituted with the observer’s relation to practice . Through the practice of participant objectivation, Bourdieu aims to make the critical and political activity of social research the ‘solvent of doxa.
Though the practice of reflexive participant objectivation, the practitioner re-looks the taken for granted assumptions in order to wake up from her epistemic sleep and helps her clients too to help them to wake up from theirs.
Praxis intervention in practice
"Praxis Intervention" as a practice involves working on the bias of the professionals and their clientele. It is a practical method of "objectifying objectification" on a collective basis . The Praxis Intervention method problematises the bias of the researcher and her clientile emerging from their social origins, class, gender coordinates; the their position in the intellectual field and in their respective social space; and also their "intellectual bias," the results of viewing the world as a spectacle.In practice it involves the clientele and the researchers collectively probing into a problem that affects the clientele and helping the clientele to find solutions to their problem through reflexive probing with the experts belonging to relevant fields. The project aims at the clientele and the researchers work together and collectively learn from each other.
Praxis Intervention can be carried out in phased manner. The first phase could involve orienting the clientele (and experts as well) of the problem under focus. The problem under focus could be anything like existing status of marginality, gender relation, health condition or status of present technology etc. Once the problem could properly be oriented from as much angles as possible the clientele , experts and others could involve discussing appropriate method to probe the issue under discussion. They could also decide on the phases through which the collective probing to be undertaken. The second phase could be clientele exploring the issue themselves through the methods collectively agreed. They could maintain a journal to record their experiences and reflexive probing. The third phase could be the clientele coming together with experts and sharing their experience with their fellow clients and experts. After discussing all the observations and experiences the method of enquiry can be further fine-tuned for better understanding. Gradually the clientele could be guided to intervene on the issue concerned and document their experience. Their action and reflexion could be discussed and fine tuned for further interventions. The phases and intervention strategies could be decided as it could be appropriate for different problems.
Praxis intervention method focuses on what happens to mindsets. In the community work situation it could be a project helping the community participants to undertake a systematic research on themselves in the areas such as history of their social relationships, land ownership patterns, critically exploring gender relations, studying the ecological changes happening in their habitat, learning historically and comparatively on their health status, nutrition status etc. The research undertook by the local residents can be converted into social actions or welfare projects.
The practice of praxis intervention can be used in many fields such as post positivist research, social work research, participatory action research
Participatory action research
Participatory action research – or action research – is a recognized form of experimental research that focuses on the effects of the researcher's direct actions of practice within a participatory community with the goal of improving the performance quality of the community or an area of...
, Local history research, Social action and social work projects, Clinical health research, Community Health research Projects, Participatory technology development
Participatory technology development
Participatory technology development is an approach to learning and innovation that is used in international development as part of projects and programmes relating to sustainable agriculture...
projects, and many other projects where people's participation and their critical reflexivity is crucial.
The method can be used in the field of education
Education
Education in its broadest, general sense is the means through which the aims and habits of a group of people lives on from one generation to the next. Generally, it occurs through any experience that has a formative effect on the way one thinks, feels, or acts...
. Educational process can be re constituted in accordance to the learning capabilities of the sets of students. Students going under the process of praxis intervention would listen to the expert opinions and explanations of the phenomenon under discussion and they would carry out experiments in the laboratory or in appropriate practical field relevant to the phenomenon under focus individually, collectively and collaboratively as they are guided by the expert teachers. They would bring back the results of experiments to the classroom setting and clarify with each other and also with the expert teachers. In this process syllabus can be indicative negotiable taking into consideration of the advancement of knowledge creation. In this process knowledge becomes creative appropriation rather than indoctrination.This may help students to gain great quantity of quality knowledge within short periods of time. The method could be effectively used in pre-primary to Higher schools of education.The method could be used in development of professional skills such as engineering, medicine, nursing, law, agricultural science, social work, management
Management
Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively...
, career guidance, expertise development, teaching and other such fields.
For instance, students of various technology oriented courses can be guided to develop and enhance technology by going under a praxis intervention experiment with users, experts and other relevant stakeholders. This could be appropriate for development and promotion of free software
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
.
Similarly praxis intervention can be used in helping patients to undergo a participatory diagnostic and experience sharing research with the medical professionals and other experts on their health conditions and take necessary action. Group of Patients suffering from similar diseases, their family members, and their significant others, medical practitioners and relevant experts can sit together and be guided through informed dialogue, systematic corrective measures, and experience sharing. . In this process both the facilitating professionals and the patients can overcome their respective personal and professional bias.
The Praxis Intervention method could be extended to the professional social work
Social work
Social Work is a professional and academic discipline that seeks to improve the quality of life and wellbeing of an individual, group, or community by intervening through research, policy, community organizing, direct practice, and teaching on behalf of those afflicted with poverty or any real or...
practice in facilitating the social workers themselves and their clients overcoming personal or social mindsets that induce suffering or marginality. The praxis mode of social work depends on the sensibility that could be provoked in a given context: sensible towards one’s own biography, historical locatedness, spatial positioning and the interaction setting. The praxis intervention practice has its implications for social work education. A social work education based on praxis model could shape the students and teachers self-reflexive, sensible. Through this method, it may be possible for students gaining theoretical and practical skills. The method can be used in other branches of education and training like the management education, medical education, agriculture extension and other fields where the clientele really matter. However, the praxis model would be yielding better results if sufficient flexibility is maintained. It could be a model for providing companionship to people in need of self-exploration. Praxis intervention as a practice can be carried on to the extent it is possible for people to take care of themselves and to the extent people require professional companionship of the social work practice. Praxis intervention practice requires the professionals and the client participants to be self-reflexive and self-critical. The model provides opportunity for the social worker to undertake a reflexive inward journey to get rid of biases that affect her practice. The context that is not suitable for self-reflexivity or self-criticism is not suitable for praxis intervention practice either.
