Precision rectifier
Encyclopedia
The precision rectifier, which is also known as a super diode, is a configuration obtained with an operational amplifier
in order to have a circuit
behaving like an ideal diode
and rectifier
. It can be useful for high-precision signal processing.
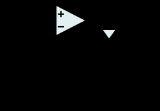
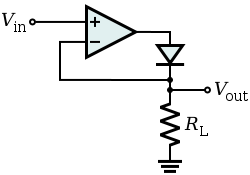 The basic circuit implementing such a feature is shown on the right, where
The basic circuit implementing such a feature is shown on the right, where 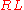 can be any load. When the input voltage
can be any load. When the input voltage
is negative, there is a negative voltage on the diode, too, so it works like an open circuit, there is no current in the load and the output voltage is zero.
When the input is positive, it is amplified by the operational amplifier and it turns the diode on. There is current in the load and, because of the feedback
, the output voltage is equal to the input.
The actual threshold of the super diode is very close to zero but it is not zero. It equals the actual threshold of the diode divided by the gain of the operational amplifier.
This basic configuration has a problem so it is not commonly used: when the input becomes (even slightly) negative, the operational amplifier is running open loop, as there is no feedback signal through the diode. With a typical high open loop gain operational amplifier, the output saturates. If the input then becomes positive again, the op-amp has to get out of the saturated state before positive amplification can take place again. This change generates some ringing and takes some time greatly reducing the frequency response
of the circuit.
.svg.png) An alternative version is given on the right.
An alternative version is given on the right.
In this case, when the input is greater than zero, D1 is OFF and D2 is ON, so the output is zero because one side of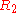 is connected to the virtual ground, and there is no current through it.
is connected to the virtual ground, and there is no current through it.
When the input is less than zero, D1 is ON and D2 is OFF, and the output is like the input with an amplification of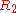 . Its input-output relationship is the following:
. Its input-output relationship is the following:
 This circuit has the benefit that the op-amp never goes into saturation; but its output must change by two diode voltage drops (about 1.2V) each time the input signal crosses zero, so the slew rate
This circuit has the benefit that the op-amp never goes into saturation; but its output must change by two diode voltage drops (about 1.2V) each time the input signal crosses zero, so the slew rate
of the operational amplifier, and its frequency response (gain-bandwidth product
) still limit high frequency performance; especially for low signal levels - although an error of less than 1% at 100kHz is possible.
Similar circuitry can be used to create a precision full-wave rectifier circuit.
keeps the peak voltage level of the signal, and a switch can be used for resetting the detected level.
Operational amplifier
An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output...
in order to have a circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
behaving like an ideal diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
and rectifier
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current , which periodically reverses direction, to direct current , which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification...
. It can be useful for high-precision signal processing.
Basic circuit

 can be any load. When the input voltage
can be any load. When the input voltageVoltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is negative, there is a negative voltage on the diode, too, so it works like an open circuit, there is no current in the load and the output voltage is zero.
When the input is positive, it is amplified by the operational amplifier and it turns the diode on. There is current in the load and, because of the feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
, the output voltage is equal to the input.
The actual threshold of the super diode is very close to zero but it is not zero. It equals the actual threshold of the diode divided by the gain of the operational amplifier.
This basic configuration has a problem so it is not commonly used: when the input becomes (even slightly) negative, the operational amplifier is running open loop, as there is no feedback signal through the diode. With a typical high open loop gain operational amplifier, the output saturates. If the input then becomes positive again, the op-amp has to get out of the saturated state before positive amplification can take place again. This change generates some ringing and takes some time greatly reducing the frequency response
Frequency response
Frequency response is the quantitative measure of the output spectrum of a system or device in response to a stimulus, and is used to characterize the dynamics of the system. It is a measure of magnitude and phase of the output as a function of frequency, in comparison to the input...
of the circuit.
Improved circuit
.svg.png)
In this case, when the input is greater than zero, D1 is OFF and D2 is ON, so the output is zero because one side of
 is connected to the virtual ground, and there is no current through it.
is connected to the virtual ground, and there is no current through it.When the input is less than zero, D1 is ON and D2 is OFF, and the output is like the input with an amplification of
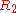 . Its input-output relationship is the following:
. Its input-output relationship is the following:
Slew rate
In electronics, the slew rate represents the maximum rate of change of a signal at any point in a circuit.Limitations in slew rate capability can give rise to non linear effects in electronic amplifiers...
of the operational amplifier, and its frequency response (gain-bandwidth product
Gain-bandwidth product
The gain–bandwidth product for an amplifier is the product of the amplifier's bandwidth, and the gain at which the bandwidth is measured....
) still limit high frequency performance; especially for low signal levels - although an error of less than 1% at 100kHz is possible.
Similar circuitry can be used to create a precision full-wave rectifier circuit.
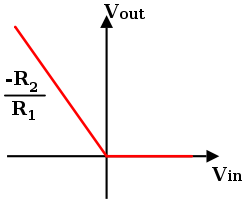
Peak detector
With little modification the basic precision rectifier can be used also for detecting peak levels of a signal. In the following circuit a capacitorCapacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
keeps the peak voltage level of the signal, and a switch can be used for resetting the detected level.


