
Presentation-abstraction-control
Encyclopedia
Presentation–abstraction–control (PAC) is a software architectural pattern
. It is an interaction-oriented software architecture, and is somewhat similar to model–view–controller (MVC) in that it separates an interactive system into three types of components responsible for specific aspects of the application's functionality. The abstraction component retrieves and processes the data, the presentation component formats the visual and audio presentation of data, and the control component handles things such as the flow of control and communication between the other two components
.
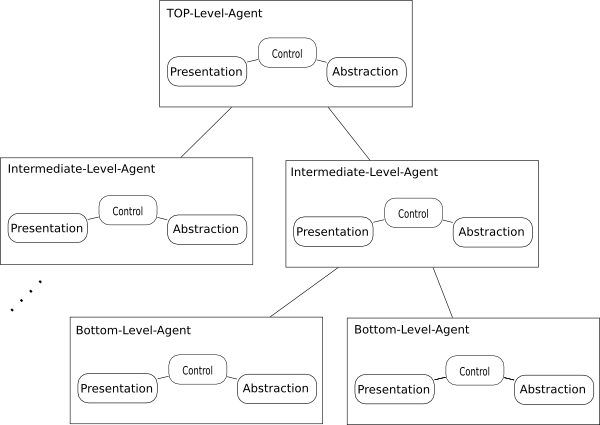
In contrast to MVC, PAC is used as a hierarchical structure of agents, each consisting of a triad of presentation, abstraction and control parts. The agents (or triads) communicate with each other only through the control part of each triad. It also differs from MVC in that within each triad, it completely insulates the presentation (view in MVC) and the abstraction (model in MVC), this provides the option to separately multithread the model and view which can give the user experience of very short program start times, as the user interface (presentation) can be shown before the abstraction has fully initialized.
Magazine, the authors apparently unaware of PAC which was published 13 years earlier. The main difference between HMVC and PAC is that HMVC is less strict in that it allows the view and model of each agent to communicate directly, thus bypassing the controller.
The controller has some oversight. The controller selects the model and then selects the view, so there is an approval mechanism by the controller. The model prevents the view from accessing the data source directly.
Architectural pattern (computer science)
An architectural pattern in software is a standard design in the field of software architecture. The concept of a software architectural pattern has a broader scope than the concept of a software design pattern...
. It is an interaction-oriented software architecture, and is somewhat similar to model–view–controller (MVC) in that it separates an interactive system into three types of components responsible for specific aspects of the application's functionality. The abstraction component retrieves and processes the data, the presentation component formats the visual and audio presentation of data, and the control component handles things such as the flow of control and communication between the other two components
.
In contrast to MVC, PAC is used as a hierarchical structure of agents, each consisting of a triad of presentation, abstraction and control parts. The agents (or triads) communicate with each other only through the control part of each triad. It also differs from MVC in that within each triad, it completely insulates the presentation (view in MVC) and the abstraction (model in MVC), this provides the option to separately multithread the model and view which can give the user experience of very short program start times, as the user interface (presentation) can be shown before the abstraction has fully initialized.

Hierarchical model–view–controller (HMVC)
A variation of MVC similar to PAC was published in an article in JavaWorldJavaWorld
JavaWorld is an online technology website focused on Java technologies, founded in 1996. Since 2006, JavaWorld has become a subsidiary of Network World...
Magazine, the authors apparently unaware of PAC which was published 13 years earlier. The main difference between HMVC and PAC is that HMVC is less strict in that it allows the view and model of each agent to communicate directly, thus bypassing the controller.
The controller has some oversight. The controller selects the model and then selects the view, so there is an approval mechanism by the controller. The model prevents the view from accessing the data source directly.
See also
- Model–view–presenter
- Model view viewmodelModel View ViewModelThe Model View ViewModel is an architectural pattern used in software engineering that originated from Microsoft as a specialization of the Presentation Model design pattern introduced by Martin Fowler...
- Presenter FirstPresenter FirstPresenter First is a software development approach that combines the ideas of the model–view–presenter design pattern, test-driven development, and Feature-driven development.-Approach:...
- PAC-Amodeus,
- PAC*
- Drupal web application framework
External links
- Architectural outline for the game WarcraftWarcraftWarcraft: Orcs & Humans is a real-time strategy game , developed by Blizzard Entertainment and published by Blizzard and Interplay Entertainment. The MS-DOS version was released in November 1994 and the Macintosh version in late 1996. Sales were fairly high, reviewers were mostly impressed, and the...
as it might be implemented using the PAC Architectural Pattern: Programming of the application PACcraft:Architecture (in french) - Pattern:Presentation-Abstraction-Control (pattern description)
- PAC description in the Portland Pattern Repository
- WengoPhone is a free softwareFree softwareFree software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
VoIP application that is written using the PAC design pattern.- description of PAC and motivation for use in WengoPhone.
- demonstration code, courtesy of the OpenWengo community.
- HMVC: The layered pattern for developing strong client tiers

