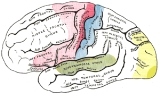
Primary auditory cortex
Overview
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
that is responsible for the processing of auditory
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing.- Outer ear :The folds of cartilage surrounding the ear canal are called the pinna...
(sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
) information. Corresponding roughly with Brodmann area
Brodmann area
A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex defined based on its cytoarchitectonics, or structure and organization of cells.-History:...
s 41 and 42, it is located on the temporal lobe
Temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is a region of the cerebral cortex that is located beneath the Sylvian fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain....
, and performs the basics of hearing—pitch and volume. Besides receiving input from the ear and lower centers of the brain, the primary auditory cortex also transmits signals back to these areas.
As with other primary sensory cortical areas, auditory sensations reach perception
Perception
Perception is the process of attaining awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information. All perception involves signals in the nervous system, which in turn result from physical stimulation of the sense organs...
only if received and processed by a cortical
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
area.
Unanswered Questions

