
Price support
Encyclopedia
In economics
, a price support may be either a subsidy
or a price control, both with the intended effect of keeping the market price
of a good higher than the competitive equilibrium level.
In the case of a price control, a price support is the minimum legal price a seller may charge, typically placed above equilibrium. It is the support of certain price level
s at or above market values by the government.
A price support scheme can also be an agreement set in order by the government, where the government agrees to purchase the surplus of at a minimum price. For example, if a price floor
were set in place for agricultural wheat commodities, the government would be forced to purchase the resulting surplus from the wheat farmers (thereby subsidizing the farmers) and store or otherwise dispose of it.
are such that the equilibrium
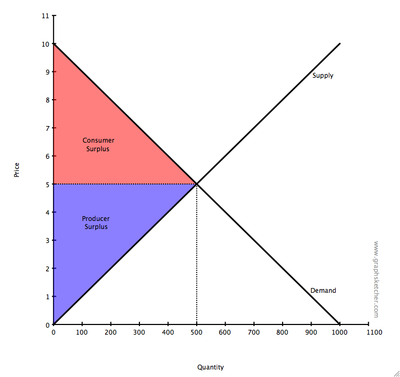
price and quantity are $5 and 500 units, respectively. The government then institutes a price support at $6 per unit.
The benefit to producers of the price support is equal to the gain in producer surplus (represented in blue).
The cost to consumers of the price support is equal to the loss in consumer surplus (represented in red).
The cost to the government of the price support is equal to the cost of the surplus in the market (represented in gray).
However, since the consumers ultimately pay taxes for the government to purchase the surplus, the total cost to consumers (in the short run) of the price support is the sum of the loss in consumer surplus and the cost of the government purchasing the surplus off the market.
In other words, consumers are paying $1,650 in order to benefit producers $550. For this reason, price supports are considered inefficient.
The dead weight loss (DWL)
is the efficiency lost by implementing price-support system. It is the change in Total Surplus and is equal to $1,100.00.
Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, a price support may be either a subsidy
Subsidy
A subsidy is an assistance paid to a business or economic sector. Most subsidies are made by the government to producers or distributors in an industry to prevent the decline of that industry or an increase in the prices of its products or simply to encourage it to hire more labor A subsidy (also...
or a price control, both with the intended effect of keeping the market price
Price
-Definition:In ordinary usage, price is the quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services.In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency...
of a good higher than the competitive equilibrium level.
In the case of a price control, a price support is the minimum legal price a seller may charge, typically placed above equilibrium. It is the support of certain price level
Price level
A price level is a hypothetical measure of overall prices for some set of goods and services, in a given region during a given interval, normalized relative to some base set...
s at or above market values by the government.
A price support scheme can also be an agreement set in order by the government, where the government agrees to purchase the surplus of at a minimum price. For example, if a price floor
Price floor
A price floor is a government- or group-imposed limit on how low a price can be charged for a product. For a price floor to be effective, it must be greater than the equilibrium price.-Effectiveness of price floors:...
were set in place for agricultural wheat commodities, the government would be forced to purchase the resulting surplus from the wheat farmers (thereby subsidizing the farmers) and store or otherwise dispose of it.
Example
Consider a hypothetical market in which supply and demandSupply and demand
Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...
are such that the equilibrium
Economic equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a state of the world where economic forces are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. It is the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal...
price and quantity are $5 and 500 units, respectively. The government then institutes a price support at $6 per unit.
|
|
 |
 |
The benefit to producers of the price support is equal to the gain in producer surplus (represented in blue).
- 1,800 - 1,250 = $550
The cost to consumers of the price support is equal to the loss in consumer surplus (represented in red).
- 1,250 - 800 = $450
The cost to the government of the price support is equal to the cost of the surplus in the market (represented in gray).
- 6 * 200 = $1,200
However, since the consumers ultimately pay taxes for the government to purchase the surplus, the total cost to consumers (in the short run) of the price support is the sum of the loss in consumer surplus and the cost of the government purchasing the surplus off the market.
- 450 + 1,200 = $1,650
In other words, consumers are paying $1,650 in order to benefit producers $550. For this reason, price supports are considered inefficient.
The dead weight loss (DWL)
Deadweight loss
In economics, a deadweight loss is a loss of economic efficiency that can occur when equilibrium for a good or service is not Pareto optimal...
is the efficiency lost by implementing price-support system. It is the change in Total Surplus and is equal to $1,100.00.