The praxis practice could also be extended to social work practice in the medical setting, AIDS care, psychiatric social work, management of juvenile delinquency, school social work, correctional administration practices in prison social work, gender related social work practice, geriatric social work, etc.

The praxis intervention model of social intervention may not be applicable in all contexts. There are sections of people who cannot take care of themselves and hence require absolute external care. For example, persons suffering from progressive, irreversible diseases characterised by degeneration of the brain cells such as Alzheimer’s disease would require complete external care. The praxis practice would be inappropriate for the people who do not need care. The approach could be helpful in accompanying people who can be helped to care for themselves. Praxis intervention practice is appropriate for working with the people who can be helped to care themselves with in a scale of caring.
We also witness from the current literature that the method is used in development of bottom-up organizational ethics, generating participatory forms of art and music and also in transformative nursing
Nursing
Nursing is a healthcare profession focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life from conception to death....
practices.
See also
- Action researchAction researchAction research or participatory action research – is a reflective process of progressive problem solving led by individuals working with others in teams or as part of a "community of practice" to improve the way they address issues and solve problems. Action research is done simply by action,...
- Appreciative InquiryAppreciative inquiryAppreciative Inquiry is primarily an organisational development method which seeks to engage all levels of an organisation to renew, change and improved performance. Its exponents view it as being applicable to organisations facing rapid change or growth...
- Communicative actionCommunicative actionCommunicative action is a concept associated with the German philosopher-sociologist Jürgen Habermas. Habermas uses this concept to describe cooperative action undertaken by individuals based upon mutual deliberation and argumentation...
- Communicative rationalityCommunicative rationalityCommunicative rationality, or communicative reason, is a theory or set of theories which describes human rationality as a necessary outcome of successful communication. In particular, it is tied to the philosophy of Karl-Otto Apel, Jürgen Habermas, and their program of universal pragmatics, along...
- Community practiceCommunity practiceCommunity Practice is a branch of social work in the United States that focuses on larger social systems and social change, and is tied to the historical roots of United States social work...
- Critical realismCritical realismIn the philosophy of perception, critical realism is the theory that some of our sense-data can and do accurately represent external objects, properties, and events, while other of our sense-data do not accurately represent any external objects, properties, and events...
- Cooperative inquiryCooperative inquiryCooperative inquiry, also known as collaborative inquiry was first proposed by John Heron in 1971 and later expanded with Peter Reason. The major idea of cooperative inquiry is to “research ‘with’ rather than ‘on’ people.” It emphasizes that all active participants are fully involved in research...
- Narrative inquiryNarrative inquiryNarrative Inquiry emerged as a discipline within the broader field of qualitative research. It is an approach to understanding/researching the way people make meaning of their lives as narratives, linked fields are narrative analysis, narratology and life writing. Narrative Inquiry should be ...
- Participatory action researchParticipatory action researchParticipatory action research – or action research – is a recognized form of experimental research that focuses on the effects of the researcher's direct actions of practice within a participatory community with the goal of improving the performance quality of the community or an area of...
- Participatory rural appraisalParticipatory rural appraisalParticipatory rural appraisal is an approach used by non-governmental organizations and other agencies involved in international development...
- PhronesisPhronesisPhronēsis is an Ancient Greek word for wisdom or intelligence which is a common topic of discussion in philosophy. In Aristotelian Ethics, for example in the Nicomachean Ethics it is distinguished from other words for wisdom as the virtue of practical thought, and is usually translated "practical...
- Phronetic social sciencePhronetic social sciencePhronetic social science is an approach to the study of social – including political and economic – phenomena based on a contemporary interpretation of the Aristotelian concept phronesis, variously translated as practical judgment, common sense, or prudence. Phronesis is the intellectual virtue...
- PostpositivismPostpositivismIn philosophy and models of scientific inquiry, postpositivism is a metatheoretical stance that critiques and amends positivism. Postpositivists believe that human knowledge is based not on unchallengeable, rock-solid foundations, but rather upon human conjectures...
- Praxis SchoolPraxis SchoolThe Praxis school was a Marxist humanist philosophical movement. It originated in Zagreb and Belgrade in the SFR Yugoslavia, during the 1960s.Prominent figures among the school's founders include Gajo Petrović and Milan Kangrga of Zagreb and Mihailo Marković of Belgrade...
- Social workSocial workSocial Work is a professional and academic discipline that seeks to improve the quality of life and wellbeing of an individual, group, or community by intervening through research, policy, community organizing, direct practice, and teaching on behalf of those afflicted with poverty or any real or...
External sources
- this is an article on using praxis intervention in Music.
- This article explores use of praxis intervention in the field of applied ethics.
- this book talks about "narative Inquiry" which is verymuch similar to "praxis Intervention". The work describes narrative inquiry in the field of expertise development.
- Praxis Intervention in nursing
- on transformative nursing using "praxis intervention" method.
- on feminist-post_structuralist praxis intervention
- Praxis intervention in health management- not a free article
- Praxis Intervention in Adult Learning (p.54)
- A training Manuel:pages 37-44
- Critical Race Feminism Praxis Intervention
- using praxis intervention in the field of primary health care- not a free article. abstract is freely downloadable
- use of praxis intervention in psychiatric setting- abstract available. not a free article
- Praxis Intervention in the field of critical psychology
- Philosophy of praxis
- Praxis in Health education- This article is not freely available
- Paulo Freire
- Teaching and praxis
- Pedagogy of the oppressed
- Borda
- action research
- hegemonic articulations of power
- Action research Handbook (archive)
- Borda article
- Health Praxis
- Participant objectivation
- Participant Objectivation method

