
Pressure swing adsorption
Encyclopedia
Molecular sieve
A molecular sieve is a material containing tiny pores of a precise and uniform size that is used as an adsorbent for gases and liquids.Molecules small enough to pass through the pores are adsorbed while larger molecules are not. It is different from a common filter in that it operates on a...
, preferentially adsorbing the target gas species at high pressure. The process then swings to low pressure to desorb the adsorbent material.
Process
Pressure swing adsorption processes rely on the fact that under pressure, gases tend to be attracted to solid surfaces, or "adsorbed". The higher the pressure, the more gas is adsorbed; when the pressure is reduced, the gas is released, or desorbed. PSA processes can be used to separate gases in a mixture because different gases tend to be attracted to different solid surfaces more or less strongly. If a gas mixture such as air, for example, is passed under pressure through a vessel containing an adsorbent bed of zeoliteZeolite
Zeolites are microporous, aluminosilicate minerals commonly used as commercial adsorbents. The term zeolite was originally coined in 1756 by Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who observed that upon rapidly heating the material stilbite, it produced large amounts of steam from water that...
that attracts nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
more strongly than it does oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, part or all of the nitrogen will stay in the bed, and the gas coming out of the vessel will be enriched in oxygen. When the bed reaches the end of its capacity to adsorb nitrogen, it can be regenerated by reducing the pressure, thereby releasing the adsorbed nitrogen. It is then ready for another cycle of producing oxygen enriched air.
This is exactly the process used in portable oxygen concentrators used by emphysema
Emphysema
Emphysema is a long-term, progressive disease of the lungs that primarily causes shortness of breath. In people with emphysema, the tissues necessary to support the physical shape and function of the lungs are destroyed. It is included in a group of diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary...
patients and others who require oxygen enriched air to breathe.
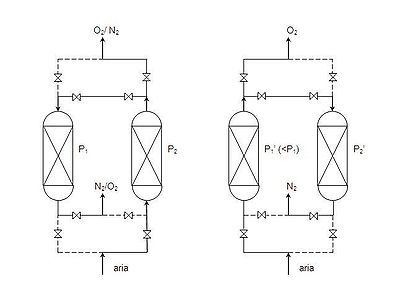
Using two adsorbent vessels allows near-continuous production of the target gas. It also permits so-called pressure equalisation, where the gas leaving the vessel being depressured is used to partially pressurise the second vessel. This results in significant energy savings, and is common industrial practice.
Adsorbents
Aside from their ability to discriminate between different gases, adsorbents for PSA systems are usually very porous materials chosen because of their large surface areas. Typical adsorbents are activated carbonActivated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
, silica gel
Silica gel
Silica gel is a granular, vitreous, porous form of silica made synthetically from sodium silicate. Despite its name, silica gel is a solid. It is a naturally occurring mineral that is purified and processed into either granular or beaded form...
, alumina and zeolite
Zeolite
Zeolites are microporous, aluminosilicate minerals commonly used as commercial adsorbents. The term zeolite was originally coined in 1756 by Swedish mineralogist Axel Fredrik Cronstedt, who observed that upon rapidly heating the material stilbite, it produced large amounts of steam from water that...
. Though the gas adsorbed on these surfaces may consist of a layer only one or at most a few molecules thick, surface areas of several hundred square meters per gram enable the adsorption of a significant portion of the adsorbent's weight in gas. In addition to their selectivity for different gases, zeolites and some types of activated carbon called carbon molecular sieves may utilize their molecular sieve characteristics to exclude some gas molecules from their structure based on the size of the molecules, thereby restricting the ability of the larger molecules to be adsorbed.
Applications
One of the primary applications of PSA is in the removal of carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
(CO2) as the final step in the large-scale commercial synthesis of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
(H2) for use in oil refineries
Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas...
and in the production of ammonia
Ammonia production
Because of its many uses, ammonia is one of the most highly-produced inorganic chemicals. There are numerous large-scale ammonia production plants worldwide, producing a total of 131,000,000 metric tons of ammonia in 2010. China produced 32.1% of the worldwide production, followed by India with...
