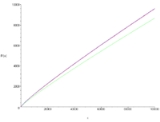
Prime number theorem
Overview
Number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers. Number theorists study prime numbers as well...
, the prime number theorem (PNT) describes the asymptotic
Asymptotic analysis
In mathematical analysis, asymptotic analysis is a method of describing limiting behavior. The methodology has applications across science. Examples are...
distribution of the prime number
Prime number
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. A natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number is called a composite number. For example 5 is prime, as only 1 and 5 divide it, whereas 6 is composite, since it has the divisors 2...
s. The prime number theorem gives a general description of how the primes are distributed amongst the positive integers.
Informally speaking, the prime number theorem states that if a random
Randomness
Randomness has somewhat differing meanings as used in various fields. It also has common meanings which are connected to the notion of predictability of events....
integer is selected near to some large integer N, the probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
that the selected integer is prime is about 1 / ln(N), where ln(N) denotes the natural logarithm
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
of N.
Discussions