(NH3). Refineries often use PSA technology in the removal of hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless, very poisonous, flammable gas with the characteristic foul odor of expired eggs perceptible at concentrations as low as 0.00047 parts per million...
(H2S) from hydrogen feed and recycle streams of hydrotreating and hydrocracking units. Another application of PSA is the separation of carbon dioxide from biogas
Biogas
Biogas typically refers to a gas produced by the biological breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Organic waste such as dead plant and animal material, animal dung, and kitchen waste can be converted into a gaseous fuel called biogas...
to increase the methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
(CH4) content. Through PSA the biogas can be upgraded to a quality similar to natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
.
Nitrogen generator
Nitrogen generator
Nitrogen generators and stations are stationary or mobile air-to-nitrogen production complexes. In advanced economies, membrane nitrogen plants have almost ousted alternative processes of nitrogen generation in all cases where nitrogen is not required in commercial volumes.- Adsorption concept :The...
units employ the PSA technique to produce high purity nitrogen gas (99.5% or greater) from a supply of compressed air.
Research is currently underway for PSA to capture CO2 in large quantities from coal-fired power plants
Fossil fuel power plant
A fossil-fuel power station is a power station that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum to produce electricity. Central station fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation...
prior to geosequestration, in order to reduce greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
production from these plants.
PSA is an economic choice for small-scale production of reasonable purity oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
or nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
from air. PSA technology has a major use in the medical industry to produce oxygen, particularly in remote or inaccessible parts of the world where bulk cryogenic or compressed cylinder storage is not possible.
PSA has also been discussed as a future alternative to the non-regenerable sorbent technology used in space suit
Space suit
A space suit is a garment worn to keep an astronaut alive in the harsh environment of outer space. Space suits are often worn inside spacecraft as a safety precaution in case of loss of cabin pressure, and are necessary for extra-vehicular activity , work done outside spacecraft...
Primary Life Support System
Primary Life Support System
A Primary Life Support System , is a device connected to an astronaut's or cosmonaut's spacesuit, which allows extra-vehicular activity with maximum freedom, independent of a spacecraft's life support system. The PLSS is generally worn like a backpack...
s, in order to save weight and extend the operating time of the suit.
Variations of PSA technology
Double Stage PSA (DS-PSA, sometimes referred to as Dual Step PSA).With this variation of PSA developed for use in Laboratory Nitrogen Generators generation of nitrogen gas is divided into two steps: in the first step, the compressed air is forced to pass through a carbon molecular sieve to produce nitrogen at a purity of approximately 98%; in the second step this nitrogen is forced to pass into a second carbon molecular sieve and the nitrogen gas reaches a final purity up to 99.999%. The purge Gas from the second step is recycled and partially used as feed gas in the first step.
In addition, the purge process is supported by active evacuation for better performance in the next cycle. The goals of both of these changes is to improve efficiency over a conventional PSA process.
See also
- AdsorptionAdsorptionAdsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
- Gas separationGas separationGas mixtures can be effectively separated by synthetic membranes. For other methods see adsorption, absorption, cryogenic distillation.Membranes are employed in:* separation of nitrogen or oxygen out of air...
- Hydrogen pinchHydrogen pinchHydrogen pinch analysis is a hydrogen management method that originates from the concept of heat pinch analysis. HPA is a systematic technique for reducing hydrogen consumption and hydrogen generation through integration of hydrogen-using activities or processes in the petrochemical industry,...
- Hydrogen purifierHydrogen purifierA hydrogen purifier is a device to purify hydrogen if hydrogen production is done from hydrocarbon sources, the ultra-high purified hydrogen is needed for applications like PEM fuel cells...
- Oxygen concentratorOxygen concentratorAn oxygen concentrator is a device providing oxygen therapy to a patient at minimally to substantially higher concentrations than available in ambient air. They are used as a safer, less expensive, and more convenient alternative to tanks of compressed oxygen. Common models retail at around US$800...
- Air dryerAir dryerA compressed air dryer is a device for removing water vapor from compressed air. Compressed air dryers are commonly found in a wide range of industrial and commercial facilities....

